Methods of Reproduction
... • Organisms that reproduce asexually cannot develop much variety, because they are “copying” the original organism exactly. ...
... • Organisms that reproduce asexually cannot develop much variety, because they are “copying” the original organism exactly. ...
Chapter 15: Reproductive system
... ________________: rod-shaped structures in the nuclei of our body cells that contain individual DNA and genes. ________________: connections that form between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, resulting in the swapping of portions of chromosomes. ________________: a cell having two sets of chro ...
... ________________: rod-shaped structures in the nuclei of our body cells that contain individual DNA and genes. ________________: connections that form between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, resulting in the swapping of portions of chromosomes. ________________: a cell having two sets of chro ...
Biology Final Jeopary 2
... A: The process in which individuals with favorable variations reproduce more successfully than those without such variations. Over time, this causes a population to adapt. ...
... A: The process in which individuals with favorable variations reproduce more successfully than those without such variations. Over time, this causes a population to adapt. ...
PlantReproduction
... 4. Fragmentation – when a piece of the parent organism breaks off and is dispersed. Each section is able to form a new organism. • Example - House plants formed from cuttings ...
... 4. Fragmentation – when a piece of the parent organism breaks off and is dispersed. Each section is able to form a new organism. • Example - House plants formed from cuttings ...
Asexual Reproduction - Manhasset Public Schools
... ■ This can occur in the leaves, roots, and stems of different types of plants ■ Ex: African Violet ...
... ■ This can occur in the leaves, roots, and stems of different types of plants ■ Ex: African Violet ...
Evolution in the Animal Kingdom
... Reproduction is the process by which living things create more of their own kind. All types of living creatures reproduce, from the tiniest bacteria to the largest plants and animals. Without reproduction, all forms of life would die out. There are two general types of reproduction—sexual and asexua ...
... Reproduction is the process by which living things create more of their own kind. All types of living creatures reproduce, from the tiniest bacteria to the largest plants and animals. Without reproduction, all forms of life would die out. There are two general types of reproduction—sexual and asexua ...
Diversity Notes
... 3. Anterior – front / head of the organism. 4. Posterior – tail / hind end of the organism. B. Symmetry – balanced arrangement of body parts around a point or a line. 1. Bilateral symmetry – each side is a mirror image of the other. a) Ex: humans, fish, birds, reptiles 2. Radial symmetry – appendage ...
... 3. Anterior – front / head of the organism. 4. Posterior – tail / hind end of the organism. B. Symmetry – balanced arrangement of body parts around a point or a line. 1. Bilateral symmetry – each side is a mirror image of the other. a) Ex: humans, fish, birds, reptiles 2. Radial symmetry – appendage ...
Chromosomes
... c. Long bridge of protein forms between and connects two bacterial cells. d. Part of genetic info of one cell, called the donor, transferred to the other cell, called the recipient. e. The recipient cell has a different set of genes from those it had before conjugation occurred. f. This increases ge ...
... c. Long bridge of protein forms between and connects two bacterial cells. d. Part of genetic info of one cell, called the donor, transferred to the other cell, called the recipient. e. The recipient cell has a different set of genes from those it had before conjugation occurred. f. This increases ge ...
Lesson 1: Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis 4. (Ex.: people
... 2. The type of cell division that takes place in one-celled or multi-celled eukaryotic organisms. 3. An embryo goes through this process after fertilization. 1. A type of reproduction in which the genetic material from two different cells combine, producing an offspring. 2. Offspring inherit the sam ...
... 2. The type of cell division that takes place in one-celled or multi-celled eukaryotic organisms. 3. An embryo goes through this process after fertilization. 1. A type of reproduction in which the genetic material from two different cells combine, producing an offspring. 2. Offspring inherit the sam ...
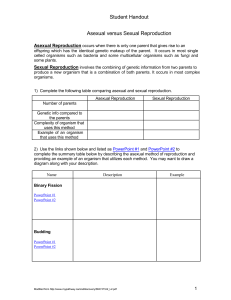
Asexual versus Sexual Reproduction
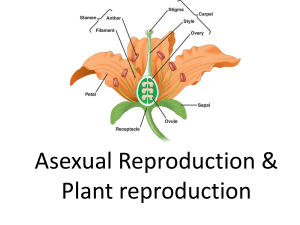
... For Sexual Reproduction to be completed pollination must occur. During this process the pollen (sperm) must be transferred from the stamen to the stigma at the top of the pistil (often plants use insects or wind to accomplish the transfer). The pollen then releases the sperm and it travels down the ...
... For Sexual Reproduction to be completed pollination must occur. During this process the pollen (sperm) must be transferred from the stamen to the stigma at the top of the pistil (often plants use insects or wind to accomplish the transfer). The pollen then releases the sperm and it travels down the ...
Reproduction, Growth and Development in Living
... – A species is defined as a group of similar organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring ...
... – A species is defined as a group of similar organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring ...
Human Development
... • The effects that androgens have on the human body --virilization, masculinization, anabolism, etc. --- are not brought about by androgens themselves, but rather are the result of androgens bound to androgen receptors ...
... • The effects that androgens have on the human body --virilization, masculinization, anabolism, etc. --- are not brought about by androgens themselves, but rather are the result of androgens bound to androgen receptors ...
File
... (2 parents; offspring not genetically identical) • The process of meiosis also shuffles genetic information (DNA) and results in variation in genes. Therefore producing a variation in offspring ...
... (2 parents; offspring not genetically identical) • The process of meiosis also shuffles genetic information (DNA) and results in variation in genes. Therefore producing a variation in offspring ...
StudentInstrSht-AsexvsSexRepro
... For Sexual Reproduction to be completed pollination must occur. During this process the pollen (sperm) must be transferred from the stamen to the stigma at the top of the pistil (often plants use insects or wind to accomplish the transfer). The pollen then releases the sperm and it travels down the ...
... For Sexual Reproduction to be completed pollination must occur. During this process the pollen (sperm) must be transferred from the stamen to the stigma at the top of the pistil (often plants use insects or wind to accomplish the transfer). The pollen then releases the sperm and it travels down the ...
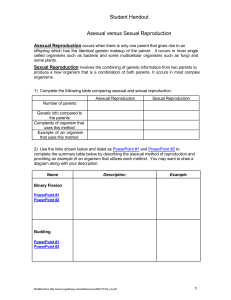
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction
... For Sexual Reproduction to be completed pollination must occur. During this process the pollen (sperm) must be transferred from the stamen to the stigma at the top of the pistil (often plants use insects or wind to accomplish the transfer). The pollen then releases the sperm and it travels down the ...
... For Sexual Reproduction to be completed pollination must occur. During this process the pollen (sperm) must be transferred from the stamen to the stigma at the top of the pistil (often plants use insects or wind to accomplish the transfer). The pollen then releases the sperm and it travels down the ...
CA3_Review_and_Sexual_vs_Asexual
... Organisms are Genetically identical, Clones No recombination or exchange of genes between parents An asexual population tends to be genetically boring, EVERYBODY IS THE SAME. ...
... Organisms are Genetically identical, Clones No recombination or exchange of genes between parents An asexual population tends to be genetically boring, EVERYBODY IS THE SAME. ...
Asexual reproduction
... Reproduction A process by which an organism produces others of the same kind. There are two kinds of reproduction Sexual reproduction – uniting of sperm and egg Asexual reproduction – creating a new life from one parent -lower animals and plants can reproduce in this manner. ...
... Reproduction A process by which an organism produces others of the same kind. There are two kinds of reproduction Sexual reproduction – uniting of sperm and egg Asexual reproduction – creating a new life from one parent -lower animals and plants can reproduce in this manner. ...
genetics
... heredity of pea plants • The process in which characteristics or traits are passed from parents to offspring is called heredity ...
... heredity of pea plants • The process in which characteristics or traits are passed from parents to offspring is called heredity ...
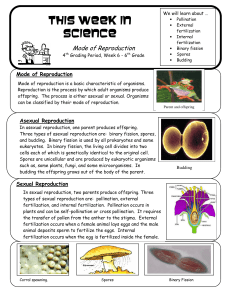
This week in science 6th - Reproduction
... eukaryotes. In binary fission, the living cell divides into two cells each of which is genetically identical to the original cell. Spores are unicellular and are produced by eukaryotic organisms such as, some plants, fungi, and some microorganisms. In budding the offspring grows out of the body of t ...
... eukaryotes. In binary fission, the living cell divides into two cells each of which is genetically identical to the original cell. Spores are unicellular and are produced by eukaryotic organisms such as, some plants, fungi, and some microorganisms. In budding the offspring grows out of the body of t ...
Sexual Reproduction
... Only needs one parent, unlike sexual reproduction, which needs two parent Since there is only one parent, there is no fusion of gametes and no mixing of genetic information – So the offspring are genetically identical to the parent and to each other (clones) ...
... Only needs one parent, unlike sexual reproduction, which needs two parent Since there is only one parent, there is no fusion of gametes and no mixing of genetic information – So the offspring are genetically identical to the parent and to each other (clones) ...
Year 9 Reproduction – Vocabulary list
... Attached to the uterus wall, this takes oxygen and food out of the mother’s blood and puts waste materials into the mother’s blood. ...
... Attached to the uterus wall, this takes oxygen and food out of the mother’s blood and puts waste materials into the mother’s blood. ...
Methods of reproduction
... Pollen is produced in the male organs of the flowers - anthers. Pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the anthers to the female organs by wind or by animals. If the female stigma is receptive to a pollen grain, the pollen produces a pollen tube, which grows through the female tissue to ...
... Pollen is produced in the male organs of the flowers - anthers. Pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the anthers to the female organs by wind or by animals. If the female stigma is receptive to a pollen grain, the pollen produces a pollen tube, which grows through the female tissue to ...
To reproduce - SDSU Heart Institute
... successfully get the egg fertilized, hatched (born), and far along enough in development to ensure it will produce another egg • The egg also wants more eggs like itself - the egg wants to pass it’ it’s genetic material to the next generation • Preservation of the species is paramount: individuals m ...
... successfully get the egg fertilized, hatched (born), and far along enough in development to ensure it will produce another egg • The egg also wants more eggs like itself - the egg wants to pass it’ it’s genetic material to the next generation • Preservation of the species is paramount: individuals m ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.