Second Semester Vocab Review
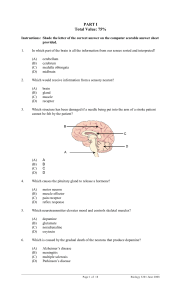
... Evolution that is described by short periods of drastic change in species, which are separated by long periods of little or no change ...
... Evolution that is described by short periods of drastic change in species, which are separated by long periods of little or no change ...
N5 Multicellular Organisms Course Notes
... walls are only one cell thick to allow materials to cross from tissues to capillaries easily. There is a dense network of capillaries giving a large surface area. Examples of materials that cross capillary walls are oxygen and glucose into cells and carbon dioxide and urea from cells to the capillar ...
... walls are only one cell thick to allow materials to cross from tissues to capillaries easily. There is a dense network of capillaries giving a large surface area. Examples of materials that cross capillary walls are oxygen and glucose into cells and carbon dioxide and urea from cells to the capillar ...
What You Absolutely Need to Know To Pass the NYS Living
... • All organisms, including plants, use respiration to get their energy. “Respiration is breathing.” • Breathing is not respiration. Breathing exchanges the gases needed for respiration. Inhaling and exhaling does not ...
... • All organisms, including plants, use respiration to get their energy. “Respiration is breathing.” • Breathing is not respiration. Breathing exchanges the gases needed for respiration. Inhaling and exhaling does not ...
Ch. 9 Sec. 4 Notes
... *Worms reproduce both sexually and asexually *Some species of worms have both female and male animals; others worms have both male and female sex organs *During asexual reproduction, worms will break itself into pieces and re-grow from each piece *During sexual reproduction, a male animal will mate ...
... *Worms reproduce both sexually and asexually *Some species of worms have both female and male animals; others worms have both male and female sex organs *During asexual reproduction, worms will break itself into pieces and re-grow from each piece *During sexual reproduction, a male animal will mate ...
Platyhelminthes
... digestive system with the mouth at the anterior end. They are characterized by a thick cuticle as well as one or more suckers surrounding the mouth. These suckers are used for attachment to the host's internal body surface. These organisms are typically hermaphroditic (have male and female sex organ ...
... digestive system with the mouth at the anterior end. They are characterized by a thick cuticle as well as one or more suckers surrounding the mouth. These suckers are used for attachment to the host's internal body surface. These organisms are typically hermaphroditic (have male and female sex organ ...
EXAM 2 REVIEW
... 4. Both fungi and arthropods have cell walls made of chitin. 5. Fungi are composed of long, thin filaments known as hyphae that make up the mycelium of each plant. This should have a large surface area in order to increase absorption rate. 6. Some fungi have cell walls in their hyphae that are calle ...
... 4. Both fungi and arthropods have cell walls made of chitin. 5. Fungi are composed of long, thin filaments known as hyphae that make up the mycelium of each plant. This should have a large surface area in order to increase absorption rate. 6. Some fungi have cell walls in their hyphae that are calle ...
Book Review: Dual Sexual Strategy in Females—Is the Mysterious
... that estrus in the human female has not been lost and that ovulation has not been concealed (Pawlowski, 1999). I also postulated that diminished signs of estrus in the human female does not have to be the result of sexual selection acting in our evolutionary past. I hope that this book may reach a w ...
... that estrus in the human female has not been lost and that ovulation has not been concealed (Pawlowski, 1999). I also postulated that diminished signs of estrus in the human female does not have to be the result of sexual selection acting in our evolutionary past. I hope that this book may reach a w ...
June 2008
... has the normal dominant allele, what percentage of their children will have hemophilia? (A) (B) (C) (D) ...
... has the normal dominant allele, what percentage of their children will have hemophilia? (A) (B) (C) (D) ...
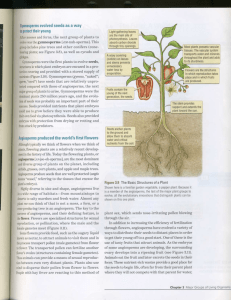
Gymnosperms evolved seeds as a way to protect their young
... evolve, all the evolutionary innovations that distinguish plants can be shown on this one plant. ...
... evolve, all the evolutionary innovations that distinguish plants can be shown on this one plant. ...
Asexual reproduction - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
... Some species alternate between the sexual and asexual strategies, an ability known as heterogamy, depending on conditions. Alternation is observed in several rotifer species (cyclical parthenogenesis e.g. in Brachionus species) and a few types of insects, such as aphids which will, under certain con ...
... Some species alternate between the sexual and asexual strategies, an ability known as heterogamy, depending on conditions. Alternation is observed in several rotifer species (cyclical parthenogenesis e.g. in Brachionus species) and a few types of insects, such as aphids which will, under certain con ...
LIFE SCIENCE GLEs
... number of cells involved (one body cell in asexual, two sex cells in sexual) and the number of gene sets (body cell has 2 sets, sex cells have 1 set each) passed from parent(s) to offspring). Identify examples of asexual reproduction (i.e., plants budding, binary fission of single cell organisms. Id ...
... number of cells involved (one body cell in asexual, two sex cells in sexual) and the number of gene sets (body cell has 2 sets, sex cells have 1 set each) passed from parent(s) to offspring). Identify examples of asexual reproduction (i.e., plants budding, binary fission of single cell organisms. Id ...
Protists and Fungi
... – Tse-tse fly, wild animal reservoirs – Necrosis (tissue death) of lymph tissue, nervous disorder ...
... – Tse-tse fly, wild animal reservoirs – Necrosis (tissue death) of lymph tissue, nervous disorder ...
system
... b. They Rose bush live part of their lives as diploid organisms and part Mammal fetuses are enclosed in a protective sack called food themselves. c.c. Tomato plants as Christmas haploid tree organisms. the placenta. 13. Transfer d.d. Mosses ofproduce pollen from one angiosperm to another. c. They To ...
... b. They Rose bush live part of their lives as diploid organisms and part Mammal fetuses are enclosed in a protective sack called food themselves. c.c. Tomato plants as Christmas haploid tree organisms. the placenta. 13. Transfer d.d. Mosses ofproduce pollen from one angiosperm to another. c. They To ...
Biology_Fishes
... movements from one place to another once a day, a year, or a lifetime 2) Feeding 3) Reproduction a) Anadromous: fish that spend their lives at sea but breed in fresh water b) Catadromous: fish that breed at sea grow and mature in fresh water37 ...
... movements from one place to another once a day, a year, or a lifetime 2) Feeding 3) Reproduction a) Anadromous: fish that spend their lives at sea but breed in fresh water b) Catadromous: fish that breed at sea grow and mature in fresh water37 ...
Answers
... mats of mycelia (singular, mycelium) below ground or fruiting bodies that often appear above ground. b. Which fungi do not share this basic body plan? The yeasts are unicellular. 2. Fungi may be said to have both plantlike and animal-like characteristics. What plantlike characteristics do fungi have ...
... mats of mycelia (singular, mycelium) below ground or fruiting bodies that often appear above ground. b. Which fungi do not share this basic body plan? The yeasts are unicellular. 2. Fungi may be said to have both plantlike and animal-like characteristics. What plantlike characteristics do fungi have ...
here
... parasite An organism that grows, feeds, and lives on or in another organism harming it. The organism that benefits in a parasitic relationship. parasite load The number of parasites on an infected host; for example, the number of OE spores on an adult butterfly. parasitoid A parasitic insect that li ...
... parasite An organism that grows, feeds, and lives on or in another organism harming it. The organism that benefits in a parasitic relationship. parasite load The number of parasites on an infected host; for example, the number of OE spores on an adult butterfly. parasitoid A parasitic insect that li ...
Biology EOC review - Duplin County Schools
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
Biology EOC Study Guide - Auburndale High School
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
Gaston County Review
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
... - Unicellular – organism that exists as a singular, independent cell - Multicellular – organism that exists as specialized groups of cells; cells are organized into tissues that perform the same function; tissues form organs and organs make up an organ system - Prokaryote – has nuclear material in t ...
Review Key
... How does it increase variation? Those organisms with beneficial mutations that are better suited for their environments live and mate passing to on to future generations the new change in the genetic code thus increasing the variety in a species. 45. How can reproductive variations benefit a species ...
... How does it increase variation? Those organisms with beneficial mutations that are better suited for their environments live and mate passing to on to future generations the new change in the genetic code thus increasing the variety in a species. 45. How can reproductive variations benefit a species ...
174 kb
... recognize the historical development of ideas in science. Organisms inherit genetic information in a variety of ways that result in continuity of structure and function between parents and offspring. ...
... recognize the historical development of ideas in science. Organisms inherit genetic information in a variety of ways that result in continuity of structure and function between parents and offspring. ...
Science4CE Biology notes
... Hostile environment The vagina is a hostile environment for sperm, producing acids which can harm them and prevent them from swimming up through the cervix. In order to combat this, semen contains an alkali to neutralise the acid produced by the vagina and allow sperm to survive. Front view ...
... Hostile environment The vagina is a hostile environment for sperm, producing acids which can harm them and prevent them from swimming up through the cervix. In order to combat this, semen contains an alkali to neutralise the acid produced by the vagina and allow sperm to survive. Front view ...
M Standard 11- - ALCOSbiologyPowerPoints
... different parents unite to form the new organism. (Not meaning that the parents have sex ).This ...
... different parents unite to form the new organism. (Not meaning that the parents have sex ).This ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.