
Organ_Systems_of_the_Body
... Female Gonads: the ovaries Accessory organs: the uterus, uterine (fallopian) tubes, and the vagina Supporting structures: the genitalia (vulva) and the mammary glands (breasts) ...
... Female Gonads: the ovaries Accessory organs: the uterus, uterine (fallopian) tubes, and the vagina Supporting structures: the genitalia (vulva) and the mammary glands (breasts) ...
Cells - STA304
... the billions of cells of cells that make up your body. • Mitosis is simple and nearly flawless (errors in mitosis are extremely rare) • Mitosis gives each cell its own copy of all your genetic information (your DNA) • Simple organisms (like the amoeba) can even reproduce by mitosis. ...
... the billions of cells of cells that make up your body. • Mitosis is simple and nearly flawless (errors in mitosis are extremely rare) • Mitosis gives each cell its own copy of all your genetic information (your DNA) • Simple organisms (like the amoeba) can even reproduce by mitosis. ...
Characteristics of Life - Glasgow Independent Schools
... Scientists know that all living things are organized. The smallest unit of organization of a living thing is the cell. A cell is a collection of living matter enclosed by a barrier known as the plasma membrane that separates it from its surroundings. Cells can perform all the functions we associate ...
... Scientists know that all living things are organized. The smallest unit of organization of a living thing is the cell. A cell is a collection of living matter enclosed by a barrier known as the plasma membrane that separates it from its surroundings. Cells can perform all the functions we associate ...
Part 6 - glenbrook s hs
... The mycelium of one humongous fungus in Oregon is 3.4 miles in diameter and spreads through 2,200 acres of forest. The fungus is at least 2,400 years old and hundreds of tons in weight, qualifying it among Earth’s oldest and largest organisms! ...
... The mycelium of one humongous fungus in Oregon is 3.4 miles in diameter and spreads through 2,200 acres of forest. The fungus is at least 2,400 years old and hundreds of tons in weight, qualifying it among Earth’s oldest and largest organisms! ...
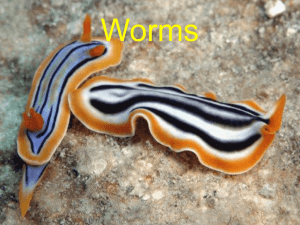
Worms - Cloudfront.net
... • Cylindrical bodies w/ mouth and anus • Separate male/female – Sexual reproduction ...
... • Cylindrical bodies w/ mouth and anus • Separate male/female – Sexual reproduction ...
Insects and relatives
... macromolecules and other complex substances like proteins, polysaccharides, fats, and nucleic acids. Macromolecules: a very large molecule commonly created by some form of polymerization. The macromolecules are then broken down into smaller molecules like amino acids and simple sugars before being u ...
... macromolecules and other complex substances like proteins, polysaccharides, fats, and nucleic acids. Macromolecules: a very large molecule commonly created by some form of polymerization. The macromolecules are then broken down into smaller molecules like amino acids and simple sugars before being u ...
Section 29–2 Form and Function in
... 2. Why aren’t more complicated systems in living animals necessarily better than simpler systems in other living animals? The fact that any system is found in living animals testifies to its success in performing functions. ...
... 2. Why aren’t more complicated systems in living animals necessarily better than simpler systems in other living animals? The fact that any system is found in living animals testifies to its success in performing functions. ...
Slide 1 - mazarelloscience.com
... A group of parts that form a complex whole- work together to achieve goals that the parts could not reach alone. Parts can interact, be related to one another, or depend on each other. ...
... A group of parts that form a complex whole- work together to achieve goals that the parts could not reach alone. Parts can interact, be related to one another, or depend on each other. ...
Biology CP - Masconomet Regional School District
... it works. 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system (skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle, bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons) works with other systems to support and allow for movement. Recognize that bones produce both red and white blood cells. 4.6 Recognize that the sexual reproductive syste ...
... it works. 4.5 Explain how the muscular/skeletal system (skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle, bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons) works with other systems to support and allow for movement. Recognize that bones produce both red and white blood cells. 4.6 Recognize that the sexual reproductive syste ...
Chapter 30: Comparing Invertebrates
... Second, cnidarians and some flatworms have a ____________________________ ______________________________________ that has a single opening through which food enters and through which solid wastes are expelled ...
... Second, cnidarians and some flatworms have a ____________________________ ______________________________________ that has a single opening through which food enters and through which solid wastes are expelled ...
Invertebrate Phylae
... 11. Hydrostatic Skeleton…annelids and certain cnidarians. Their muscles surround a fluid filled cavity that supports the muscles 12. Endoskeleton---structural support within the organism; echinoderms 13. Exoskeleton----external skeleton made up of chitin…arthropods 14. Sexual reproduction---producti ...
... 11. Hydrostatic Skeleton…annelids and certain cnidarians. Their muscles surround a fluid filled cavity that supports the muscles 12. Endoskeleton---structural support within the organism; echinoderms 13. Exoskeleton----external skeleton made up of chitin…arthropods 14. Sexual reproduction---producti ...
File - HABITAT (Home)
... heterotrophic nutritional mode, usually organ and tissue development, and motility sometime during the organism's life history One of three domains. This domain only has one kingdom, the archeabacteria. Taxonomic kingdom of ancient (over 3.5 billion years old) group of prokaryotes; These bacteria te ...
... heterotrophic nutritional mode, usually organ and tissue development, and motility sometime during the organism's life history One of three domains. This domain only has one kingdom, the archeabacteria. Taxonomic kingdom of ancient (over 3.5 billion years old) group of prokaryotes; These bacteria te ...
Chapter 1
... The Domain Eukarya may be unicellular or multicellular o Eukaryote cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles o The Kingdom Protista includes single-celled organisms such as the bloblike ameba and the oval-shaped paramecium o The Kingdom Fungi includes molds, mushrooms, and certain parasit ...
... The Domain Eukarya may be unicellular or multicellular o Eukaryote cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles o The Kingdom Protista includes single-celled organisms such as the bloblike ameba and the oval-shaped paramecium o The Kingdom Fungi includes molds, mushrooms, and certain parasit ...
Kingdom Animalia (Animals)
... - Body organization (cells organized into tissues, organs and organ systems) - Number of germ layers (tissues from which more specialized tissues develop) - Body symmetry - A complete or incomplete digestive tract - Development (or not) of an internal cavity called a coelom ...
... - Body organization (cells organized into tissues, organs and organ systems) - Number of germ layers (tissues from which more specialized tissues develop) - Body symmetry - A complete or incomplete digestive tract - Development (or not) of an internal cavity called a coelom ...
A Brief Survey of Animals
... development of animals. In early stages of development, the embryo looks like a ball of cells which begin to differentiate into 2 or 3 layers of cells. These layers independently differentiate into various tissues of the animal body. Animals contain either two or three embryonic cell layers. Simpler ...
... development of animals. In early stages of development, the embryo looks like a ball of cells which begin to differentiate into 2 or 3 layers of cells. These layers independently differentiate into various tissues of the animal body. Animals contain either two or three embryonic cell layers. Simpler ...
powerpoint notes - Social Circle City Schools
... Unlike ferns and mosses, seed plants don’t need water to reproduce. Seed plants rely on wind and animals to disperse their seeds for reproduction. ...
... Unlike ferns and mosses, seed plants don’t need water to reproduce. Seed plants rely on wind and animals to disperse their seeds for reproduction. ...
REPTILE REVIEW
... 1. Male reptiles have a __ __ __ __ __ to transfer sperm inside the female’s body. 2. In an amniotic egg the fat rich food supply (yolk) is surrounded by a membrane called the __ __ __ __ sac. 3. In reptiles the sperm and egg join inside the female’s body. This is called __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ fert ...
... 1. Male reptiles have a __ __ __ __ __ to transfer sperm inside the female’s body. 2. In an amniotic egg the fat rich food supply (yolk) is surrounded by a membrane called the __ __ __ __ sac. 3. In reptiles the sperm and egg join inside the female’s body. This is called __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ fert ...
Questions (Use notes ot textbook)
... development of animals. In early stages of development, the embryo looks like a ball of cells which begin to differentiate into 2 or 3 layers of cells. These layers independently differentiate into various tissues of the animal body. Animals contain either two or three embryonic cell layers. Simpler ...
... development of animals. In early stages of development, the embryo looks like a ball of cells which begin to differentiate into 2 or 3 layers of cells. These layers independently differentiate into various tissues of the animal body. Animals contain either two or three embryonic cell layers. Simpler ...
Development
... Development of the primary sexual characteristics depends directly on the endocrine environment during development. An individual can be forced into either a female development or a male development by application of the appropriate hormones, regardless of genetic makeup. In the absence of hormonal ...
... Development of the primary sexual characteristics depends directly on the endocrine environment during development. An individual can be forced into either a female development or a male development by application of the appropriate hormones, regardless of genetic makeup. In the absence of hormonal ...
Arthropods (Phylum Arthropoda)
... They also have a series of ganglia (nerve bundles) which help to coordinate movement of the many body segments. Many arthropods have very specialized sense organs. ...
... They also have a series of ganglia (nerve bundles) which help to coordinate movement of the many body segments. Many arthropods have very specialized sense organs. ...
Biology 102 Exam II
... Phylum Annelida has a fundamentally important characteristic, they were the first to show real serial repetition of body parts called. What do we call this? The Water Vascular System is a unique characteristic of which Phylum? What are some characteristics shared by all chordates? Do animal cells ha ...
... Phylum Annelida has a fundamentally important characteristic, they were the first to show real serial repetition of body parts called. What do we call this? The Water Vascular System is a unique characteristic of which Phylum? What are some characteristics shared by all chordates? Do animal cells ha ...
Blog resource: http://tinyurl
... 14. A diploid cell carries genes A and B. There are dominant and recessive alleles for these genes. The cell is heterozygous for both genes. a. What combination of gametes could be produced if there was no crossing over? AB or ____ ...
... 14. A diploid cell carries genes A and B. There are dominant and recessive alleles for these genes. The cell is heterozygous for both genes. a. What combination of gametes could be produced if there was no crossing over? AB or ____ ...
Chapter 2: Living Things Notes
... Objective 1.0: Describe characteristics common to living things, including growth & development, reproduction, cellular organization, use of energy, exchange of gases, and response to the environment. Identify homeostasis as the process by which an organism responds to its internal or external envir ...
... Objective 1.0: Describe characteristics common to living things, including growth & development, reproduction, cellular organization, use of energy, exchange of gases, and response to the environment. Identify homeostasis as the process by which an organism responds to its internal or external envir ...
Fungi: Eumycota
... • Homothallic: Sexually-compatible gametes are formed on the same mycelium (self-fertilizing) • Heterothallic: Require outcrossing between different, yet compatible mycelia (+ and – mating strains) – A dikaryotic stage can exist temporarily prior to fusion of two haploid nuclei ...
... • Homothallic: Sexually-compatible gametes are formed on the same mycelium (self-fertilizing) • Heterothallic: Require outcrossing between different, yet compatible mycelia (+ and – mating strains) – A dikaryotic stage can exist temporarily prior to fusion of two haploid nuclei ...
Biology Summary [PDF Document]
... Fertilisation is the fusion of a male and female gamete. The fusion of the male and female gametes forms a zygote. After an egg has been fertilised it attaches itself to the lining of the uterus. This is called implantation. ...
... Fertilisation is the fusion of a male and female gamete. The fusion of the male and female gametes forms a zygote. After an egg has been fertilised it attaches itself to the lining of the uterus. This is called implantation. ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.




















![Biology Summary [PDF Document]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015201071_1-645f2d1eb761f177f20a3a1ed550cdc7-300x300.png)