Frog Dissection Questions
... 8. Suppose in a living frog the spinal nerve extending to the leg muscle were cut. What ability would the frog lose? Why? ...
... 8. Suppose in a living frog the spinal nerve extending to the leg muscle were cut. What ability would the frog lose? Why? ...
Role of reproductive hormones
... During sexual intercourse (copulation), sexual arousal causes the penis to become stiff and erect. This erection is due to blood being pumped in quicker to the blood vessels in the wall of the penis faster than it can drain away. In females sexual arousal results in the erection of the clitoris and ...
... During sexual intercourse (copulation), sexual arousal causes the penis to become stiff and erect. This erection is due to blood being pumped in quicker to the blood vessels in the wall of the penis faster than it can drain away. In females sexual arousal results in the erection of the clitoris and ...
Distribution and reproductive effects of Wolbachia i n stalk-eyed flies
... University of Rochester, Rochester, IVY 14627, USA ...
... University of Rochester, Rochester, IVY 14627, USA ...
EXAM 2 REVIEW
... False (they are only 5% of all organisms!) 64. What distinguishes vertebrates from the rest of the chordates? Distinct cephalization, vertebral column that encloses the nerve chord (has the function of the notochord), endoskeletons that grow with the animal and a closed circulatory system (more effi ...
... False (they are only 5% of all organisms!) 64. What distinguishes vertebrates from the rest of the chordates? Distinct cephalization, vertebral column that encloses the nerve chord (has the function of the notochord), endoskeletons that grow with the animal and a closed circulatory system (more effi ...
Annelida
... • Possess cylindrical ring used in reproduction – Formation of a cocoon for the embryos ...
... • Possess cylindrical ring used in reproduction – Formation of a cocoon for the embryos ...
Arthropods Notes
... 2. The ____________________ is made of a material called _______________. 3. As the animal grows it must get rid of the exoskeleton through a process called ____________________. Immediately after this process the arthropod is somewhat vulnerable because the exoskeleton takes time to harden. 4. Arth ...
... 2. The ____________________ is made of a material called _______________. 3. As the animal grows it must get rid of the exoskeleton through a process called ____________________. Immediately after this process the arthropod is somewhat vulnerable because the exoskeleton takes time to harden. 4. Arth ...
MCAS and Final Review Packet 2014
... conservation of the genetic code. Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes. Distinguish among the end products of replication, transcription, and translation. 3.3 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not re ...
... conservation of the genetic code. Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes. Distinguish among the end products of replication, transcription, and translation. 3.3 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not re ...
Round Worms, Flat Worms and Annelids
... is warm They can take up to three months to hatch when it is cold Usually one or two earthworms hatch out of each egg The young worms are about 12 millimeters long and light pink in color Earthworms are able to mate when they are twelve months old. ...
... is warm They can take up to three months to hatch when it is cold Usually one or two earthworms hatch out of each egg The young worms are about 12 millimeters long and light pink in color Earthworms are able to mate when they are twelve months old. ...
Interactions in Animals
... Interactions in Animals These same animals can also reproduce through fragmentation, in which an organism’s body is broken into pieces, and some or all of these become separate individuals. The animal must be able to regenerate, or grow back, lost body parts, for fragmentation to occur. Parthenogen ...
... Interactions in Animals These same animals can also reproduce through fragmentation, in which an organism’s body is broken into pieces, and some or all of these become separate individuals. The animal must be able to regenerate, or grow back, lost body parts, for fragmentation to occur. Parthenogen ...
Living Things Reproduce
... Organisms make other organisms like themselves. They can do this in one of two ways: asexual reproduction, or sexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction a parent produces offspring that are identical to the parent. (Hydra producing buds on page 38). In sexual reproduction, it requires two organism ...
... Organisms make other organisms like themselves. They can do this in one of two ways: asexual reproduction, or sexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction a parent produces offspring that are identical to the parent. (Hydra producing buds on page 38). In sexual reproduction, it requires two organism ...
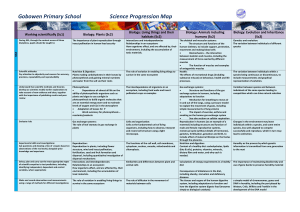
File - Gobowen Primary School
... which they are suited and describe how different habitats provide for the basic needs of different kinds of animals and plants, and how they depend on each other Identify and name a variety of plants and animals in their habitats, including microhabitats. Describe how animals obtain their food from ...
... which they are suited and describe how different habitats provide for the basic needs of different kinds of animals and plants, and how they depend on each other Identify and name a variety of plants and animals in their habitats, including microhabitats. Describe how animals obtain their food from ...
MCAS and Final Review Packet 2014
... conservation of the genetic code. Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes. Distinguish among the end products of replication, transcription, and translation. 3.3 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not re ...
... conservation of the genetic code. Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes. Distinguish among the end products of replication, transcription, and translation. 3.3 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not re ...
Unit 4 Review
... Aeorbe bacteria require what to grow? ________________________________________. Anaerobic bacteria do not require what to grow? ______________________________________. What is meant by normal flora with bacteria? _______________________________________________. Chapter 19 Protists contain what type ...
... Aeorbe bacteria require what to grow? ________________________________________. Anaerobic bacteria do not require what to grow? ______________________________________. What is meant by normal flora with bacteria? _______________________________________________. Chapter 19 Protists contain what type ...
Spring Semester Exam Review
... variations for a specific trait. The organisms with the higher fitness for that trait survive and reproduce passing down that fit trait. The organisms with lower fitness for that trait die off and the trait is not passed down. OVER time, there will only be the trait that gave higher fitness because ...
... variations for a specific trait. The organisms with the higher fitness for that trait survive and reproduce passing down that fit trait. The organisms with lower fitness for that trait die off and the trait is not passed down. OVER time, there will only be the trait that gave higher fitness because ...
Hierarchy of Life
... Three types of relationships can exist: 1. Mutualism (+;+) BOTH organisms benefit.) (For example, E. Coli in the intestines of most animals. They help with reabsorbing water from the process of digestion.) 2. Commensalism (+; 0) Only ONE organism benefits) (These are rare.) 3. Parasitism ( - ; +) On ...
... Three types of relationships can exist: 1. Mutualism (+;+) BOTH organisms benefit.) (For example, E. Coli in the intestines of most animals. They help with reabsorbing water from the process of digestion.) 2. Commensalism (+; 0) Only ONE organism benefits) (These are rare.) 3. Parasitism ( - ; +) On ...
Body Systems Booklet All Body System Information 2014
... - Regulates body temperature (sweating) - Works as a sensory organ (touch) - Helps eliminate wastes from the body - Produces Vitamin D in the presence of Ultraviolet Light ...
... - Regulates body temperature (sweating) - Works as a sensory organ (touch) - Helps eliminate wastes from the body - Produces Vitamin D in the presence of Ultraviolet Light ...
Chapter 29
... Blastocyst implants outside uterus 1 out of 300 pregnancies most cases occur in uterine tube (tubal pregnancy) occurs because of tubal obstruction from previous pelvic inflammations, repeated abortions or tubal surgery ...
... Blastocyst implants outside uterus 1 out of 300 pregnancies most cases occur in uterine tube (tubal pregnancy) occurs because of tubal obstruction from previous pelvic inflammations, repeated abortions or tubal surgery ...
Benchmarks by Topic - maineindianeducation
... C. The Scientific and Technological Enterprise: Students understand the history and nature of scientific knowledge and technology, the process of inquiry and technological design, and the impacts science and technology have on society and the environment. C1. Understandings of Inquiry Students descr ...
... C. The Scientific and Technological Enterprise: Students understand the history and nature of scientific knowledge and technology, the process of inquiry and technological design, and the impacts science and technology have on society and the environment. C1. Understandings of Inquiry Students descr ...
Lab 9: Adaptations for Survival in Terrestrial Environments
... In earlier laboratories, you studied certain cellular features that allowed the movement onto land, including root hairs to absorb water and nutrients, tracheids and vessels to carry them, and epidermal cells, including guard cells, to restrict water loss. You also studied features of angiosperm rep ...
... In earlier laboratories, you studied certain cellular features that allowed the movement onto land, including root hairs to absorb water and nutrients, tracheids and vessels to carry them, and epidermal cells, including guard cells, to restrict water loss. You also studied features of angiosperm rep ...
The 6 Kingdoms of Life plus Viruses
... Multicellular fungi have all similar looking cells that organize in long slender filaments called hyphae. ...
... Multicellular fungi have all similar looking cells that organize in long slender filaments called hyphae. ...
S1 – Body Systems Summary Notes
... The Reproductive System – The Reproductive Organs 9 – We are learning about the organs of the reproductive system. ...
... The Reproductive System – The Reproductive Organs 9 – We are learning about the organs of the reproductive system. ...
Document
... The domains formed by ionic interactions in different parts of a polypeptide d. The overall configuration of a polypeptide chain e. None of the above ...
... The domains formed by ionic interactions in different parts of a polypeptide d. The overall configuration of a polypeptide chain e. None of the above ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.