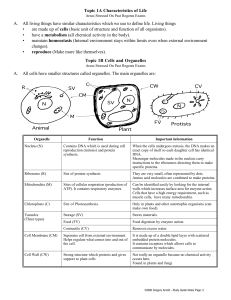
Topic 1A Characteristics of Life A. All living things have similar
... Plasmolysis, a special case of diffusion that occurs when a living thing that does not normally live in salt water, is exposed to salt or salt water. Since there is a greater concentration of water inside the cell than outside the cell, water moves out of the cell causing it to shrink and die. (Note ...
... Plasmolysis, a special case of diffusion that occurs when a living thing that does not normally live in salt water, is exposed to salt or salt water. Since there is a greater concentration of water inside the cell than outside the cell, water moves out of the cell causing it to shrink and die. (Note ...
cms/lib/NY01001456/Centricity/Domain/535/TaxHsilent teaparty
... The KINGDOM that is has organisms with eukaryotic cells, are usually multicellular, have filamentous structures that are multinucleate, lack chloroplasts, are heterotrophic, lack a digestive system, are absorptive feeders, and are classified as decomposers. ...
... The KINGDOM that is has organisms with eukaryotic cells, are usually multicellular, have filamentous structures that are multinucleate, lack chloroplasts, are heterotrophic, lack a digestive system, are absorptive feeders, and are classified as decomposers. ...
DIVERSITY IN LIVING ORGANISMS
... of all individuals whether an animal, a plant or a microbe. The diversity is boundless because different places have different living beings. To study diversity effectively, it is necessary to arrange various kinds of organisms in an orderly manner. This diversity is originated during the past 3.5 b ...
... of all individuals whether an animal, a plant or a microbe. The diversity is boundless because different places have different living beings. To study diversity effectively, it is necessary to arrange various kinds of organisms in an orderly manner. This diversity is originated during the past 3.5 b ...
Parasitic Helminths
... digestive system. Their reproductive system, however, is often complex, which ensures infection of new hosts. Some flukes can produce 25,000 eggs per day. Adult helminths may be dioecious; male reproductive organs are in one individual, and female reproductive organs are in another. In those species ...
... digestive system. Their reproductive system, however, is often complex, which ensures infection of new hosts. Some flukes can produce 25,000 eggs per day. Adult helminths may be dioecious; male reproductive organs are in one individual, and female reproductive organs are in another. In those species ...
عناوين محاضرات التشريح العملي فرع العلوم الاساسية 2016\2017
... The muscles of the upper and lower limbs The muscles of the abdominal region ...
... The muscles of the upper and lower limbs The muscles of the abdominal region ...
PSEUDOCOELOMATE LABORATORY Phylum Gastrotricha 1
... Reproduction in rotifers is rather unusual as are their morphology and feeding habits. Several types of reproduction have been observed in rotifers. Some species consist only of females that produce their daughters from unfertilized eggs, a type of reproduction called parthenogenesis. In other words ...
... Reproduction in rotifers is rather unusual as are their morphology and feeding habits. Several types of reproduction have been observed in rotifers. Some species consist only of females that produce their daughters from unfertilized eggs, a type of reproduction called parthenogenesis. In other words ...
Biology 2201 Holy Spirit High School Name: ANSWER KEY Part A
... C) Species A has internal development D) Species B has internal development 9.) Why is the heart of an amphibian considered to be less efficient than that of osteichthyes? A) Amphibians are larger than osteichthyes B) Osteichthyes are more evolutionary advanced than amphibians C) Osteichthyes have m ...
... C) Species A has internal development D) Species B has internal development 9.) Why is the heart of an amphibian considered to be less efficient than that of osteichthyes? A) Amphibians are larger than osteichthyes B) Osteichthyes are more evolutionary advanced than amphibians C) Osteichthyes have m ...
Structure of Fungi - Scienceiskool.com
... the fungi that are not placed in another group because no sexual cycle has been observed (yet!) • Reproductive structure =Conidium ...
... the fungi that are not placed in another group because no sexual cycle has been observed (yet!) • Reproductive structure =Conidium ...
Lecture 2 and text (pg. 1,2,12-14) 1. What are some properties of life
... Unchecked, over reproduction results in an extraordinary number Artificial Selection, Natural Selection, and Adaptation •Darwin noted that humans have modified other species by selecting and breeding individuals with desired traits, a process called artificial selection •Darwin then described four o ...
... Unchecked, over reproduction results in an extraordinary number Artificial Selection, Natural Selection, and Adaptation •Darwin noted that humans have modified other species by selecting and breeding individuals with desired traits, a process called artificial selection •Darwin then described four o ...
Living things - Beck-Shop
... In ecology, the place where an organism lives is called its habitat. The habitat of a fish might be a pond. There will probably be many fish in the pond, forming a population of fish. A population is a group of organisms of the same species, living in the same place at the same time and able to bree ...
... In ecology, the place where an organism lives is called its habitat. The habitat of a fish might be a pond. There will probably be many fish in the pond, forming a population of fish. A population is a group of organisms of the same species, living in the same place at the same time and able to bree ...
SLB-013 (10-1-06) Spiritual Life Basics Part II: What is Life? Lesson
... development can be a simple switch in a cell that says, "Don't divide yet," or the many complicated stages that multicellular organisms go through between one zygote (the very first cell, usually created from the fusion of a sperm and an egg cell) and the next generation's zygote-generating adult. ...
... development can be a simple switch in a cell that says, "Don't divide yet," or the many complicated stages that multicellular organisms go through between one zygote (the very first cell, usually created from the fusion of a sperm and an egg cell) and the next generation's zygote-generating adult. ...
organ systems of the body
... • Primary functions are to produce sperm cells and transport them to the female reproductive tract. Female reproductive system • Consists of ovaries, uterus, uterine tubes, vagina, vulva, and mammary glands. ...
... • Primary functions are to produce sperm cells and transport them to the female reproductive tract. Female reproductive system • Consists of ovaries, uterus, uterine tubes, vagina, vulva, and mammary glands. ...
Lesson Plans for Fred Hopson, 010
... discusion/ meiosis Power point (power model of meiosis in order to show their point is on line) we will finish the power understanding of the topic. point on meiosis as an intro to gamete production. Procedures: warm up/ begin meiosis project (claymation) the students will work Accommodations/Modifi ...
... discusion/ meiosis Power point (power model of meiosis in order to show their point is on line) we will finish the power understanding of the topic. point on meiosis as an intro to gamete production. Procedures: warm up/ begin meiosis project (claymation) the students will work Accommodations/Modifi ...
Name: John D. Ransom Institution: Oklahoma State University
... Sigmoid Curve to Represent the Growth Rate of Plants Due to Auxin Concentration ...
... Sigmoid Curve to Represent the Growth Rate of Plants Due to Auxin Concentration ...
Biology 2201
... Aristotle (2000 yrs ago). Aristotle made the First attempt at classification. He divided ALL organisms into TWO large groups he called kingdoms. The two groups were called kingdom Animalia and kingdom Plantae ...
... Aristotle (2000 yrs ago). Aristotle made the First attempt at classification. He divided ALL organisms into TWO large groups he called kingdoms. The two groups were called kingdom Animalia and kingdom Plantae ...
Arthropoda
... • Terrestrial: usually sexual • Marine: Females usually lay eggs that are fertilized by the male. • Parthenogenesis in some species. – Asexual – Growth and development of embryos occurs without fertilization. ...
... • Terrestrial: usually sexual • Marine: Females usually lay eggs that are fertilized by the male. • Parthenogenesis in some species. – Asexual – Growth and development of embryos occurs without fertilization. ...
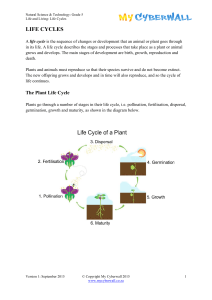
life cycles - My Cyberwall
... Salmon live in the sea but move to freshwater to reproduce.The female makes a nest and lays the eggs in it. The male salmon then fertilises the eggs. When the salmon hatch, they are known as alevins. They stay in the nest and have a food sac attached to their bodies. Once the food sac is used up, th ...
... Salmon live in the sea but move to freshwater to reproduce.The female makes a nest and lays the eggs in it. The male salmon then fertilises the eggs. When the salmon hatch, they are known as alevins. They stay in the nest and have a food sac attached to their bodies. Once the food sac is used up, th ...
Human Growth and Development Powerpoint
... At its center, the egg contains half the chromosomes (n or haploid) number for its species. ...
... At its center, the egg contains half the chromosomes (n or haploid) number for its species. ...
Animals Part I - CCRI Faculty Web
... – Organs are free within the cavity and will move around easily when you manipulate them Coelomate – Cavity that contains organs – Lined with mesoderm ...
... – Organs are free within the cavity and will move around easily when you manipulate them Coelomate – Cavity that contains organs – Lined with mesoderm ...
STB 112 Theory - Unesco
... Excretory openings are minute, located laterally on the dorsal surface and are difficult to see. Genital pare are found on the ventral surface behind the mouth. The body is covered by epidermis and its ciliated. They lock of mouth, pharynx and intestines. There is no skeleton, no respiratory system. ...
... Excretory openings are minute, located laterally on the dorsal surface and are difficult to see. Genital pare are found on the ventral surface behind the mouth. The body is covered by epidermis and its ciliated. They lock of mouth, pharynx and intestines. There is no skeleton, no respiratory system. ...
Sex

Organisms of many species are specialized into male and female varieties, each known as a sex. Sexual reproduction involves the combining and mixing of genetic traits: specialized cells known as gametes combine to form offspring that inherit traits from each parent. Gametes can be identical in form and function (known as isogamy), but in many cases an asymmetry has evolved such that two sex-specific types of gametes (heterogametes) exist (known as anisogamy). By definition, male gametes are small, motile, and optimized to transport their genetic information over a distance, while female gametes are large, non-motile and contain the nutrients necessary for the early development of the young organism. Among humans and other mammals, males typically carry XY chromosomes, whereas females typically carry XX chromosomes, which are a part of the XY sex-determination system. Other animals have a sex-determination system as well, such as the ZW sex-determination system in birds, and the X0 sex-determination system in insects. The gametes produced by an organism are determined by its sex: males produce male gametes (spermatozoa, or sperm, in animals; pollen in plants) while females produce female gametes (ova, or egg cells); individual organisms which produce both male and female gametes are termed hermaphroditic. Frequently, physical differences are associated with the different sexes of an organism; these sexual dimorphisms can reflect the different reproductive pressures the sexes experience.