Document
... •Homologues of mutS and mutL genes exist so enzymes involved in eukaryotic mismatch repair likely to be similar to prokaryotic enzymes. •BUT, no homologue of MutH (protein that recognizes unmethylated newly synthesized strand) so recognition of newly synthesized strand does not appear to occur via a ...
... •Homologues of mutS and mutL genes exist so enzymes involved in eukaryotic mismatch repair likely to be similar to prokaryotic enzymes. •BUT, no homologue of MutH (protein that recognizes unmethylated newly synthesized strand) so recognition of newly synthesized strand does not appear to occur via a ...
Genetic Recombination www.AssignmentPoint.com Genetic
... information exchange between the chromosomes. The information exchange may occur without physical exchange (a section of genetic material is copied from one chromosome to another, without the donating chromosome being changed) (see SDSA pathway in Figure); or by the breaking and rejoining of DNA str ...
... information exchange between the chromosomes. The information exchange may occur without physical exchange (a section of genetic material is copied from one chromosome to another, without the donating chromosome being changed) (see SDSA pathway in Figure); or by the breaking and rejoining of DNA str ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... 3. in a 5' to 3' direction on both the leading and lagging strands. 4. in a 3' to 5' direction on both the leading and lagging strands. ...
... 3. in a 5' to 3' direction on both the leading and lagging strands. 4. in a 3' to 5' direction on both the leading and lagging strands. ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... eutherian mammals this requires a random switch and subsequent maintenance of the active and inactive states. Holliday and Pugh discussed these fundamental features in the wider context of development. Both publications proposed that the hemimethylated DNA after replication is a substrate for a main ...
... eutherian mammals this requires a random switch and subsequent maintenance of the active and inactive states. Holliday and Pugh discussed these fundamental features in the wider context of development. Both publications proposed that the hemimethylated DNA after replication is a substrate for a main ...
Creating an animated tutorial for the online classroom
... “I don’t think the mRNA strand is exactly like the DNA strand. I believe the template DNA strand will have the complementary base sequence of the mRNA strand using U instead of T for a pair with A. Then after you get the template strand, the other DNA strand will be the complementary base pair sequ ...
... “I don’t think the mRNA strand is exactly like the DNA strand. I believe the template DNA strand will have the complementary base sequence of the mRNA strand using U instead of T for a pair with A. Then after you get the template strand, the other DNA strand will be the complementary base pair sequ ...
Ch. 16 Molecular Basis Heredity AND Replication Activity
... sugar/phosphate backbone runs in opposite directions (Crick); • one strand runs 5’ to 3’, while the other runs 3’ to 5’; • DNA polymerase only adds nucleotides at the free 3’ end, forming new DNA strands in the 5’ to 3’ direction only ...
... sugar/phosphate backbone runs in opposite directions (Crick); • one strand runs 5’ to 3’, while the other runs 3’ to 5’; • DNA polymerase only adds nucleotides at the free 3’ end, forming new DNA strands in the 5’ to 3’ direction only ...
protein synthesis - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... review any problems. PART 1 - Transcription During transcription, the DNA double helix “unzips”. As the hydrogen bonds between the two strands break, nucleotides floating in the nucleus line up next to the nucleotides of one DNA strand (“master strand”) to form mRNA. (Remember that uracil replaces t ...
... review any problems. PART 1 - Transcription During transcription, the DNA double helix “unzips”. As the hydrogen bonds between the two strands break, nucleotides floating in the nucleus line up next to the nucleotides of one DNA strand (“master strand”) to form mRNA. (Remember that uracil replaces t ...
DNA Replication, Repair, and Recombination
... 1: Helicase unwinds parental DNA strands 2: Single strand regions are bound and stabilized by multible copies of the protein RPA (stabilizes a DNA conformation optimal for processing by DNA pol δ) 3: Leading strand synthesis via an enzymatic complex: DNA Pol δ, PCNA, and Rfc 4: Primers for lagging s ...
... 1: Helicase unwinds parental DNA strands 2: Single strand regions are bound and stabilized by multible copies of the protein RPA (stabilizes a DNA conformation optimal for processing by DNA pol δ) 3: Leading strand synthesis via an enzymatic complex: DNA Pol δ, PCNA, and Rfc 4: Primers for lagging s ...
DNA
... structure of DNA was a simple repeating unit of GATCGATCGATC This is why no one thought it could be the genetic material with a structure this simple • Purines - Large organic bases – Adenine and Guanine • Pyrimidines - Small organic bases – Cytosine and Thymine, Uracil (RNA) ...
... structure of DNA was a simple repeating unit of GATCGATCGATC This is why no one thought it could be the genetic material with a structure this simple • Purines - Large organic bases – Adenine and Guanine • Pyrimidines - Small organic bases – Cytosine and Thymine, Uracil (RNA) ...
DNA REPLICATION
... DNA REPLICATION(Use you notes and pages 444-445) The process by which DNA makes copies of itself is called DNA _______________________. The following are the steps for DNA Replication: 1. The double helix _________________________. 2. The hydrogen bonds that hold the base pairs together are broken b ...
... DNA REPLICATION(Use you notes and pages 444-445) The process by which DNA makes copies of itself is called DNA _______________________. The following are the steps for DNA Replication: 1. The double helix _________________________. 2. The hydrogen bonds that hold the base pairs together are broken b ...
Discovery of a “transforming principle”
... structure of DNA was a simple repeating unit of GATCGATCGATC This is why no one thought it could be the genetic material with a structure this simple • Purines - Large organic bases – Adenine and Guanine • Pyrimidines - Small organic bases – Cytosine and Thymine, Uracil (RNA) ...
... structure of DNA was a simple repeating unit of GATCGATCGATC This is why no one thought it could be the genetic material with a structure this simple • Purines - Large organic bases – Adenine and Guanine • Pyrimidines - Small organic bases – Cytosine and Thymine, Uracil (RNA) ...
Dna rEPLICATION - Manning`s Science
... fork on one strand, and away from the fork on the other. In eukaryotes, more than one replication fork may exist on a DNA molecule. A replication bubble forms when 2 replication forks are in close proximity to each other ...
... fork on one strand, and away from the fork on the other. In eukaryotes, more than one replication fork may exist on a DNA molecule. A replication bubble forms when 2 replication forks are in close proximity to each other ...
Name
... 15. Translation of mRNA in a ribosome proceeds __. a. from the middle simultaneously toward the 3' and 5' ends b. from either the 5' or 3' end, depending on the enzymes present c. from the 5' end to the 3' end d. from the 3' end to the 5' end 16. Most inborn disorders of metabolism associated with ...
... 15. Translation of mRNA in a ribosome proceeds __. a. from the middle simultaneously toward the 3' and 5' ends b. from either the 5' or 3' end, depending on the enzymes present c. from the 5' end to the 3' end d. from the 3' end to the 5' end 16. Most inborn disorders of metabolism associated with ...
Energy Transfer in Living Things (Chapter 6)
... –Rosalind Franklin got an ‘X’ pattern from X-ray crystallography of DNA –Chargaff figured out base pairing (A to T and C to G) ...
... –Rosalind Franklin got an ‘X’ pattern from X-ray crystallography of DNA –Chargaff figured out base pairing (A to T and C to G) ...
END OF SEMESTER EXAM PREPARATION AND REVISION
... − G≡C is a strong bond – hydrogen bonding − Two complementary strands in DNA – double helix − Direction is from 5’ –> 3’ ends ...
... − G≡C is a strong bond – hydrogen bonding − Two complementary strands in DNA – double helix − Direction is from 5’ –> 3’ ends ...
Introduction continued
... Produces nearly data that have errors (so algorithms are to be extended to handle errors. Virus and bacteria (organisms most used in genetic research) Virus consists of a protein cap (capsid) with DNA (or RNA) inside - cells starts producing-coded proteins which promotes viral DNA replication (new c ...
... Produces nearly data that have errors (so algorithms are to be extended to handle errors. Virus and bacteria (organisms most used in genetic research) Virus consists of a protein cap (capsid) with DNA (or RNA) inside - cells starts producing-coded proteins which promotes viral DNA replication (new c ...
Human DNA Dance - University of Wisconsin Biotechnology Center
... You can show how DNA can melt into two single strands by asking the two lines to release their handshakes and take one step to the left, while keeping their right hands in the C, T, G or A form. You can show how two complementary single strands of DNA can anneal (come together) by then having the tw ...
... You can show how DNA can melt into two single strands by asking the two lines to release their handshakes and take one step to the left, while keeping their right hands in the C, T, G or A form. You can show how two complementary single strands of DNA can anneal (come together) by then having the tw ...
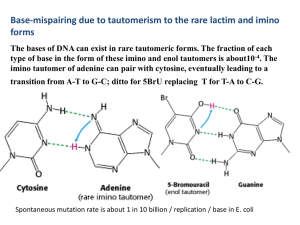
4 . The imino tautomer of adenine can pair with cytosine
... consequence in base pairing. With thymine instead of uracil in DNA, U can be recognized and repaired ...
... consequence in base pairing. With thymine instead of uracil in DNA, U can be recognized and repaired ...
Slide 1
... Both orientations of insert DNA possible. Tandem copies of insert possible. Restriction sites at junctions often eliminated. Tandem copies of insert DNA possible. Both orientations possible. Restriction sites at junctions preserved. Background of non-recombinants is low. One possible orientation of ...
... Both orientations of insert DNA possible. Tandem copies of insert possible. Restriction sites at junctions often eliminated. Tandem copies of insert DNA possible. Both orientations possible. Restriction sites at junctions preserved. Background of non-recombinants is low. One possible orientation of ...
13. DNA Replication
... 1. Review of DNA structure DNA double helix model: DNA made of nucleotide building blocks linked into polymer chains Bases are on inside, sugars and phosphates form a backbone on outside Two strands exist in an antiparallel arrangement ...
... 1. Review of DNA structure DNA double helix model: DNA made of nucleotide building blocks linked into polymer chains Bases are on inside, sugars and phosphates form a backbone on outside Two strands exist in an antiparallel arrangement ...
PPT3
... What we want is a deterministic algorithm for applying the inter- and intramolecular recombination operations to descramble an arbitrary gene. ...
... What we want is a deterministic algorithm for applying the inter- and intramolecular recombination operations to descramble an arbitrary gene. ...
DNA stucture - worldofbiology09
... For cells to divide into new cells and still contain all the necessary instructions (genes), DNA must have the ability to replicate itself. DNA replication is said to be semi-conservative as each new DNA molecule contains one strand from the original and one newly synthesised ...
... For cells to divide into new cells and still contain all the necessary instructions (genes), DNA must have the ability to replicate itself. DNA replication is said to be semi-conservative as each new DNA molecule contains one strand from the original and one newly synthesised ...
RNA - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... 8. Why is DNA replication called "semi-conservative"? __________________________________________ 9. The two sides of the DNA helix are held together by ________________________ 10. What are the DNA base pairing rules? What are the RNA base pairing rules? DNA ______________________ RNA ______________ ...
... 8. Why is DNA replication called "semi-conservative"? __________________________________________ 9. The two sides of the DNA helix are held together by ________________________ 10. What are the DNA base pairing rules? What are the RNA base pairing rules? DNA ______________________ RNA ______________ ...
In 1953 Watson and Crick developed a double helix model for DNA
... The two nucleic acid strands are _______________________ to each other. That means that one strand is “_____________________” compared to the other. The 2 nucleic acid strands are held together by ____________ _ _____________ between the nitrogen bases. When the nitrogen bases bond together they fol ...
... The two nucleic acid strands are _______________________ to each other. That means that one strand is “_____________________” compared to the other. The 2 nucleic acid strands are held together by ____________ _ _____________ between the nitrogen bases. When the nitrogen bases bond together they fol ...
Holliday junction

A Holliday junction is a branched nucleic acid structure that contains four double-stranded arms joined together. These arms may adopt one of several conformations depending on buffer salt concentrations and the sequence of nucleobases closest to the junction. The structure is named after the molecular biologist Robin Holliday, who proposed its existence in 1964.In biology, Holliday junctions are a key intermediate in many types of genetic recombination, as well as in double-strand break repair. These junctions usually have a symmetrical sequence and are thus mobile, meaning that the four individual arms may slide though the junction in a specific pattern that largely preserves base pairing. Additionally, four-arm junctions similar to Holliday junctions appear in some functional RNA molecules.Immobile Holliday junctions, with asymmetrical sequences that lock the strands in a specific position, were artificially created by scientists to study their structure as a model for natural Holliday junctions. These junctions also later found use as basic structural building blocks in DNA nanotechnology, where multiple Holliday junctions can be combined into specific designed geometries that provide molecules with a high degree of structural rigidity.