DNA
... • DNA is found in the mitochondria. • mDNA is only found in the egg. Sperm has no mitochondria so mDNA is passed to offspring from the mother. • One sequence of DNA is a genome or gene. • Unwind all our DNA, it will stretch from the moon and back 6000X. ...
... • DNA is found in the mitochondria. • mDNA is only found in the egg. Sperm has no mitochondria so mDNA is passed to offspring from the mother. • One sequence of DNA is a genome or gene. • Unwind all our DNA, it will stretch from the moon and back 6000X. ...
The Genetic Code
... DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. ...
... DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. ...
You Light Up My Life - Sarasota Military Academy
... • DNA polymerase can read correct sequence from complementary strand and, together with DNA ligase, can repair mistakes in incorrect strand ...
... • DNA polymerase can read correct sequence from complementary strand and, together with DNA ligase, can repair mistakes in incorrect strand ...
Directed evolution
... revealed that they can be grouped onto families that are similar in size and amino acid sequence. Enzyme belonging to the same family have evolved from a common ancestor to acquire a new catabolic function through various genetic events, such as gene transfer, recombination, duplication, multiple po ...
... revealed that they can be grouped onto families that are similar in size and amino acid sequence. Enzyme belonging to the same family have evolved from a common ancestor to acquire a new catabolic function through various genetic events, such as gene transfer, recombination, duplication, multiple po ...
Gene rearrangements occur via various mechanisms
... without the donating chromosome being changed. Gene conversion occurs at high frequency at the actual site of the recombination event during meiosis. It is a process by which a DNA sequence is copied from one DNA helix (which remains unchanged) to another DNA helix, whose sequence is altered. Gene c ...
... without the donating chromosome being changed. Gene conversion occurs at high frequency at the actual site of the recombination event during meiosis. It is a process by which a DNA sequence is copied from one DNA helix (which remains unchanged) to another DNA helix, whose sequence is altered. Gene c ...
GOALS OF THE HUMAN GENOME PROJECT
... Double stranded RNA: Possible secondary structures of RNA molecules. The double-stranded regions are depicted by connecting hydrogen bonds. Loops are noncomplementary regions that are not hydrogen bonded with complementary bases. Double-stranded RNA structures can form within a single RNA molecule ...
... Double stranded RNA: Possible secondary structures of RNA molecules. The double-stranded regions are depicted by connecting hydrogen bonds. Loops are noncomplementary regions that are not hydrogen bonded with complementary bases. Double-stranded RNA structures can form within a single RNA molecule ...
goals of the human genome project
... Double stranded RNA: Possible secondary structures of RNA molecules. The double-stranded regions are depicted by connecting hydrogen bonds. Loops are noncomplementary regions that are not hydrogen bonded with complementary bases. Double-stranded RNA structures can form within a single RNA molecule ...
... Double stranded RNA: Possible secondary structures of RNA molecules. The double-stranded regions are depicted by connecting hydrogen bonds. Loops are noncomplementary regions that are not hydrogen bonded with complementary bases. Double-stranded RNA structures can form within a single RNA molecule ...
DNA replication
... - Thus when each strand of the double stranded parental DNA molecules separates from its complement during replication, each ...
... - Thus when each strand of the double stranded parental DNA molecules separates from its complement during replication, each ...
7.014 Problem Set 3
... i. Double stranded DNA where both strands are labeled ii. Double stranded DNA where one strand is labeled iii. Double stranded DNA where neither strand is labled Semi-conservative replication was only one of the models of DNA replication proposed after the discovery of DNA structure. One of the ot ...
... i. Double stranded DNA where both strands are labeled ii. Double stranded DNA where one strand is labeled iii. Double stranded DNA where neither strand is labled Semi-conservative replication was only one of the models of DNA replication proposed after the discovery of DNA structure. One of the ot ...
Part 1
... other. The strands are also complementary as the adenine base of one strand always binds, via two hydrogen bonds, to the thymine base of the other strand, or vice versa. Likewise, the guanine base of one strand always binds by three hydrogen bonds to the cytosine base of the other strand, or vice ve ...
... other. The strands are also complementary as the adenine base of one strand always binds, via two hydrogen bonds, to the thymine base of the other strand, or vice versa. Likewise, the guanine base of one strand always binds by three hydrogen bonds to the cytosine base of the other strand, or vice ve ...
DNA REPLICATION Review of DNA Structure
... • When nucleotide triphosphates are linked to the sugar-phosphate backbone it loses two of its phosphates • Replication always occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction ...
... • When nucleotide triphosphates are linked to the sugar-phosphate backbone it loses two of its phosphates • Replication always occurs in the 5’ to 3’ direction ...
DNA Notes
... • One bacteriophage had radioactive phosphorus-32 in its DNA & was used to infect a bacterial cell • The other had radioactive sulfur-35 in its protein coat & was used to infect a bacterial cell ...
... • One bacteriophage had radioactive phosphorus-32 in its DNA & was used to infect a bacterial cell • The other had radioactive sulfur-35 in its protein coat & was used to infect a bacterial cell ...
Chapter 30 DNA replication, repair and recombination
... Nucleotide excision repair (NER): In response to helix distortions, the demaged nucleotides are removed and replaced – E. coli UvrABC endonuclease – Repair of pyrimidine dimer – Genetic diseases caused by defective NER – Hypersensitivity to UV light and many pathological outcomes including skin canc ...
... Nucleotide excision repair (NER): In response to helix distortions, the demaged nucleotides are removed and replaced – E. coli UvrABC endonuclease – Repair of pyrimidine dimer – Genetic diseases caused by defective NER – Hypersensitivity to UV light and many pathological outcomes including skin canc ...
Lecture 19-Chap15
... 15.12 Strand-Transfer Proteins Catalyze Single-Strand Assimilation • RecA forms filaments with single-stranded or duplex DNA and catalyzes the ability of a single-stranded DNA with a free 3′ end to displace its counterpart in a DNA duplex. • presynaptic filaments – Single-stranded DNA bound in a he ...
... 15.12 Strand-Transfer Proteins Catalyze Single-Strand Assimilation • RecA forms filaments with single-stranded or duplex DNA and catalyzes the ability of a single-stranded DNA with a free 3′ end to displace its counterpart in a DNA duplex. • presynaptic filaments – Single-stranded DNA bound in a he ...
What is the NUTRIENT needed for growth and repair
... Exponential increase in the amount of DNA produced in PCR ...
... Exponential increase in the amount of DNA produced in PCR ...
8.2 * 8.3 Notes
... molecule that carries most of the genetic instructions used in the development, functioning and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses. ...
... molecule that carries most of the genetic instructions used in the development, functioning and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses. ...
MCB 421-2006: Homologous Recombination
... 1) substrate analysis; 2) epistatic analysis. Substrate analysis involves varying the physical nature of recombinational substrates and detecting the resulting recombination frequencies in various rec mutants. One popular substrate configuration is a linear piece of a donor chromosome, which is intr ...
... 1) substrate analysis; 2) epistatic analysis. Substrate analysis involves varying the physical nature of recombinational substrates and detecting the resulting recombination frequencies in various rec mutants. One popular substrate configuration is a linear piece of a donor chromosome, which is intr ...
Chapter 9 DNA and the Molecular Structure of Chromosomes
... two strands held together by hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs: adenine paired with thymine and guanine paired with cytosine. ...
... two strands held together by hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs: adenine paired with thymine and guanine paired with cytosine. ...
DNA - Royal Society of Chemistry
... DNA are responsible for switching genes on and off and regulating how much of each type of protein is made. A detailed discussion of DNA/RNA function and the fundamental processes of replication, transcription and translation can be found in any good textbook on molecular biology. However, the Watso ...
... DNA are responsible for switching genes on and off and regulating how much of each type of protein is made. A detailed discussion of DNA/RNA function and the fundamental processes of replication, transcription and translation can be found in any good textbook on molecular biology. However, the Watso ...
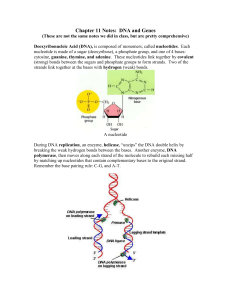
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
No Slide Title
... Bacteria have > 1 protein/mRNA (polycistronic) • Mutations can have polar effects: mutations in upstream genes may affect expression of perfectly good downstream genes! ...
... Bacteria have > 1 protein/mRNA (polycistronic) • Mutations can have polar effects: mutations in upstream genes may affect expression of perfectly good downstream genes! ...
05E-NucleicAcids
... • Because of their shapes, only some bases are compatible with each other. • Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T) and guanine (G) with cytosine (C). ...
... • Because of their shapes, only some bases are compatible with each other. • Adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T) and guanine (G) with cytosine (C). ...
DNA
... –Rosalind Franklin got an ‘X’ pattern from X-ray crystallography of DNA –Chargaff figured out base pairing (A to T and C to G) ...
... –Rosalind Franklin got an ‘X’ pattern from X-ray crystallography of DNA –Chargaff figured out base pairing (A to T and C to G) ...
Holliday junction

A Holliday junction is a branched nucleic acid structure that contains four double-stranded arms joined together. These arms may adopt one of several conformations depending on buffer salt concentrations and the sequence of nucleobases closest to the junction. The structure is named after the molecular biologist Robin Holliday, who proposed its existence in 1964.In biology, Holliday junctions are a key intermediate in many types of genetic recombination, as well as in double-strand break repair. These junctions usually have a symmetrical sequence and are thus mobile, meaning that the four individual arms may slide though the junction in a specific pattern that largely preserves base pairing. Additionally, four-arm junctions similar to Holliday junctions appear in some functional RNA molecules.Immobile Holliday junctions, with asymmetrical sequences that lock the strands in a specific position, were artificially created by scientists to study their structure as a model for natural Holliday junctions. These junctions also later found use as basic structural building blocks in DNA nanotechnology, where multiple Holliday junctions can be combined into specific designed geometries that provide molecules with a high degree of structural rigidity.