Dopamine neurons projecting to the posterior striatum form an
... the position of each labeled cell body. Therefore, we only needed to image with sufficient resolution to distinguish every cell body throughout the brain (Figure 2C). This resulted in ~2Tb of image data from each brain, allowing us to image many brains, whereas imaging with even 2x higher magnificat ...
... the position of each labeled cell body. Therefore, we only needed to image with sufficient resolution to distinguish every cell body throughout the brain (Figure 2C). This resulted in ~2Tb of image data from each brain, allowing us to image many brains, whereas imaging with even 2x higher magnificat ...
J Neurophysiol - University of Connecticut
... endeavored to draw thalamocortical comparisons from nonsimultaneous recordings (Barone et al. 1996; Clarey et al. 1995; Pelleg-Toiba and Wollberg 1989; Samson et al. 2000). Because differences in animal model, anesthesia, stimuli, and measured response parameters could affect results, the literature ...
... endeavored to draw thalamocortical comparisons from nonsimultaneous recordings (Barone et al. 1996; Clarey et al. 1995; Pelleg-Toiba and Wollberg 1989; Samson et al. 2000). Because differences in animal model, anesthesia, stimuli, and measured response parameters could affect results, the literature ...
NG2+ CNS Glial Progenitors Remain Committed to the Oligodendrocyte Lineage in Postnatal Life and following Neurodegeneration
... cells can differentiate into OLs, astrocytes, or neurons in vitro, depending on the growth conditions (Kondo and Raff, 2000), and studies in which NG2+ cells have been labeled in vivo using transgenic approaches suggest that they also have the capacity to develop into interneurons in the hippocampus ...
... cells can differentiate into OLs, astrocytes, or neurons in vitro, depending on the growth conditions (Kondo and Raff, 2000), and studies in which NG2+ cells have been labeled in vivo using transgenic approaches suggest that they also have the capacity to develop into interneurons in the hippocampus ...
Is the Lateral Septum's Inhibitory Influence on the Amygdala Mediated... GABA-ergic Neurons? Mason Austin
... for the fight or flight responses that are necessary to escape predators, avoid natural hazards, and challenge competitors in order to pass on genetic material. As useful as fear may be however, it also comes at a steep price. A highly fearful state is very taxing, both physically and emotionally, a ...
... for the fight or flight responses that are necessary to escape predators, avoid natural hazards, and challenge competitors in order to pass on genetic material. As useful as fear may be however, it also comes at a steep price. A highly fearful state is very taxing, both physically and emotionally, a ...
Cortex, Cognition and the Cell: New Insights into the Pyramidal
... and Tees, 2000; Jerison, 2001). In keeping with this dogma, regional differences in cortical function such as vision, somatosensation and hearing, were attributed solely to the source of their inputs. However, if circuitry in prefrontal cortex, the region of the brain often implicated in cognitive p ...
... and Tees, 2000; Jerison, 2001). In keeping with this dogma, regional differences in cortical function such as vision, somatosensation and hearing, were attributed solely to the source of their inputs. However, if circuitry in prefrontal cortex, the region of the brain often implicated in cognitive p ...
Psychology
... with the external world and the world inside our bodies. It carries information to the brain from our senses so the brain can interpret the incoming information and respond to it by transmitting messages initiating action or movement in nerves in different parts of our bodies. It is helpful to think ...
... with the external world and the world inside our bodies. It carries information to the brain from our senses so the brain can interpret the incoming information and respond to it by transmitting messages initiating action or movement in nerves in different parts of our bodies. It is helpful to think ...
Sample pages PDF
... functions. Lesioning or destruction of any given area from trauma, tumoral compression, or ischemia causes alteration or loss of that function. In fact, such lesions are what allowed brain functions to be mapped over the centuries. In the early 1950s, researchers, including Montreal neurosurgeon Wil ...
... functions. Lesioning or destruction of any given area from trauma, tumoral compression, or ischemia causes alteration or loss of that function. In fact, such lesions are what allowed brain functions to be mapped over the centuries. In the early 1950s, researchers, including Montreal neurosurgeon Wil ...
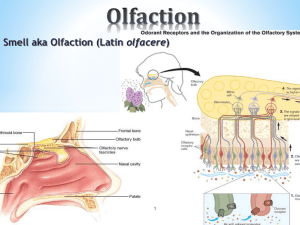
olfaction
... paleocortex) adjacent to lateral olfactory tract in temporal lobe. This is only sense that does not have relay in thalamus on way from receptors to cerebral cortex. From piriform cortex there are projections to hypothalamus, the thalamus, amygdala, entorhinal cortex. From thalamus there is a project ...
... paleocortex) adjacent to lateral olfactory tract in temporal lobe. This is only sense that does not have relay in thalamus on way from receptors to cerebral cortex. From piriform cortex there are projections to hypothalamus, the thalamus, amygdala, entorhinal cortex. From thalamus there is a project ...
Goodwin S.F., Taylor, B.J., Villella, A., Foss, M., Ryner, L. C., Baker, B. S., and Hall, J. C.
... splice acceptor sites that create alternative processing pathways. In situ hybridization revealed no alterations in the locations of cells expressing the P1-fru-promoter-derived transcripts in fru2, fru3, fru4, and frusat pharate adults. For the fru1 mutant (which is due to an inversion breakpoint n ...
... splice acceptor sites that create alternative processing pathways. In situ hybridization revealed no alterations in the locations of cells expressing the P1-fru-promoter-derived transcripts in fru2, fru3, fru4, and frusat pharate adults. For the fru1 mutant (which is due to an inversion breakpoint n ...
Postnatal Development of the Corticospinal Tract in the Reeler Mouse
... of the animals used in the present DiI study were as follows: 2 normal and 4 reeler on P0.5, 3 normal and 5 reeler on P1, 2 normal and 2 reeler on P2, 2 normal and 3 reeler on P3, 3 normal and 3 reeler on P4, 3 normal and 4 reeler on P5, 3 normal and 4 reeler on P7, 2 normal and 4 reeler on P9/ P10. ...
... of the animals used in the present DiI study were as follows: 2 normal and 4 reeler on P0.5, 3 normal and 5 reeler on P1, 2 normal and 2 reeler on P2, 2 normal and 3 reeler on P3, 3 normal and 3 reeler on P4, 3 normal and 4 reeler on P5, 3 normal and 4 reeler on P7, 2 normal and 4 reeler on P9/ P10. ...
166 - UCSF Physiology - University of California, San Francisco
... use of a null allele of 1 integrin gene (Stephens et al., 1995) and generated heterozygous animals with one null allele and one Figure 1. emx1–cre induces recombination in excitatory but not inhibitory neurons in the hippocampus. a– c, Confocal conditional allele. This ensures the effi- micrographs ...
... use of a null allele of 1 integrin gene (Stephens et al., 1995) and generated heterozygous animals with one null allele and one Figure 1. emx1–cre induces recombination in excitatory but not inhibitory neurons in the hippocampus. a– c, Confocal conditional allele. This ensures the effi- micrographs ...
Horizontal Interactions in Cat Striate Cortex: 1. Anatomical Substrate
... The system of tangential connections was studied in area 17 of normally reared (NR), binocularly deprived (BD) and dark-reared (DR) kittens and adult cats. Connections were labelled antero- and retrogradely by intracortical micro-injections of several fluorescent markers and horseradish peroxidase c ...
... The system of tangential connections was studied in area 17 of normally reared (NR), binocularly deprived (BD) and dark-reared (DR) kittens and adult cats. Connections were labelled antero- and retrogradely by intracortical micro-injections of several fluorescent markers and horseradish peroxidase c ...
PDF - Stanford University
... More than 75% of depressed patients have more than one depressive episode, often relapsing within two years of recovery from a depressive episode (Boland & Keller, 2009). Indeed, between one-half and two-thirds of people who have ever been clinically depressed will be in an episode in any given year ...
... More than 75% of depressed patients have more than one depressive episode, often relapsing within two years of recovery from a depressive episode (Boland & Keller, 2009). Indeed, between one-half and two-thirds of people who have ever been clinically depressed will be in an episode in any given year ...
Embryonic development of the Drosophila brain: formation of
... microscopy to determine how the commissural and descending pathways are established. We find that commissural interconnections are formed by axons that project along an interhemispheric cell bridge and that descending interconnections are prefigured by a chain of glial cells along which pioneering a ...
... microscopy to determine how the commissural and descending pathways are established. We find that commissural interconnections are formed by axons that project along an interhemispheric cell bridge and that descending interconnections are prefigured by a chain of glial cells along which pioneering a ...
A Simple Biophysically Plausible Model for Long Time
... Eq. (1) presents two major challenges for a biological circuit: 1. In order for the model to describe neural firing and behavioral effects up to long time scales, there should be neurons with time constants on the order of that time scale. The time constant of each unit in Eq. (1) is 1/s. 2. Rapid e ...
... Eq. (1) presents two major challenges for a biological circuit: 1. In order for the model to describe neural firing and behavioral effects up to long time scales, there should be neurons with time constants on the order of that time scale. The time constant of each unit in Eq. (1) is 1/s. 2. Rapid e ...
a needle into the sub- and the dorsal funiculi. Preganglionic
... described in 1952, names were given to many of the cell columns, with all but a few of these names now having fallen into disuse. They were used differently by different authors, and ...
... described in 1952, names were given to many of the cell columns, with all but a few of these names now having fallen into disuse. They were used differently by different authors, and ...
19. Senses General and Special
... The receptive field of a receptor is the entire area through which the sensitive ends of the receptor cell are distributed (figure 19.1). There is an inverse relationship between the size of the receptive field and our ability to identify the exact location of a stimulus. If the receptive field is s ...
... The receptive field of a receptor is the entire area through which the sensitive ends of the receptor cell are distributed (figure 19.1). There is an inverse relationship between the size of the receptive field and our ability to identify the exact location of a stimulus. If the receptive field is s ...
Neural Control of the Pancreas
... plasticity and can be modulated by numerous neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, hormones and physiological conditions (10). Studies using injections of transsynaptic retrograde tracers into the pancreas of sympathectomised rats have demonstrated the distribution of higher order neurons that innervat ...
... plasticity and can be modulated by numerous neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, hormones and physiological conditions (10). Studies using injections of transsynaptic retrograde tracers into the pancreas of sympathectomised rats have demonstrated the distribution of higher order neurons that innervat ...
mGluR-dependent persistent firing in entorhinal cortex layer III neurons SYNAPTIC MECHANISMS Motoharu Yoshida,
... 2007; Mikami et al., 2007). It has also been shown that group I mGluRs can modulate ICAN and transient receptor potential-like (TRP) channels, which are strong candidates as molecular correlates for ICAN (Congar et al., 1997; Gee et al., 2003; Ene et al., 2007; Fowler et al., 2007). These findings su ...
... 2007; Mikami et al., 2007). It has also been shown that group I mGluRs can modulate ICAN and transient receptor potential-like (TRP) channels, which are strong candidates as molecular correlates for ICAN (Congar et al., 1997; Gee et al., 2003; Ene et al., 2007; Fowler et al., 2007). These findings su ...
Sensory Pathways and Emotional Context for Action
... the external and internal environments. The pOFC also has the most specialized connections with the amygdala and the most robust connections with the magnocellular sector of the mediodorsal (MDmc) nucleus of the thalamus. These connections set pOFC apart from other prefrontal areas, including rostra ...
... the external and internal environments. The pOFC also has the most specialized connections with the amygdala and the most robust connections with the magnocellular sector of the mediodorsal (MDmc) nucleus of the thalamus. These connections set pOFC apart from other prefrontal areas, including rostra ...
Chapter 5 Learning to attend in primary visual cortex
... Previous studies on the effects of learning on activity in visual cortex usually investigated the effects of extensive training protocols where animals were trained across many days (Kobatake et al. 1998; Schoups 2001; Schwartz et al 2002; Lee et al 2002; Furmanski et al 2004; Sigman and Gilbert 200 ...
... Previous studies on the effects of learning on activity in visual cortex usually investigated the effects of extensive training protocols where animals were trained across many days (Kobatake et al. 1998; Schoups 2001; Schwartz et al 2002; Lee et al 2002; Furmanski et al 2004; Sigman and Gilbert 200 ...
The Ventral Striatopallidum and Extended Amygdala in
... located between the striatum (amygdalostriatal transition area) dorsolaterally and the interstitial nucleus of the ansa lenticularis at its dorsomedial side. The central nucleus can further be subdivided into a medial, lateral and lateral capsular central nucleus. Functionally, the central nucleus i ...
... located between the striatum (amygdalostriatal transition area) dorsolaterally and the interstitial nucleus of the ansa lenticularis at its dorsomedial side. The central nucleus can further be subdivided into a medial, lateral and lateral capsular central nucleus. Functionally, the central nucleus i ...
Evolution of the Pallium in Birds and Reptiles
... relatively unique feature in the medial part of their PDVR called the nucleus sphericus, which is involved in accessory olfactory bulb function and is not found avians, crocodilians, or turtles [4,9]; nucleus sphericus is thought to be the homologue of portions of mammalian pallial amygdala nuclei ( ...
... relatively unique feature in the medial part of their PDVR called the nucleus sphericus, which is involved in accessory olfactory bulb function and is not found avians, crocodilians, or turtles [4,9]; nucleus sphericus is thought to be the homologue of portions of mammalian pallial amygdala nuclei ( ...
Figure 15.9
... • White rami communicantes: structures containing sympathetic preganglionic axons that connect the anterior ramus of the spinal nerve with the ganglia of the sympathetic ...
... • White rami communicantes: structures containing sympathetic preganglionic axons that connect the anterior ramus of the spinal nerve with the ganglia of the sympathetic ...
Autonomic NS
... • White rami communicantes: structures containing sympathetic preganglionic axons that connect the anterior ramus of the spinal nerve with the ganglia of the sympathetic ...
... • White rami communicantes: structures containing sympathetic preganglionic axons that connect the anterior ramus of the spinal nerve with the ganglia of the sympathetic ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.