Encoding of conditioned fear in central amygdala inhibitory circuits
... the central nucleus of the amygdala (CEA) has been considered to be primarily involved in the behavioural expression of conditioned fear responses. CEA output neurons, most of which are located in its medial subdivision (CEm), project to downstream targets in the brainstem and in the hypothalamus wh ...
... the central nucleus of the amygdala (CEA) has been considered to be primarily involved in the behavioural expression of conditioned fear responses. CEA output neurons, most of which are located in its medial subdivision (CEm), project to downstream targets in the brainstem and in the hypothalamus wh ...
Lecture 2: Structure and function of the NS
... Figure 1–21 Synapses densely distributed over the surface of CNS neu campal neuron developing in tissue culture. The cell body (not seen in directed against MAP2, a microtubule-associated protein restricted to the originating from other neurons not visible in this field form a dense netw directed ag ...
... Figure 1–21 Synapses densely distributed over the surface of CNS neu campal neuron developing in tissue culture. The cell body (not seen in directed against MAP2, a microtubule-associated protein restricted to the originating from other neurons not visible in this field form a dense netw directed ag ...
Impaired Cl Extrusion in Layer V Pyramidal Neurons of Chronically
... the undercut and control group was surprising because previous experiments have shown decreased KCC2 immunoreactivity in neurons of layer V of undercut cortex (Prince et al. 2000; D. A. Prince, unpublished data) and decreased KCC2 expression resulting in a positive shift in ECl and depolarizing GABA ...
... the undercut and control group was surprising because previous experiments have shown decreased KCC2 immunoreactivity in neurons of layer V of undercut cortex (Prince et al. 2000; D. A. Prince, unpublished data) and decreased KCC2 expression resulting in a positive shift in ECl and depolarizing GABA ...
PDF - Folia Biologica
... the majority of cortical layers and because the axon initial segment of pyramidal neurons appears to be the strategical region where the action potential is generated, ChCs are considered to be the most powerful cortical inhibitory neurons. On the basis of immunocytochemistry, ChCs are defined as GAB ...
... the majority of cortical layers and because the axon initial segment of pyramidal neurons appears to be the strategical region where the action potential is generated, ChCs are considered to be the most powerful cortical inhibitory neurons. On the basis of immunocytochemistry, ChCs are defined as GAB ...
vikram_slides1
... Periodicity is constant and not considered same weighing window are applied across the stimulus ...
... Periodicity is constant and not considered same weighing window are applied across the stimulus ...
TotalPT - Department of Computer Engineering
... But biological learning is not a single process: some forms are very quick and others relatively slow. Short-term biological memory, in particular, works very quickly, so slow neural network models are not plausible candidates in this case ...
... But biological learning is not a single process: some forms are very quick and others relatively slow. Short-term biological memory, in particular, works very quickly, so slow neural network models are not plausible candidates in this case ...
Neural Networks Architecture
... if h j 0 and u j 1 then u j will not change u j h j h j 0 if h j 0 and u j 0 then u j will change u j h j 0 if h j 0 and u j 1 then u j will not change u j h j 0 if h j 0 and u j 1 then u j will change u j h j h j 0 in each case u j h j is maximum when u j does no ...
... if h j 0 and u j 1 then u j will not change u j h j h j 0 if h j 0 and u j 0 then u j will change u j h j 0 if h j 0 and u j 1 then u j will not change u j h j 0 if h j 0 and u j 1 then u j will change u j h j h j 0 in each case u j h j is maximum when u j does no ...
FOREFRONT REVIEW WHAT IS THE MAMMALIAN DENTATE GYRUS GOOD FOR?
... Computational models have hypothesized that the function of the MF is to enforce a new, well-separated pattern of activity onto CA3 cells, to represent a new memory, prevailing over the interference produced by the traces of older memories already stored on CA3 recurrent collateral connections. Alth ...
... Computational models have hypothesized that the function of the MF is to enforce a new, well-separated pattern of activity onto CA3 cells, to represent a new memory, prevailing over the interference produced by the traces of older memories already stored on CA3 recurrent collateral connections. Alth ...
operant conditioning of feeding behavior in aplysia
... conditioning. In contrast, the cellular mechanisms underlying operant conditioning are poorly understood. This deficit results, in part, from the lack of a suitably tractable preparation that exhibits operant conditioning and that is amenable to cellular analysis. To address this issue, the feeding ...
... conditioning. In contrast, the cellular mechanisms underlying operant conditioning are poorly understood. This deficit results, in part, from the lack of a suitably tractable preparation that exhibits operant conditioning and that is amenable to cellular analysis. To address this issue, the feeding ...
How to recognise collateral damage in partial nerve injury models... pain Commentary
... model, emphasising the need to minimise tissue damage in adjacent segments. Secondly, they found significant differences in the neurochemical responses of damaged (ATF3+) and undamaged (ATF3 ) L4 neurons. Specifically, neuropeptide Y was only upregulated in damaged neurons (as reported previously [15] ...
... model, emphasising the need to minimise tissue damage in adjacent segments. Secondly, they found significant differences in the neurochemical responses of damaged (ATF3+) and undamaged (ATF3 ) L4 neurons. Specifically, neuropeptide Y was only upregulated in damaged neurons (as reported previously [15] ...
Stress induces atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA3
... this responsiveness is drastically reduced with the destruction of the mossy fibers 6. CA3 neurons may also be more vulnerable to damage because they lack both calbindin D28k and parvalbumin, calcium-binding proteins that are present in dentate granule neurons as well as in CA1 and CA2 pyramidal neu ...
... this responsiveness is drastically reduced with the destruction of the mossy fibers 6. CA3 neurons may also be more vulnerable to damage because they lack both calbindin D28k and parvalbumin, calcium-binding proteins that are present in dentate granule neurons as well as in CA1 and CA2 pyramidal neu ...
Chapter 49 and 50 Presentations-Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... The membrane potential can change from its resting value when the membrane’s permeability to a particular ion changes—due to the opening/closing of ion channels. Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl- all play major roles in nerve signal ...
... The membrane potential can change from its resting value when the membrane’s permeability to a particular ion changes—due to the opening/closing of ion channels. Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Cl- all play major roles in nerve signal ...
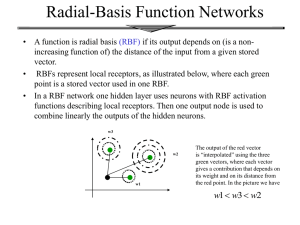
Radial-Basis Function Networks
... • A hidden neuron is more sensitive to data points near its center. • For Gaussian RBF this sensitivity may be tuned by adjusting the spread , where a larger spread implies less sensitivity. • Biological example: cochlear stereocilia cells (in our ears ...) have locally tuned frequency responses. ...
... • A hidden neuron is more sensitive to data points near its center. • For Gaussian RBF this sensitivity may be tuned by adjusting the spread , where a larger spread implies less sensitivity. • Biological example: cochlear stereocilia cells (in our ears ...) have locally tuned frequency responses. ...
THE SENSORIMOTOR SYSTEM (p.l) 1. Introduction Like the
... Lesions --- S unable to move one body part without moving other parts (loses the precision of movement) --- astereognosia (difficulty recognizing objects by touch) --- reduced speed, accuracy & force of movement --- but S still above to move (less precise, “clumsy” movements) 6. Cerebellum and Basal ...
... Lesions --- S unable to move one body part without moving other parts (loses the precision of movement) --- astereognosia (difficulty recognizing objects by touch) --- reduced speed, accuracy & force of movement --- but S still above to move (less precise, “clumsy” movements) 6. Cerebellum and Basal ...
B42010712
... Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is an information processing paradigm that is inspired by the way biological nervous systems, such as the brain, process information. The key element of this paradigm is the novel structure of the information processing system. Neural networks, have remarkable ability ...
... Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is an information processing paradigm that is inspired by the way biological nervous systems, such as the brain, process information. The key element of this paradigm is the novel structure of the information processing system. Neural networks, have remarkable ability ...
Receptive Field Properties of Single Neurons in Rat Primary Visual
... used for recording single units extracellularly. The recording microelectrode was introduced into the tiny craniotomy made over V1. As the microelectrode was advanced slowly, various stimuli were displayed across the animal’s visual field to activate cells, many of which had very low or no spontaneo ...
... used for recording single units extracellularly. The recording microelectrode was introduced into the tiny craniotomy made over V1. As the microelectrode was advanced slowly, various stimuli were displayed across the animal’s visual field to activate cells, many of which had very low or no spontaneo ...
Neural Darwinism
... view (see Postscript in Edelman, 1992) that the actions of the nervous system can be accounted for by information processing operating ...
... view (see Postscript in Edelman, 1992) that the actions of the nervous system can be accounted for by information processing operating ...
Instrumental Conditioning Driven by Apparently Neutral Stimuli: A
... precede gaze shifts (latency 70-100 ms and 150-200 ms respectively), meaning that they are too fast to be based on a complex computational analysis of the stimulus, which would be required to evaluate the true “economic value” of reward. Based on these findings, Redgrave and Gurney (2006) proposed a ...
... precede gaze shifts (latency 70-100 ms and 150-200 ms respectively), meaning that they are too fast to be based on a complex computational analysis of the stimulus, which would be required to evaluate the true “economic value” of reward. Based on these findings, Redgrave and Gurney (2006) proposed a ...
Spatial learning in the Morris water maze in mice genetically
... to the genome of catalepsy-resistant AKR strain reduced acquisition in the Morris water maze and elevated Il-6 mRNA levels in the cortex and hippocampus in catalepsy-prone D13 mice. An acute ivc administration of BDNF restored the reduced acquisition, improved retention in the Morris water maze, b ...
... to the genome of catalepsy-resistant AKR strain reduced acquisition in the Morris water maze and elevated Il-6 mRNA levels in the cortex and hippocampus in catalepsy-prone D13 mice. An acute ivc administration of BDNF restored the reduced acquisition, improved retention in the Morris water maze, b ...
Use of rabies virus as a transneuronal tracer of neuronal
... Transneuronal tracing with rabies virus: 1 - Amplification of the signal: selfamplifying marker. 2 - Exclusive tropism for neurones in vivo. 3 - Absence of degeneration of infected neurones: possibility of combined visualisation of neurotransmitters & other tracers. 4 - Specificity: propagation excl ...
... Transneuronal tracing with rabies virus: 1 - Amplification of the signal: selfamplifying marker. 2 - Exclusive tropism for neurones in vivo. 3 - Absence of degeneration of infected neurones: possibility of combined visualisation of neurotransmitters & other tracers. 4 - Specificity: propagation excl ...
3- Hopfield networks
... In 1982, John Hopfield introduced an artificial neural network to store and retrieve memory like the human brain. Here, a neuron either is on (firing) or is off (not firing), a vast simplification of the real situation. The state of a neuron (on: +1 or off: -1) will be renewed depending on the input ...
... In 1982, John Hopfield introduced an artificial neural network to store and retrieve memory like the human brain. Here, a neuron either is on (firing) or is off (not firing), a vast simplification of the real situation. The state of a neuron (on: +1 or off: -1) will be renewed depending on the input ...
powerpoint version - University of Arizona
... Stretch receptor = muscle spindle organ - contains intrafusal fibers (as opposed to extrafusal) - Sensitive to stretch (stretch -> APs) ...
... Stretch receptor = muscle spindle organ - contains intrafusal fibers (as opposed to extrafusal) - Sensitive to stretch (stretch -> APs) ...
Nervous System - An-Najah Staff - An
... Postsynaptic Potentials and Synaptic Integration • Binding of neurotransmitter at excitatory chemical synapses results in local graded potentials called excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSPs), caused by the opening of channels that allow simultaneous passage of Na+ and K+. • Neurotransmitter bin ...
... Postsynaptic Potentials and Synaptic Integration • Binding of neurotransmitter at excitatory chemical synapses results in local graded potentials called excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSPs), caused by the opening of channels that allow simultaneous passage of Na+ and K+. • Neurotransmitter bin ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.