Chemical Communication PowerPoint
... cleft and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing it to generate an action potential. ...
... cleft and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing it to generate an action potential. ...
Artificial neural network
... Before discussing the specifics of artificial neural nets though, let us examine what makes real neural nets - brains - function the way they do. Perhaps the single most important concept in neural net research is the idea of connection strength. Neuroscience has given us good evidence for the idea ...
... Before discussing the specifics of artificial neural nets though, let us examine what makes real neural nets - brains - function the way they do. Perhaps the single most important concept in neural net research is the idea of connection strength. Neuroscience has given us good evidence for the idea ...
Fast Rhythmic Bursting Cells: The Horizontal
... brain has to locate the object’s viewing position, distance, and identify the its illumination, shape, color, size, etc. [1]. The temporal coding mechanism or the temporal correlation hypothesis [2], suggests that precise synchronization of feature-related neurons codes for the perceptual coherence. ...
... brain has to locate the object’s viewing position, distance, and identify the its illumination, shape, color, size, etc. [1]. The temporal coding mechanism or the temporal correlation hypothesis [2], suggests that precise synchronization of feature-related neurons codes for the perceptual coherence. ...
General anaesthesia: from molecular targets to neuronal
... Two-pore-domain K+ channels. The opening of K + channels by anaesthetics has long been considered to be potentially important47, and there is growing evidence that K+ channels mediate at least some of the effects of volatile agents. Anaesthetic-activated K+ channels were first characterized in the m ...
... Two-pore-domain K+ channels. The opening of K + channels by anaesthetics has long been considered to be potentially important47, and there is growing evidence that K+ channels mediate at least some of the effects of volatile agents. Anaesthetic-activated K+ channels were first characterized in the m ...
(from quizzes) Bergen 14 Which of the following is true regarding a
... a. The degree of diffusion anisotropy b. The direction of fiber projection c. The volume of gray matter d. The accuracy of word identification e. The thickness of cortex Brain morphometry is a way to: a. Parameterize brain anatomy, enabling the tracking of structural changes over time. b. Image brai ...
... a. The degree of diffusion anisotropy b. The direction of fiber projection c. The volume of gray matter d. The accuracy of word identification e. The thickness of cortex Brain morphometry is a way to: a. Parameterize brain anatomy, enabling the tracking of structural changes over time. b. Image brai ...
Dynamical systems view
... Criticism of the representational approach An epic, twenty-year battle was fought over the cortical representation of movement. Do motor cortex neurons represent the direction of the hand during reaching, or do they represent other features of movement such as joint rotation or muscle output? Grazi ...
... Criticism of the representational approach An epic, twenty-year battle was fought over the cortical representation of movement. Do motor cortex neurons represent the direction of the hand during reaching, or do they represent other features of movement such as joint rotation or muscle output? Grazi ...
EEG Alpha Oscillations The inhibition
... An increase in inhibition (driving an oscillation) is accompanied by an increase in oscillatory activity that results in a stricter timing of neural activity. oscillations are an extremely useful mechanism to control the time window in which neurons are most likely to fire. In a complex network, com ...
... An increase in inhibition (driving an oscillation) is accompanied by an increase in oscillatory activity that results in a stricter timing of neural activity. oscillations are an extremely useful mechanism to control the time window in which neurons are most likely to fire. In a complex network, com ...
More Mind Bogglers!
... cells (neurons). Glial cells are the “support cells” of the nervous system; they perform a number of important jobs that help keep the nervous system running smoothly. Neurons are specialized to receive and transmit information. In fact, almost all functions of the nervous system are based on electr ...
... cells (neurons). Glial cells are the “support cells” of the nervous system; they perform a number of important jobs that help keep the nervous system running smoothly. Neurons are specialized to receive and transmit information. In fact, almost all functions of the nervous system are based on electr ...
Cell dispersion patterns in different cortical regions
... of a cell has the same inactive X-chromosome throughout all successive cell divisions (for review, see Grant and Chapman, 1988). Heterozygous female embryos from line H253 have the lacZ transgene on only one of the two X chromosomes, therefore random inactivation would produce approximately 50% lacZ ...
... of a cell has the same inactive X-chromosome throughout all successive cell divisions (for review, see Grant and Chapman, 1988). Heterozygous female embryos from line H253 have the lacZ transgene on only one of the two X chromosomes, therefore random inactivation would produce approximately 50% lacZ ...
Nerves and Special Senses
... Continuation of the Nerve Impulse between Neurons • Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve – Neurotransmitter is released from a nerve’s axon terminal – The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter – An action potential is started in the ...
... Continuation of the Nerve Impulse between Neurons • Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve – Neurotransmitter is released from a nerve’s axon terminal – The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter – An action potential is started in the ...
Wang et al 2photon calcium imaging of odor in fly brain cell 2003
... glomeruli do not necessarily respond together to a given odor. Each glomerulus visualized anatomically appears to be a functional unit. No partial activity is observed in subcompartments of the glomerular structure. Thus, these imaging results demonstrate that each odorant activates a sparse, conser ...
... glomeruli do not necessarily respond together to a given odor. Each glomerulus visualized anatomically appears to be a functional unit. No partial activity is observed in subcompartments of the glomerular structure. Thus, these imaging results demonstrate that each odorant activates a sparse, conser ...
Cation-Chloride Cotransporters and Neuronal Function
... GABAA and glycine receptors, CCCs also show close interactions with glutamatergic signaling. A crosstalk among CCCs and trophic factors is important in short-term and long-term modification of neuronal properties. CCCs appear to be multifunctional proteins that are also involved in shaping neuronal ...
... GABAA and glycine receptors, CCCs also show close interactions with glutamatergic signaling. A crosstalk among CCCs and trophic factors is important in short-term and long-term modification of neuronal properties. CCCs appear to be multifunctional proteins that are also involved in shaping neuronal ...
Long-term channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) expression
... (H134R)-EYFP-WPRE, in L2/3 pyramidal cells in rat somatosensory cortex via in utero DNA electroporation (IUE). L2/3 pyramidal cells expressed ChR2-EYFP, but histology revealed abnormal morphology and targeting of ChR2-EYFP expressing axons, beginning at postnatal day (P) 33 and increasing with age. ...
... (H134R)-EYFP-WPRE, in L2/3 pyramidal cells in rat somatosensory cortex via in utero DNA electroporation (IUE). L2/3 pyramidal cells expressed ChR2-EYFP, but histology revealed abnormal morphology and targeting of ChR2-EYFP expressing axons, beginning at postnatal day (P) 33 and increasing with age. ...
part ii: the animal mind - Neural and Mental Evolution
... Battistuzzi et al., 2004). The archaebacteria are believed to have been chemoautotrophs that obtained substrates and energy from abiotic organic resources of the early Earth and depended mainly on anaerobic metabolism. The proliferation of photoautotrophs, the cyanobacteria (blue-green algae), which ...
... Battistuzzi et al., 2004). The archaebacteria are believed to have been chemoautotrophs that obtained substrates and energy from abiotic organic resources of the early Earth and depended mainly on anaerobic metabolism. The proliferation of photoautotrophs, the cyanobacteria (blue-green algae), which ...
judasMRT99
... In the developing neocortex of rats and mice, nitrinergic neurons are usually not observed in the marginal zone (MZ), i.e., the developing layer I (Bravo et al., 1997; Derer and Derer, 1993; Iwase et al., 1998; Tomić et al., 1994; Van Eden et al., 1996); they were also not observed in the neocortex ...
... In the developing neocortex of rats and mice, nitrinergic neurons are usually not observed in the marginal zone (MZ), i.e., the developing layer I (Bravo et al., 1997; Derer and Derer, 1993; Iwase et al., 1998; Tomić et al., 1994; Van Eden et al., 1996); they were also not observed in the neocortex ...
Report - Anatomical Society
... motor neurons from the spinal cord and to extract, amplify and purify RNA for use in microarray analysis. This training is required in order for me to be able to perform experiments answering the question: what are the molecular characteristics of motor neurons that make them vulnerable in the child ...
... motor neurons from the spinal cord and to extract, amplify and purify RNA for use in microarray analysis. This training is required in order for me to be able to perform experiments answering the question: what are the molecular characteristics of motor neurons that make them vulnerable in the child ...
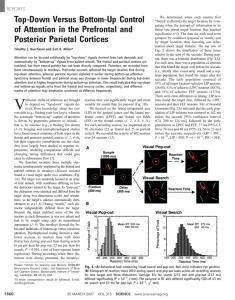
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
PDF
... (Stewart, 1978), at different stages of development. The neuron trios lie immediately beneath the limiting membrane on the dorsal surface of the nervous system. If an embryo is freed from yolk and pinned out with its dorsal side uppermost, the neurons are easy to identify with a compound microscope ...
... (Stewart, 1978), at different stages of development. The neuron trios lie immediately beneath the limiting membrane on the dorsal surface of the nervous system. If an embryo is freed from yolk and pinned out with its dorsal side uppermost, the neurons are easy to identify with a compound microscope ...
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control of Attention in the Prefrontal
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
Anatomy Nervous System Learning Objectives
... o Describe the protective coverings of the brain o List the four principal divisions of the brain and brief ly state their functions o Describe the gross anatomy of the brain; identify the major brain structures visible externally and in mid-sagittal section o Explain the formation and circulation o ...
... o Describe the protective coverings of the brain o List the four principal divisions of the brain and brief ly state their functions o Describe the gross anatomy of the brain; identify the major brain structures visible externally and in mid-sagittal section o Explain the formation and circulation o ...
(SCI) patients in the United States
... causing slight contractions in muscles, proving electricity could be applied centrally with peripheral effects. In the recent past, experiment on stimulating certain parts of the brain or spinal cord to contract certain muscles has been performed (Tarsey, 2008). Modern experiments looking into the s ...
... causing slight contractions in muscles, proving electricity could be applied centrally with peripheral effects. In the recent past, experiment on stimulating certain parts of the brain or spinal cord to contract certain muscles has been performed (Tarsey, 2008). Modern experiments looking into the s ...
Durand and Barlow Chapter 2: An Integrative Approach to
... – Anger, hostility, emotional suppression, illness, and ...
... – Anger, hostility, emotional suppression, illness, and ...
ARTICLES
... negative by forming an unproductive complex with NgR1 and p75 which would be incapable of signaling. To test this possibility, we transfected P7 rat CG neurons with either a construct directing the expression of a dominant negative (DN)-LINGO-1, or with a vector control, and looked for cellular resp ...
... negative by forming an unproductive complex with NgR1 and p75 which would be incapable of signaling. To test this possibility, we transfected P7 rat CG neurons with either a construct directing the expression of a dominant negative (DN)-LINGO-1, or with a vector control, and looked for cellular resp ...
Heterogeneity of the Population of Command Neurons in the Lamprey
... The influences could be seen in the ventral root branches both ipsilateral and contralateral to an RS neuron. The amplitude of the response, that is, a deviation of the summated M N activity from the level observed before the arrival of the RS spike, and the response duration varied considerably. Fo ...
... The influences could be seen in the ventral root branches both ipsilateral and contralateral to an RS neuron. The amplitude of the response, that is, a deviation of the summated M N activity from the level observed before the arrival of the RS spike, and the response duration varied considerably. Fo ...
Visual Coding and the Retinal Receptors
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
... in space from which light strikes it. • For other visual cells, receptive fields are derived from the visual field of cells that either excite or inhibit. – Example: ganglion cells converge to form the receptive field of the next level of cells. ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.