The Nervous System
... of the work of Fernando Nottebohm (1989). Nottebohm’s research shows that new neurons are produced (neurogenesis) throughout the lifetime of canaries and zebra finches. The cells are formed near the ventricle of the forebrain and migrate along fibers of cells known as radial glia. After migrating, a ...
... of the work of Fernando Nottebohm (1989). Nottebohm’s research shows that new neurons are produced (neurogenesis) throughout the lifetime of canaries and zebra finches. The cells are formed near the ventricle of the forebrain and migrate along fibers of cells known as radial glia. After migrating, a ...
Document
... • a compound synthesized from histidine, an amino acid • You are undoubtedly aware that antihistamines, which are used to treat allergies, can cause drowsiness. • They do so by blocking histamine H 1 receptors in the brain. More modern antihistamines cannot cross the blood–brain barrier, so they do ...
... • a compound synthesized from histidine, an amino acid • You are undoubtedly aware that antihistamines, which are used to treat allergies, can cause drowsiness. • They do so by blocking histamine H 1 receptors in the brain. More modern antihistamines cannot cross the blood–brain barrier, so they do ...
Anatomy of the Sympathetic (Thoracolumbar) Division
... The cell bodies of the preganglionic neurons in the sympathetic division lie in the lateral horns of the spinal cord from the segments T1 through L2. The axon of the preganglionic neuron typically exits at the same level to synapse with the cell bodies and dendrites of the postsynaptic sympathetic n ...
... The cell bodies of the preganglionic neurons in the sympathetic division lie in the lateral horns of the spinal cord from the segments T1 through L2. The axon of the preganglionic neuron typically exits at the same level to synapse with the cell bodies and dendrites of the postsynaptic sympathetic n ...
Cognitive Ability is Associated with Altered
... the full range of capacities that comprise executive function, including working memory and attention are altered in 22q11DS (Karayiorgou et al. 2010). Thus, in the LgDel 22q11DS mouse model, we focused on visual discrimination/ reversal performance as an indication of cognitive capacity relevant to ...
... the full range of capacities that comprise executive function, including working memory and attention are altered in 22q11DS (Karayiorgou et al. 2010). Thus, in the LgDel 22q11DS mouse model, we focused on visual discrimination/ reversal performance as an indication of cognitive capacity relevant to ...
Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity Orchestrates the Response of Pyramidal
... interneurons receive from pyramidal cells can therefore be used as an additional classification scheme. Taken together with the trans-membrane currents peculiar to each interneuron class, these properties can result in a considerable temporal separation of the response of pyramidal cells with that o ...
... interneurons receive from pyramidal cells can therefore be used as an additional classification scheme. Taken together with the trans-membrane currents peculiar to each interneuron class, these properties can result in a considerable temporal separation of the response of pyramidal cells with that o ...
Serotonin 1B Receptor Modulates Frequency Response Curves and
... Neuromodulatory signals such as serotonin are broadly released in the brain in response to changes in internal state (Trulson and Jacobs 1979, 1981) but transform the response properties of sensory neurons in highly specific ways (Hurley et al. 2004; Mooney et al. 1996; Xiang and Prince 2003). This ...
... Neuromodulatory signals such as serotonin are broadly released in the brain in response to changes in internal state (Trulson and Jacobs 1979, 1981) but transform the response properties of sensory neurons in highly specific ways (Hurley et al. 2004; Mooney et al. 1996; Xiang and Prince 2003). This ...
Natural signal statistics and sensory gain control
... auditory nerve fiber shift to the right (on a log scale) in the presence of the masking tone (Fig. 6c and d). This shift is larger when the mask frequency is closer to the optimal frequency for the cell. Again, the model behavior is due to variations in suppressive weighting across neurons tuned for ...
... auditory nerve fiber shift to the right (on a log scale) in the presence of the masking tone (Fig. 6c and d). This shift is larger when the mask frequency is closer to the optimal frequency for the cell. Again, the model behavior is due to variations in suppressive weighting across neurons tuned for ...
A Model of Distributed Sensorimotor Control in the Cockroach
... Any sudden puff of wind directed toward the American cockroach (Periplaneta americana), such as from an attacking predator, evokes a rapid directional turn away from the wind source followed by a run (Ritzmann, 1984). The initial turn is generally completed in approximately 60 msec after the onset o ...
... Any sudden puff of wind directed toward the American cockroach (Periplaneta americana), such as from an attacking predator, evokes a rapid directional turn away from the wind source followed by a run (Ritzmann, 1984). The initial turn is generally completed in approximately 60 msec after the onset o ...
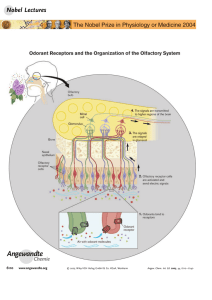
Scents and Sensibility: A Molecular Logic of Olfactory Perception
... that to understand gene control and gene function, however, required a functional assay. Within months of establishing my own laboratory in 1974, Michael Wigler, my first graduate student along with Sol Silverstein, a Professor at Columbia, developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transf ...
... that to understand gene control and gene function, however, required a functional assay. Within months of establishing my own laboratory in 1974, Michael Wigler, my first graduate student along with Sol Silverstein, a Professor at Columbia, developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transf ...
Categorical perception of somesthetic stimuli: psychophysical
... We have recorded the responses of neurons of SI cortex with receptive fields on the finger tips during the categorization of the stimulus speeds (Romo et al., 1996). The results indicate that a class of neurons of SI cortex respond by increasing their impulse rates as a function of the stimulus spee ...
... We have recorded the responses of neurons of SI cortex with receptive fields on the finger tips during the categorization of the stimulus speeds (Romo et al., 1996). The results indicate that a class of neurons of SI cortex respond by increasing their impulse rates as a function of the stimulus spee ...
Non-Cell-Autonomous Effect of Human SOD1G37R
... Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative adult disease characterized by fatal paralysis in both the brain and spinal cord motor neurons. ALS can be induced by inherited mutations in the gene encoding the ubiquitously expressed enzyme superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) (Boill ...
... Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative adult disease characterized by fatal paralysis in both the brain and spinal cord motor neurons. ALS can be induced by inherited mutations in the gene encoding the ubiquitously expressed enzyme superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) (Boill ...
MR of Neuronal Migration Anomalies
... features that they attempt to correlate with specific clinical syndromes. The clinical and CT findings in these classes have been thoroughly discussed [9, 10, 12]. Van Allen and Clarren [13] and Alvarez et al. [14] have disputed these classifications, demonstrating similar clinical manifestations in ...
... features that they attempt to correlate with specific clinical syndromes. The clinical and CT findings in these classes have been thoroughly discussed [9, 10, 12]. Van Allen and Clarren [13] and Alvarez et al. [14] have disputed these classifications, demonstrating similar clinical manifestations in ...
Head direction cells
... different levels of the hippocampus: the dorsal end of the EC projects to the dorsal hippocampus, the ventral end to the ventral hippocampus.[8] . This was relevant because several studies had shown that place cells in the dorsal hippocampus have considerably sharper place fields than cells from mor ...
... different levels of the hippocampus: the dorsal end of the EC projects to the dorsal hippocampus, the ventral end to the ventral hippocampus.[8] . This was relevant because several studies had shown that place cells in the dorsal hippocampus have considerably sharper place fields than cells from mor ...
Is neuroimaging measuring information in the brain? | SpringerLink
... that, whilst many areas project back to V1, V1 itself only sends input to a smaller number of visual areas (Kravitz, Saleem, Baker, Ungerleider, & Mishkin, 2013). From this perspective, V2 or MT are plausible ‘receivers’ for V1, but the motor cortex probably is not. The key question then becomes: Do ...
... that, whilst many areas project back to V1, V1 itself only sends input to a smaller number of visual areas (Kravitz, Saleem, Baker, Ungerleider, & Mishkin, 2013). From this perspective, V2 or MT are plausible ‘receivers’ for V1, but the motor cortex probably is not. The key question then becomes: Do ...
Communication
... Identify the limited range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum detected by humans and compare this range with those of other vertebrates and invertebrates. Humans use the sense of sight to interpret much of the world around them. What we see is called “light”. However, humans only see a ...
... Identify the limited range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum detected by humans and compare this range with those of other vertebrates and invertebrates. Humans use the sense of sight to interpret much of the world around them. What we see is called “light”. However, humans only see a ...
Chapter 2 Functional Neuroanatomy
... the brain, and (3) studying brain dysfunction and its relationship to behavioral disorders (Kolb & Fantie, 1989). Although these approaches can yield useful information about the developing brain, they are not without shortcomings. For example, because of the plasticity of the developing brain follo ...
... the brain, and (3) studying brain dysfunction and its relationship to behavioral disorders (Kolb & Fantie, 1989). Although these approaches can yield useful information about the developing brain, they are not without shortcomings. For example, because of the plasticity of the developing brain follo ...
Chapter 13 - next2eden.net
... binds groups of fibers into bundles contains sensory neurons only ...
... binds groups of fibers into bundles contains sensory neurons only ...
Nerve Tissue
... – nerve signal approaching the synapse, opens the voltage-regulated calcium gates in synaptic knob – Ca2+ enters the knob – triggers exocytosis of synaptic vesicles releasing ACh – empty vesicles drop back into the cytoplasm to be refilled with ACh – reserve pool of synaptic vesicles move to the act ...
... – nerve signal approaching the synapse, opens the voltage-regulated calcium gates in synaptic knob – Ca2+ enters the knob – triggers exocytosis of synaptic vesicles releasing ACh – empty vesicles drop back into the cytoplasm to be refilled with ACh – reserve pool of synaptic vesicles move to the act ...
Reinforcement Learning and the Basal Ganglia
... basal ganglia efferents (via basal ganglionic influence on the thalamus). The general organization of the basal ganglia is that of a feed-forward network (Bergman et al., 1998). The input stage of the basal ganglia is the striatum, which is innervated by excitatory (glutmatergic) pyramidal neurons ...
... basal ganglia efferents (via basal ganglionic influence on the thalamus). The general organization of the basal ganglia is that of a feed-forward network (Bergman et al., 1998). The input stage of the basal ganglia is the striatum, which is innervated by excitatory (glutmatergic) pyramidal neurons ...
Layer Specification of Transplanted Interneurons in Developing
... separate embryological origins for these two cellular populations. However, it remains uncertain how interneurons arising from the subcortical ganglionic eminences are able to participate in the orderly stratification of the cortical layers. A related question concerns whether or not early and late ...
... separate embryological origins for these two cellular populations. However, it remains uncertain how interneurons arising from the subcortical ganglionic eminences are able to participate in the orderly stratification of the cortical layers. A related question concerns whether or not early and late ...
ciliated mucous membrane
... - Necessary for a stable mood - Stimulant medications or caffeine in your daily can cause a decrease in serotonin over time. - Many researchers believe that an imbalance in serotonin levels may lead to depression. Possible problems include low brain cell production of serotonin, a lack of receptor s ...
... - Necessary for a stable mood - Stimulant medications or caffeine in your daily can cause a decrease in serotonin over time. - Many researchers believe that an imbalance in serotonin levels may lead to depression. Possible problems include low brain cell production of serotonin, a lack of receptor s ...
Cranial Nerves
... • The head and neck are not innervated by spinal nerves; rather, they receive sensory information and send motor information via the 12 cranial nerves located in the brain. Although they are located within the skull, cranial nerves are considered part of the peripheral nervous system because they co ...
... • The head and neck are not innervated by spinal nerves; rather, they receive sensory information and send motor information via the 12 cranial nerves located in the brain. Although they are located within the skull, cranial nerves are considered part of the peripheral nervous system because they co ...
L14- Physiology of T..
... From TS cross the midline to ascend in the medial lemniscus to the thalamus ...
... From TS cross the midline to ascend in the medial lemniscus to the thalamus ...
Neuronal Correlates of Sensorimotor Association in Stimulus
... delay between the precue and the RS. The first activation was related to the location of the precue and the second to the direction of the movement. In another study (Vaadia, Gottlieb, & Abeles, 1982), single-neuron activity was recorded in a monkey who was performing a task in which the mapping bet ...
... delay between the precue and the RS. The first activation was related to the location of the precue and the second to the direction of the movement. In another study (Vaadia, Gottlieb, & Abeles, 1982), single-neuron activity was recorded in a monkey who was performing a task in which the mapping bet ...
From sensorimotor learning to memory cells in prefrontal and
... modulation of extracellular calcium concentrations would therefore be most pronounced. Hence, experiments using visual stimuli should elicit stronger memory cell activity in the directly stimulated primary sensory areas, but not in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, where stimulus-elicited activation t ...
... modulation of extracellular calcium concentrations would therefore be most pronounced. Hence, experiments using visual stimuli should elicit stronger memory cell activity in the directly stimulated primary sensory areas, but not in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, where stimulus-elicited activation t ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.