NOTE Mixed-Ligand Complexes of Cu2+, Ni2+, Co2+, Zn2+ with 2,2
... pH which indicates that ABDA does not combine with metal ion where primary complexation takes place. However, curve E diverges from curve C after pH 3-4 suggesting the coordination of ABDA with primary complex, since the dissociation of primary complex does not take place in the pH range 4-8. It can ...
... pH which indicates that ABDA does not combine with metal ion where primary complexation takes place. However, curve E diverges from curve C after pH 3-4 suggesting the coordination of ABDA with primary complex, since the dissociation of primary complex does not take place in the pH range 4-8. It can ...
transition metals
... The iron achieves a co-ordination number of 6 by bonding to the protein globin and to either an oxygen or water molecule. If the sixth bond is to oxygen, the complex produced is oxyhaemoglobin. If the sixth bond is to water the complex is ...
... The iron achieves a co-ordination number of 6 by bonding to the protein globin and to either an oxygen or water molecule. If the sixth bond is to oxygen, the complex produced is oxyhaemoglobin. If the sixth bond is to water the complex is ...
A1982PM90700001
... metal ions, especially in aqueous solution. By the mid-1950s, the pioneering work of ...
... metal ions, especially in aqueous solution. By the mid-1950s, the pioneering work of ...
Inorganic Chemistry: Study Guide – Exam 4 – Fall... Study Guide – Suggested Topics A periodic table will be given.
... o Rules for more and less than half-filled Complexes and color, be able to predict color of complex given spectrum/absorption color for simple absorption. Understand relationships between ligands, Δo, energy, color Charge transfer absorption, what type of compound is likely to exhibit. o MLCT ...
... o Rules for more and less than half-filled Complexes and color, be able to predict color of complex given spectrum/absorption color for simple absorption. Understand relationships between ligands, Δo, energy, color Charge transfer absorption, what type of compound is likely to exhibit. o MLCT ...
13.2: First Row D
... – A co-ordinate bond (also called a dative covalent bond) is a covalent bond (a shared pair of electrons) in which both electrons come from the same atom. ...
... – A co-ordinate bond (also called a dative covalent bond) is a covalent bond (a shared pair of electrons) in which both electrons come from the same atom. ...
Experimental study on transition metal complexes containing N,S
... configuration, where the HOMO are predominantly ligand centered. On the other hand, in the case of the neutral cobalt complex (6), the observed ligand bond lengths clearly suggest a CoIII (d6) electron configuration. In the monoanion 6b, the ligand bond distances indicate dianionic form of ligands l ...
... configuration, where the HOMO are predominantly ligand centered. On the other hand, in the case of the neutral cobalt complex (6), the observed ligand bond lengths clearly suggest a CoIII (d6) electron configuration. In the monoanion 6b, the ligand bond distances indicate dianionic form of ligands l ...
Set 6
... What factors account for the ligand field strength of different ligands? It is clear that rr-acidity cannot be a requirement for a position high in the spectrochemical series, since f1 is a very strong field ligand but is not a rr-acid (it has no low energy acceptor orbitals of local rr-symmetry). H ...
... What factors account for the ligand field strength of different ligands? It is clear that rr-acidity cannot be a requirement for a position high in the spectrochemical series, since f1 is a very strong field ligand but is not a rr-acid (it has no low energy acceptor orbitals of local rr-symmetry). H ...
Topic 15 specification content - A
... excited state of the d electrons is given by ∆E = hν = hc/λ, that changes in oxidation state, coordination number and ligand alter ∆E and this leads to a change in colour, and I can explain that the absorption of visible light is used in spectroscopy and that a simple colorimeter can be used to dete ...
... excited state of the d electrons is given by ∆E = hν = hc/λ, that changes in oxidation state, coordination number and ligand alter ∆E and this leads to a change in colour, and I can explain that the absorption of visible light is used in spectroscopy and that a simple colorimeter can be used to dete ...
Sem4ch3 Assignment
... In a complex, the highest possible coordination number is (a) 6 (b) 12 (c) 4 (d) 8 The number of neutral molecules or negative groups attached to the central metal atom in a complex ion is called (a) Atomic number (b) Effective atomic number (c) Coordination number (d) Primary valency EDTA combines ...
... In a complex, the highest possible coordination number is (a) 6 (b) 12 (c) 4 (d) 8 The number of neutral molecules or negative groups attached to the central metal atom in a complex ion is called (a) Atomic number (b) Effective atomic number (c) Coordination number (d) Primary valency EDTA combines ...
Chapter 7 7.4 Name and draw structures of the following complexes?
... The colors of metal complexes are frequently due to ligand-field transitions involving electron promotion from one subset of d orbitals to another (e.g. from t2g to e g for octahedral complexes or from e to t2 for tetrahedral complexes). Of the three complexes given, the lowest energy transition pro ...
... The colors of metal complexes are frequently due to ligand-field transitions involving electron promotion from one subset of d orbitals to another (e.g. from t2g to e g for octahedral complexes or from e to t2 for tetrahedral complexes). Of the three complexes given, the lowest energy transition pro ...
Changing Coordination Numbers: Nickel Complexes
... A complex ion is a metal ion with Lewis bases attached to it through coordinate covalent bonds. A complex or coordination compound is a compound consisting either of complex ions with other ions of opposite charge or of a neutral complex species. Ligands are the Lewis bases attached to the metal ato ...
... A complex ion is a metal ion with Lewis bases attached to it through coordinate covalent bonds. A complex or coordination compound is a compound consisting either of complex ions with other ions of opposite charge or of a neutral complex species. Ligands are the Lewis bases attached to the metal ato ...
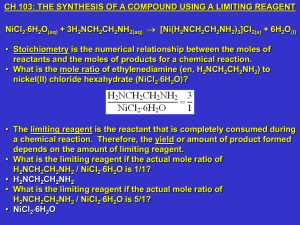
Week #10: The Synthesis of a Compound using a Limiting Reagent
... a chemical reaction. Therefore, the yield or amount of product formed depends on the amount of limiting reagent. • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl26H2O is 1/1? • H2NCH2CH2NH2 • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl2 ...
... a chemical reaction. Therefore, the yield or amount of product formed depends on the amount of limiting reagent. • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl26H2O is 1/1? • H2NCH2CH2NH2 • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl2 ...
Document
... a chemical reaction. Therefore, the yield or amount of product formed depends on the amount of limiting reagent. • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl26H2O is 1/1? • H2NCH2CH2NH2 • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl2 ...
... a chemical reaction. Therefore, the yield or amount of product formed depends on the amount of limiting reagent. • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl26H2O is 1/1? • H2NCH2CH2NH2 • What is the limiting reagent if the actual mole ratio of H2NCH2CH2NH2 / NiCl2 ...
Stability and Kinetics of the Acid
... cryptand, reacts with NH3, KSCN and NaN3 to form the binuclear tertiary complexes Cu2L(NH3)24+, Cu2L(SCN)3+ and Cu2L(N3)3+. The equilibrium constants show a special stabilisation of the complexes with ligands able to bridge the CuII centres, with a maximum stabilisation for azide. Upon addition of a ...
... cryptand, reacts with NH3, KSCN and NaN3 to form the binuclear tertiary complexes Cu2L(NH3)24+, Cu2L(SCN)3+ and Cu2L(N3)3+. The equilibrium constants show a special stabilisation of the complexes with ligands able to bridge the CuII centres, with a maximum stabilisation for azide. Upon addition of a ...
Reaction mechanism of Coordination Complexes
... Reaction mechanism of Coordination Complexes Complexes are classified as Inert and Labile ( kinetic stability) depending on their reactivity. According to Henry Taube, a Nobel Laureate, the definition is ...
... Reaction mechanism of Coordination Complexes Complexes are classified as Inert and Labile ( kinetic stability) depending on their reactivity. According to Henry Taube, a Nobel Laureate, the definition is ...













![Coordination Compounds [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000678035_1-c20c75fd4abb97d3ba4a0b0fce26e10b-300x300.png)