Transition Metals and Complex Ion Chemistry - Ars
... mirror images of each other. In a symmetrical environment the two isomers have the same physical properties (solubilities, melting points, colors). They can be distinguished by how they rotate plane polarized light. Because of this they are also known as optically active compounds. Is the compound r ...
... mirror images of each other. In a symmetrical environment the two isomers have the same physical properties (solubilities, melting points, colors). They can be distinguished by how they rotate plane polarized light. Because of this they are also known as optically active compounds. Is the compound r ...
Chapter 15 Complexation and Precipitation
... In contrast to complexation equilibria, which are most often treated as formation reactions, solubility equilibria are usually treated as dissociation reactions MxAy(s) ...
... In contrast to complexation equilibria, which are most often treated as formation reactions, solubility equilibria are usually treated as dissociation reactions MxAy(s) ...
coordination chemistry relevant to biological systems and material
... and efficiently hydrolyze the phosphodiester bonds of DNA, understanding the factors that might affect the DNA cleavage is considered to be the key step in synthesizing “efficient artificial nucleases” for DNA cleavage. Our group has focused on the synthesis and characterization of a number of monon ...
... and efficiently hydrolyze the phosphodiester bonds of DNA, understanding the factors that might affect the DNA cleavage is considered to be the key step in synthesizing “efficient artificial nucleases” for DNA cleavage. Our group has focused on the synthesis and characterization of a number of monon ...
Solution 18. - TutorBreeze.com
... When a ligand approaches a transition metal , the d- orbitals split into two sets .one set has lower energy and the other set has higher energy.The difference in energy between the two sets is called crystal field splitting energy. Ligands which cause a large splitting Δ of the d-orbitals are referr ...
... When a ligand approaches a transition metal , the d- orbitals split into two sets .one set has lower energy and the other set has higher energy.The difference in energy between the two sets is called crystal field splitting energy. Ligands which cause a large splitting Δ of the d-orbitals are referr ...
Mercury(II) Complexes of Imidazole and Histidine
... (1) For a general review, see J. Bjerrum. G. Schwarzenbach, L. S i l k , "Stability Constants, P a r t I." Special Publication No. 6, T h e Chemical Society, T.ondon, 1957, Tables 26 and 207; see also t h e speciiic references in Table 111. (2) F. R. N. Gurd and D. S. Goodman, THISJ O U R N A L , 74 ...
... (1) For a general review, see J. Bjerrum. G. Schwarzenbach, L. S i l k , "Stability Constants, P a r t I." Special Publication No. 6, T h e Chemical Society, T.ondon, 1957, Tables 26 and 207; see also t h e speciiic references in Table 111. (2) F. R. N. Gurd and D. S. Goodman, THISJ O U R N A L , 74 ...
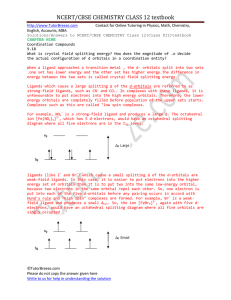
H H H H H N HO O NC[ ]- - Teacher`s Tools® Chemistry
... Transition metals can behave like Lewis Acids (electron pair acceptors) in the formation of what are called complex ions. A coordination compound typically consists of a complex ion and counter ion. The molecules or ions that surround the metal in a complex ion are called ligands. The ligands act li ...
... Transition metals can behave like Lewis Acids (electron pair acceptors) in the formation of what are called complex ions. A coordination compound typically consists of a complex ion and counter ion. The molecules or ions that surround the metal in a complex ion are called ligands. The ligands act li ...
Alkanes and xenon as ligands: NMR studies of photolytically
... are highly unstable and usually have only fleeting existences even at low temperatures. Hence, the observation of alkane and xenon complexes has been mostly restricted to using “fast” spectroscopies such as UV and IR. This talk will describe our studies on complexes of the type Cp’Re(CO)(L)(alkane) ...
... are highly unstable and usually have only fleeting existences even at low temperatures. Hence, the observation of alkane and xenon complexes has been mostly restricted to using “fast” spectroscopies such as UV and IR. This talk will describe our studies on complexes of the type Cp’Re(CO)(L)(alkane) ...
(Marine Bioinorganic Chemistry) 12.755 Lecture 2
... - high affinity uptake systems - ecological warfare between species 2. Protection from scavenging processes 3. Increases in solubility • How do you study something at picomolar quantities which we don’t know much about? ...
... - high affinity uptake systems - ecological warfare between species 2. Protection from scavenging processes 3. Increases in solubility • How do you study something at picomolar quantities which we don’t know much about? ...
The potential of incorporating β-diketone ligand derivatives into
... unusual supramolecular structures. For example, bis-β-diketonato derivatives in which the βdiketone fragments are linked via a 1,3- or 1,4-substituted aryl group, or by corresponding pyridyl, bipyridyl or biphenylene groups, have been employed to construct new neutral dinuclear platforms, dinuclear ...
... unusual supramolecular structures. For example, bis-β-diketonato derivatives in which the βdiketone fragments are linked via a 1,3- or 1,4-substituted aryl group, or by corresponding pyridyl, bipyridyl or biphenylene groups, have been employed to construct new neutral dinuclear platforms, dinuclear ...
Extract for Activity 9.12
... The presence of the neutral cyclam ligand in [Ru(cyclam)Cl(NO)]21 leads to the formation of a positively charged complex in which p-donation from the metal centre to the NO ligand is inhibited. By increasing the negative charge on the ligand set around the metal centre to promote back donation to co ...
... The presence of the neutral cyclam ligand in [Ru(cyclam)Cl(NO)]21 leads to the formation of a positively charged complex in which p-donation from the metal centre to the NO ligand is inhibited. By increasing the negative charge on the ligand set around the metal centre to promote back donation to co ...
(activity) of hydrogen ions
... indicator added. (2-3) The acid is titrated with the alkali in the burette until the indicator turns green and the volume of alkali noted. (1-3) are repeated with both known volumes mixed together BUT without the contaminating indicator. (4) The solution is transferred to an evaporating dish and hea ...
... indicator added. (2-3) The acid is titrated with the alkali in the burette until the indicator turns green and the volume of alkali noted. (1-3) are repeated with both known volumes mixed together BUT without the contaminating indicator. (4) The solution is transferred to an evaporating dish and hea ...
Document
... A chelate is a complex ion that involves ligands with two or more bonding sites forming a ring structure complex 4. Chelating agent A substance whose molecules can form several bonds to single metal ion. In other words, a chelating agent is a multidentate ligand ...
... A chelate is a complex ion that involves ligands with two or more bonding sites forming a ring structure complex 4. Chelating agent A substance whose molecules can form several bonds to single metal ion. In other words, a chelating agent is a multidentate ligand ...
Theoretical Modelling of Europium(III) and Americium(III
... examined. The cationic complexes of the stoichiometries 1:1 and 1:2, as well as the neutral [M(BTBP)(NO3)3] species, were modelled. The calculations were done by using Gaussian 03 package. Becke three-parameter hybrid functional B3LYP was used. Stuttgart-Dresden SDD small-core ECP pseudo-relativisti ...
... examined. The cationic complexes of the stoichiometries 1:1 and 1:2, as well as the neutral [M(BTBP)(NO3)3] species, were modelled. The calculations were done by using Gaussian 03 package. Becke three-parameter hybrid functional B3LYP was used. Stuttgart-Dresden SDD small-core ECP pseudo-relativisti ...
4-Physical Chemistry of SW-Equilibrium-ion
... times an activity coefficient (i), which is the fraction of the ion that is available to react at any given time ai = i * m i Thus an equilibrium constant should be expressed in terms of its activities (the effective concentrations): Keq = {Ca2+}1 {CO32-}1 / {CaCO3}1 or Keq = (Ca2+ mCa2+)1 (CO3 ...
... times an activity coefficient (i), which is the fraction of the ion that is available to react at any given time ai = i * m i Thus an equilibrium constant should be expressed in terms of its activities (the effective concentrations): Keq = {Ca2+}1 {CO32-}1 / {CaCO3}1 or Keq = (Ca2+ mCa2+)1 (CO3 ...
Transition Metals
... The 3d orbitals are not as important for bonding as are the 4s and 4p, but the details of what happens to the 3d orbitals determine the properties of transition metal complexes. ...
... The 3d orbitals are not as important for bonding as are the 4s and 4p, but the details of what happens to the 3d orbitals determine the properties of transition metal complexes. ...
Experiment 4 Spectroscopic study of Cu(II) Complexes: Crystal Field
... characteristic properties. These colors are due to the absorption and subsequent emission of light in the visible part of the spectrum. Light in this region of the spectrum caused promotion of d–electrons from a lower to a higher energy level. The spectra which result are generally referred to as El ...
... characteristic properties. These colors are due to the absorption and subsequent emission of light in the visible part of the spectrum. Light in this region of the spectrum caused promotion of d–electrons from a lower to a higher energy level. The spectra which result are generally referred to as El ...
CoordinationCompounds
... Coordination Compounds • Transition metals have s, d and p orbitals all available for bonding • Don’t obey the octet rule • They are most stable with filled d, s and p orbitals – s2d10p6 (18 e-) • Transition metals act like a Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor) so as to fill valence orbitals • Tran ...
... Coordination Compounds • Transition metals have s, d and p orbitals all available for bonding • Don’t obey the octet rule • They are most stable with filled d, s and p orbitals – s2d10p6 (18 e-) • Transition metals act like a Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor) so as to fill valence orbitals • Tran ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... a) Soft Pt2+ should react strongly with soft bases, not well with hard bases b) Example k(PPh3)/k(CH3OH) = 9 x 108 ...
... a) Soft Pt2+ should react strongly with soft bases, not well with hard bases b) Example k(PPh3)/k(CH3OH) = 9 x 108 ...
Complex forming reactions and complexometry Complex forming
... the determination of metal ions, with the aid of complex formation (mainly chelate) reactions. The following conditions need to be met for the successful use of a complex reaction in titrimetry: • the complex needs to be very stable, with a high formation constant so the reaction is stochiometric (c ...
... the determination of metal ions, with the aid of complex formation (mainly chelate) reactions. The following conditions need to be met for the successful use of a complex reaction in titrimetry: • the complex needs to be very stable, with a high formation constant so the reaction is stochiometric (c ...
Transition Metal Chemistry - WordPress.com
... • Transition metals are defined as metallic elements with an incomplete d sub-shell in at least one of their ions. • Form positive (+) ions by losing electrons. • These electrons come from the 4s sub-shell first, then from the 3d sub-shell: Fe atom: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d6 Fe2+ ion: ...
... • Transition metals are defined as metallic elements with an incomplete d sub-shell in at least one of their ions. • Form positive (+) ions by losing electrons. • These electrons come from the 4s sub-shell first, then from the 3d sub-shell: Fe atom: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d6 Fe2+ ion: ...





![H H H H H N HO O NC[ ]- - Teacher`s Tools® Chemistry](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017018154_1-68467b392d8cadb27de319df72045839-300x300.png)