Nucleophilic addition and abstraction
... Favored when the metal is a weak σ acid but a strong π base. ...
... Favored when the metal is a weak σ acid but a strong π base. ...
Slide 1
... 2. Most salts of Na+, K+, and NH4+ are soluble. 3. Most chloride salts are soluble. Notable exceptions are AgCl, PbCl2, and Hg2Cl2. 4. Most sulfate salts are soluble. Notable exceptions are BaSO4, PbSO4, and CaSO4. 5. Most hydroxide compounds are only slightly soluble.* The important exceptions are ...
... 2. Most salts of Na+, K+, and NH4+ are soluble. 3. Most chloride salts are soluble. Notable exceptions are AgCl, PbCl2, and Hg2Cl2. 4. Most sulfate salts are soluble. Notable exceptions are BaSO4, PbSO4, and CaSO4. 5. Most hydroxide compounds are only slightly soluble.* The important exceptions are ...
Solubility & Complex Ions
... its solubility. Solubility, as with all equilibria, is highly temperature dependent. Solubility may be expressed as grams of compound/100 mL of H2O, or as molarity, M. ...
... its solubility. Solubility, as with all equilibria, is highly temperature dependent. Solubility may be expressed as grams of compound/100 mL of H2O, or as molarity, M. ...
Transition Metal Basics
... (b) (i) Cu+(aq) ions are not stable in solution and undergo a disproportionation reaction. Suggest an equation for this reaction, including state symbols. ...
... (b) (i) Cu+(aq) ions are not stable in solution and undergo a disproportionation reaction. Suggest an equation for this reaction, including state symbols. ...
Chapter 20. - Bryn Mawr College
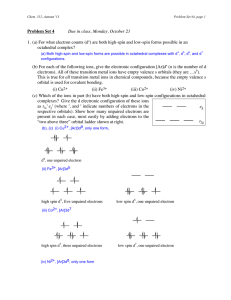
... (a) Diagram 21.11 shows the d^ configuration in an octahedral field. There is no vacant e^ orbital and so no possibility of promoting an electi'on from a fully occupied t^^ orbital to generate a high-spin configuration. .-. Only one configuration. (b) Consider an example, e.g. octahedral d-^, that c ...
... (a) Diagram 21.11 shows the d^ configuration in an octahedral field. There is no vacant e^ orbital and so no possibility of promoting an electi'on from a fully occupied t^^ orbital to generate a high-spin configuration. .-. Only one configuration. (b) Consider an example, e.g. octahedral d-^, that c ...
Ultraviolet and visible molecular absorption spectroscopy
... For volatile compounds, however, gas-phase spectra are often more useful than liquid-phase or solution spectra. A solvent for ultraviolet/visible spectroscopy must be transparent in the ...
... For volatile compounds, however, gas-phase spectra are often more useful than liquid-phase or solution spectra. A solvent for ultraviolet/visible spectroscopy must be transparent in the ...
Molecular Insight into Hydrothermal Solution Geochemistry
... Aqueous fluids under extreme conditions of temperature and pressure occur ubiquitously throughout the Earth’s crust and upper mantle. Throughout geological time, they have been and still are responsible for the transport of enormous amounts of heat and chemical mass within the crust. They discharge ...
... Aqueous fluids under extreme conditions of temperature and pressure occur ubiquitously throughout the Earth’s crust and upper mantle. Throughout geological time, they have been and still are responsible for the transport of enormous amounts of heat and chemical mass within the crust. They discharge ...
Steric and Electronic Effects Induced by Ancillary Ligand
... protonated with H2C(SO2CF3)2 in CDFCl2 at -130 °C. 1H NMR spectroscopy was used to identify the cisoid methyl hydride protonation products in solution. Spin saturation transfer experiments were used to abstract a ΔG‡ value for hydrogen exchange of 8.47 kcal/mol at -110 °C for [(C5H4Me)Os(dmpm)H(Me)+ ...
... protonated with H2C(SO2CF3)2 in CDFCl2 at -130 °C. 1H NMR spectroscopy was used to identify the cisoid methyl hydride protonation products in solution. Spin saturation transfer experiments were used to abstract a ΔG‡ value for hydrogen exchange of 8.47 kcal/mol at -110 °C for [(C5H4Me)Os(dmpm)H(Me)+ ...
Transition Metal Series
... 5. Would it be better to use octahedral complexes of Cr3+ or Co3+ to determine whether a given ligand is a strong-field or a weak-field ligand? Illustrate using crystal-field splitting diagrams. (Co3+ because Cr3+ does not exhibit high and low spin complexes – there are only 3 3d-electrons in Cr3+ a ...
... 5. Would it be better to use octahedral complexes of Cr3+ or Co3+ to determine whether a given ligand is a strong-field or a weak-field ligand? Illustrate using crystal-field splitting diagrams. (Co3+ because Cr3+ does not exhibit high and low spin complexes – there are only 3 3d-electrons in Cr3+ a ...
Synthesis and characterization of mixed ligand complexes of cobalt
... frequencies associated with C N, C = C, C - S and M-S from complexes of i-MNT2-; aryl ring vibrations with metal heterocyclic nitrogen vibrations from o-phen, bipy, py, -pic, -pic and -pic . The (CN) band appearing at 2195cm-1 with a shoulder at 2200 cm-1 in K2i-MNT.H2O, is a sharp absorption ...
... frequencies associated with C N, C = C, C - S and M-S from complexes of i-MNT2-; aryl ring vibrations with metal heterocyclic nitrogen vibrations from o-phen, bipy, py, -pic, -pic and -pic . The (CN) band appearing at 2195cm-1 with a shoulder at 2200 cm-1 in K2i-MNT.H2O, is a sharp absorption ...
A comparative DNA binding study for heteroleptic platinum (II
... * transitions of complex 1 were 27.9 % for dsDNA at a DNA-to-Pt concentration ratio of 4.8 and 12.2 % for Q-DNA at a DNA-to-Pt concentration ratio of 0.03. The similar case could be seen for complex 2. Hypochromism at low R values for QDNA indicated strong interactions between the Gquadruplex for ...
... * transitions of complex 1 were 27.9 % for dsDNA at a DNA-to-Pt concentration ratio of 4.8 and 12.2 % for Q-DNA at a DNA-to-Pt concentration ratio of 0.03. The similar case could be seen for complex 2. Hypochromism at low R values for QDNA indicated strong interactions between the Gquadruplex for ...
Biomimetic oxidation of catechol employing complexes formed in
... In order to investigate the ability of the copper complexes formed in-situ to act as catalysts for catecholase-like activity, the catalytic oxidation of the substrate catechol by the a combination of ligands L1-L7 and different metallic salts (Cu(CH3COO)2, CuSO4, Cu(NO3)2, NiCl2, Co(NO3)2, ZnCl2), w ...
... In order to investigate the ability of the copper complexes formed in-situ to act as catalysts for catecholase-like activity, the catalytic oxidation of the substrate catechol by the a combination of ligands L1-L7 and different metallic salts (Cu(CH3COO)2, CuSO4, Cu(NO3)2, NiCl2, Co(NO3)2, ZnCl2), w ...
SYNTHESIS, PHYSICO-CHEMICAL STUDIES AND ANTIMICROBIAL EVALUATION OF NOVEL 2- H COMPLEXES Research Article
... analysis. The molecular weights of metal complexes were confirmed by the Rast’s Camphor method. All the synthesized compounds were micro analyzed satisfactorily for Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Sulfur on EURO EA Elemental Analyzer, EA-3000, and RS-232; IR spectra were recorded on a SHIMADZU-FT-IR ...
... analysis. The molecular weights of metal complexes were confirmed by the Rast’s Camphor method. All the synthesized compounds were micro analyzed satisfactorily for Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen and Sulfur on EURO EA Elemental Analyzer, EA-3000, and RS-232; IR spectra were recorded on a SHIMADZU-FT-IR ...
chapter 4 review: types of chemical reactions and solution
... Assign oxidation numbers to atoms in a compound/polyatomic ion. 8. Determine the oxidation number for each atom in the following compound or ion: (a) P4O10 (b) NH4ClO4 (c) ClF4- ...
... Assign oxidation numbers to atoms in a compound/polyatomic ion. 8. Determine the oxidation number for each atom in the following compound or ion: (a) P4O10 (b) NH4ClO4 (c) ClF4- ...
WCH05_01_que_20140617
... is compared to the calculated enthalpy change for the hydrogenation of the theoretical compound cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene to cyclohexane, benzene is calculated to have a stabilization energy of 150 kJ mol−1. This means that A the enthalpy change for the hydrogenation of benzene is +150 kJ mol−1. B the ...
... is compared to the calculated enthalpy change for the hydrogenation of the theoretical compound cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene to cyclohexane, benzene is calculated to have a stabilization energy of 150 kJ mol−1. This means that A the enthalpy change for the hydrogenation of benzene is +150 kJ mol−1. B the ...
III. Solubility Equilibria Solbility and Equilibrium
... Complex Ions Complex ion: a charged species consisting of a metal ion surrounded by ligands Ligands: ions or molecules that bond to a metal ion. Common ligands include Cl-, F-, CN-, OH-, NH3, and H2O Coordination Number: the number of ligands that surround a metal ion. In general, the coordination ...
... Complex Ions Complex ion: a charged species consisting of a metal ion surrounded by ligands Ligands: ions or molecules that bond to a metal ion. Common ligands include Cl-, F-, CN-, OH-, NH3, and H2O Coordination Number: the number of ligands that surround a metal ion. In general, the coordination ...