Chapter 4 Packet
... a weak electrolyte. I will also be able to predict the ions formed by electrolytes when they dissociate or ionize. A solution is a homogeneous mixture made by dissolving one substance (the solute) in another substance (the solvent). An aqueous solution is a solution where water is the solvent. Elect ...
... a weak electrolyte. I will also be able to predict the ions formed by electrolytes when they dissociate or ionize. A solution is a homogeneous mixture made by dissolving one substance (the solute) in another substance (the solvent). An aqueous solution is a solution where water is the solvent. Elect ...
Types of Reactions:
... Give the formulas to show the reactants and the products for the following chemical reactions. Each occurs in aqueous solution unless otherwise indicated. Represent substances in solution as ions if the substance is extensively ionized. Omit formulas for any ions or molecules that are unchanged by t ...
... Give the formulas to show the reactants and the products for the following chemical reactions. Each occurs in aqueous solution unless otherwise indicated. Represent substances in solution as ions if the substance is extensively ionized. Omit formulas for any ions or molecules that are unchanged by t ...
Valence Bond Theory
... In order to predict the actual molecular structure, the µ value is needed. To understand this fact, try to refer to the [Co(NH3)6]3+ and [CoF6]3- complexes. ...
... In order to predict the actual molecular structure, the µ value is needed. To understand this fact, try to refer to the [Co(NH3)6]3+ and [CoF6]3- complexes. ...
Metal aqua ions
... The effect of electronegativity of the metal on the acidity of its aquo ion: 3) Electronegativity. This was discussed in lecture 5, but is repeated here briefly as a reminder. The closer a metal is to Au in the periodic table, the higher will its electronegativity be. Electronegativity tends to ove ...
... The effect of electronegativity of the metal on the acidity of its aquo ion: 3) Electronegativity. This was discussed in lecture 5, but is repeated here briefly as a reminder. The closer a metal is to Au in the periodic table, the higher will its electronegativity be. Electronegativity tends to ove ...
GLA 151-4 Nomenclature Worksheet Key
... http://www.canyons.edu/Departments/CHEM/GLA for additional materials. Part A – Naming Ions To correctly name chemical compounds, first one must be familiar with the names of common ions. Recall that many ions that form are simply elemental atoms that have gained or lost an electron. In general, when ...
... http://www.canyons.edu/Departments/CHEM/GLA for additional materials. Part A – Naming Ions To correctly name chemical compounds, first one must be familiar with the names of common ions. Recall that many ions that form are simply elemental atoms that have gained or lost an electron. In general, when ...
Introduction
... ◦ FeO: iron doesn’t have a +1 charge, so we have to know that oxygen is usually a –2. Then we know that iron must have a +2 charge in this compound. ...
... ◦ FeO: iron doesn’t have a +1 charge, so we have to know that oxygen is usually a –2. Then we know that iron must have a +2 charge in this compound. ...
Chapter 4 Stoichiometry Power Point
... In its compound, fluorine is always assigned an oxidation sate of -1. Oxygen is usually assigned an oxidation of -2 in its covalent compounds, such as CO, CO2, SO2. Exceptions to this rule includes peroxides (compounds containing the O22- group), where each oxygen is assigned an oxidation state of - ...
... In its compound, fluorine is always assigned an oxidation sate of -1. Oxygen is usually assigned an oxidation of -2 in its covalent compounds, such as CO, CO2, SO2. Exceptions to this rule includes peroxides (compounds containing the O22- group), where each oxygen is assigned an oxidation state of - ...
Slide 1
... Aquation refers to the reaction [Co(NH3)5X]n+ + H2O [Co(NH3)5(H2O)]3+ + X Rate constants vary by 6 orders of manitude Strongly dependent on the nature of the leaving group Anation refers to the reaction [Co(NH3)5(H2O)]3+ + Y [Co(NH3)5(H2O)]n+ + H2O Rate constants vary by a factor of 10 Weakl ...
... Aquation refers to the reaction [Co(NH3)5X]n+ + H2O [Co(NH3)5(H2O)]3+ + X Rate constants vary by 6 orders of manitude Strongly dependent on the nature of the leaving group Anation refers to the reaction [Co(NH3)5(H2O)]3+ + Y [Co(NH3)5(H2O)]n+ + H2O Rate constants vary by a factor of 10 Weakl ...
Chemistry
... weight of non-volatile solute from osmotic pressure. Abnormal Colligative properties. Van’t Hoff factor, degree of dissociation and association. Electrochemistry Specific conductance, equivalent conductance, measurement of equivalent conductance. Variation of equivalent conductance with dilution. Mi ...
... weight of non-volatile solute from osmotic pressure. Abnormal Colligative properties. Van’t Hoff factor, degree of dissociation and association. Electrochemistry Specific conductance, equivalent conductance, measurement of equivalent conductance. Variation of equivalent conductance with dilution. Mi ...
CHEM 115 EXAM #2
... neutralized by 46.40 mL of 0.875 M sodium hydroxide [NaOH (aq)]. Balance the chemical reaction below and calculate the molarity of the original 5.00 mL H2SO4 (aq) sample. H2SO4 (aq) + ...
... neutralized by 46.40 mL of 0.875 M sodium hydroxide [NaOH (aq)]. Balance the chemical reaction below and calculate the molarity of the original 5.00 mL H2SO4 (aq) sample. H2SO4 (aq) + ...
Activity 151-4 Nomenclature for Chemical Compounds
... http://www.canyons.edu/Departments/CHEM/GLA/ for additional materials. ...
... http://www.canyons.edu/Departments/CHEM/GLA/ for additional materials. ...
Chemistry primer Atom = the smallest unit of an element Element
... (the more reliable ones for mineral identification) Hardness: Resistance to scratching. Greater hardness due to: strong bonds, tight structure, small ions Cleavage: Planes of weakness along which a mineral breaks. Reflect crystalline structure, Cleavage occurs along planes of weakness between atoms. ...
... (the more reliable ones for mineral identification) Hardness: Resistance to scratching. Greater hardness due to: strong bonds, tight structure, small ions Cleavage: Planes of weakness along which a mineral breaks. Reflect crystalline structure, Cleavage occurs along planes of weakness between atoms. ...
A Density Functional Theory and Quantum Theory of
... donor of electron density to a Lewis acid than Cy 2 EN. ...
... donor of electron density to a Lewis acid than Cy 2 EN. ...
MnAcacfinal - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Your report should consist of: • Your NMR spectrum, with chemical shifts labeled • Calculations of M, ’M, and n • Note: In Table 12-1 (p. 122), the M values given have been multiplied by 106; the correct values are on the order of 10-6 cm3 mol-1. This also applies to the value for the metal given ...
... Your report should consist of: • Your NMR spectrum, with chemical shifts labeled • Calculations of M, ’M, and n • Note: In Table 12-1 (p. 122), the M values given have been multiplied by 106; the correct values are on the order of 10-6 cm3 mol-1. This also applies to the value for the metal given ...
Answers to Assignment #5
... elements belongs to those species with d n configurations from d 1 to d 9 in at least one common oxidation state. Thus Sc3+ and Zn2+ do not behave like typical TM, but Ti3+, Ti2+ and Ti+ , as well as Cu 2+ behave are typical. A coordination compound is a compound formed by Lewis acid/base donor acce ...
... elements belongs to those species with d n configurations from d 1 to d 9 in at least one common oxidation state. Thus Sc3+ and Zn2+ do not behave like typical TM, but Ti3+, Ti2+ and Ti+ , as well as Cu 2+ behave are typical. A coordination compound is a compound formed by Lewis acid/base donor acce ...
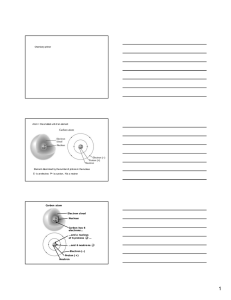
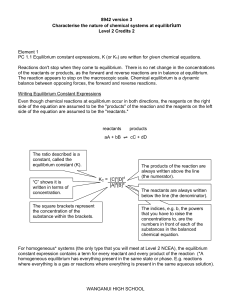
Wanganui High School
... Addition / removal o Amount of reactant / product / equilibrium position is unchanged. (But of catalyst equilibrium is reached much faster) ...
... Addition / removal o Amount of reactant / product / equilibrium position is unchanged. (But of catalyst equilibrium is reached much faster) ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... CED2-; aryl heterocyclic ring vibrations with metal heterocyclic nitrogen vibrations from o-phenanthroline (ophen), pyridine (py), -picoline (-pic), -picoline (-pic) and -picoline (-pic). The (CN) band appearing at 2190cm-1 in K2CED.H2O is observed in the range 2190-2199 cm-1 in its mixed li ...
... CED2-; aryl heterocyclic ring vibrations with metal heterocyclic nitrogen vibrations from o-phenanthroline (ophen), pyridine (py), -picoline (-pic), -picoline (-pic) and -picoline (-pic). The (CN) band appearing at 2190cm-1 in K2CED.H2O is observed in the range 2190-2199 cm-1 in its mixed li ...
chemistry important question i
... (iii) Antacids Write the structures and names of all the stereoisomers of the following compounds: (i) [Co(en)3]Cl3 (ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] (iii) [Fe(NH3)4Cl2]Cl (i) State Henry’s law about partial pressure of a gas in a mixture (ii) A 0.561 m solution of an unknown electrolyte depresses the freezing poi ...
... (iii) Antacids Write the structures and names of all the stereoisomers of the following compounds: (i) [Co(en)3]Cl3 (ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] (iii) [Fe(NH3)4Cl2]Cl (i) State Henry’s law about partial pressure of a gas in a mixture (ii) A 0.561 m solution of an unknown electrolyte depresses the freezing poi ...
Electron Rule.
... resulting in eight electrons around the central atom. You have been told this is because elements desire a pseudo-noble gas configuration. ...
... resulting in eight electrons around the central atom. You have been told this is because elements desire a pseudo-noble gas configuration. ...
Chemistry and “Magic Numbers” 18
... resulting in eight electrons around the central atom. You have been told this is because elements desire a pseudo-noble gas configuration. This is a VAST simplification. Stable Fullerenes: The allotrope of Carbon known as fullerenes (C60 or “Bucky-ball” is the most famous) take on a cage structure a ...
... resulting in eight electrons around the central atom. You have been told this is because elements desire a pseudo-noble gas configuration. This is a VAST simplification. Stable Fullerenes: The allotrope of Carbon known as fullerenes (C60 or “Bucky-ball” is the most famous) take on a cage structure a ...