Methods in Cognitive Neuroscience I
... • Takes advantage of the fact that neural activity is followed by blood flow in a highly predictable manner • Altered blood flow alters RF signal from active brain regions ...
... • Takes advantage of the fact that neural activity is followed by blood flow in a highly predictable manner • Altered blood flow alters RF signal from active brain regions ...
The Nervous System
... At the back of this chamber is the iris, the color part of the eye with an opening called the pupil. ...
... At the back of this chamber is the iris, the color part of the eye with an opening called the pupil. ...
Chapter 03 - Jen Wright
... 1. What is a neuron? Please describe the parts of a neuron and what they do. Also describe the three major types of neurons and their function. 2. What is the myelin sheath and why is it so important to neural functioning? What do you think happens when the myelin sheath is damaged or destroyed? 3. ...
... 1. What is a neuron? Please describe the parts of a neuron and what they do. Also describe the three major types of neurons and their function. 2. What is the myelin sheath and why is it so important to neural functioning? What do you think happens when the myelin sheath is damaged or destroyed? 3. ...
Outline for cognitive neuroscience Chapter 1 Introduction to Method
... brain while the subject is engaged in cognitive tasks. Therefore, these methods are correlational. PET Underlying assumption: there will be increased blood flow to the brain regions that engaged in cognitive processes. Measured index: regional cerebral blood flow(rCBF) Inject tracer to the blo ...
... brain while the subject is engaged in cognitive tasks. Therefore, these methods are correlational. PET Underlying assumption: there will be increased blood flow to the brain regions that engaged in cognitive processes. Measured index: regional cerebral blood flow(rCBF) Inject tracer to the blo ...
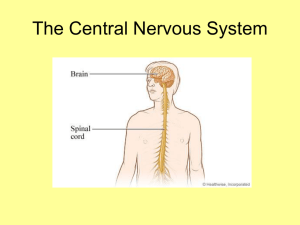
Physiology Notes: The Central Nervous System
... 1) What structure connects the cerebrum’s hemispheres? _________________________________________ 2) What structure bridges the cerebrum’s right and left hemispheres? ________________________________ 3) What main structure helps to maintain homeostasis? ___________________________________________ ...
... 1) What structure connects the cerebrum’s hemispheres? _________________________________________ 2) What structure bridges the cerebrum’s right and left hemispheres? ________________________________ 3) What main structure helps to maintain homeostasis? ___________________________________________ ...
Alcohol - INSIDE CFISD.NET Home Page
... • Alcohol is a drug contained in drinks such as beer, wine, wine coolers and hard liquor. • After you drink it, alcohol is absorbed through the walls of the stomach and intestines, directly into the blood stream. The alcohol then travels through the blood to the brain. • Once it reaches the brain, i ...
... • Alcohol is a drug contained in drinks such as beer, wine, wine coolers and hard liquor. • After you drink it, alcohol is absorbed through the walls of the stomach and intestines, directly into the blood stream. The alcohol then travels through the blood to the brain. • Once it reaches the brain, i ...
Verlamde man bestuurt computer via gedachten
... But BrainGate's creators argue that such techniques only give a general picture of brain activity, and that the more direct approach allows more numerous and more specific signals to be translated. "This array has 100 electrodes, so one can theoretically tap into 100 neurons," says Jon Mukand, an in ...
... But BrainGate's creators argue that such techniques only give a general picture of brain activity, and that the more direct approach allows more numerous and more specific signals to be translated. "This array has 100 electrodes, so one can theoretically tap into 100 neurons," says Jon Mukand, an in ...
Cerebral Palsy
... Seizures believed to be a result of spontaneous uncontrolled electrical activity of neurons Cause – Uncertain Diagnosed with EEG (electroencephalogram) ...
... Seizures believed to be a result of spontaneous uncontrolled electrical activity of neurons Cause – Uncertain Diagnosed with EEG (electroencephalogram) ...
Module 05
... Unlike EEGs, newer neuroimaging techniques give us that Supermanlike ability to see inside the living brain. Modern technological means of viewing the brain (newer neuroimaging techniques), such as the PET scan, MRI, and fMRI, provide us with a greater-than-normal ability (a Supermanlike ability) to ...
... Unlike EEGs, newer neuroimaging techniques give us that Supermanlike ability to see inside the living brain. Modern technological means of viewing the brain (newer neuroimaging techniques), such as the PET scan, MRI, and fMRI, provide us with a greater-than-normal ability (a Supermanlike ability) to ...
Myers` Psychology for AP
... 5. Identify the brain areas involved in language, and explain how these areas coordinate to produce speech. aphasia – 6. Discuss the brain’s plasticity following injury or illness. LO #5 plasticity – neurogenesis – Our Divided Brain LO #6 7. Describe split-brain research, and explain how it helps us ...
... 5. Identify the brain areas involved in language, and explain how these areas coordinate to produce speech. aphasia – 6. Discuss the brain’s plasticity following injury or illness. LO #5 plasticity – neurogenesis – Our Divided Brain LO #6 7. Describe split-brain research, and explain how it helps us ...
science guide 2016-Final2.indd
... something new, anticipate the future or recall a memory, a unique set of electrical signals sweeps through your brain. How do these pulses contain all the information necessary to form a thought or memory? The sheer quantity of the billions of cells—and exponentially more routes that a signal can ta ...
... something new, anticipate the future or recall a memory, a unique set of electrical signals sweeps through your brain. How do these pulses contain all the information necessary to form a thought or memory? The sheer quantity of the billions of cells—and exponentially more routes that a signal can ta ...
W10 Brain Development
... ▫ Logic and understanding of consequences ▫ Governs impulsivity, aggression, ▫ Organizing thoughts, planning for the future ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
... ▫ Logic and understanding of consequences ▫ Governs impulsivity, aggression, ▫ Organizing thoughts, planning for the future ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
SNS—brain and spinal cord
... exit the cranial cavity so they are a part of the PNS pg 1472 fig. 54-11 Vagus nerve extends the furthest—into the upper abdominal/chest cavity area. Other 11 nerves are in the head and neck region. ...
... exit the cranial cavity so they are a part of the PNS pg 1472 fig. 54-11 Vagus nerve extends the furthest—into the upper abdominal/chest cavity area. Other 11 nerves are in the head and neck region. ...
vocabulary - Web Adventures
... The variety of cells grouped together in the brain. These tissues contain millions of nerve cells (neurons) as well as cells that hold the shape of the neurons, supply nutrition, digest parts of dead neurons, and provide insulation. ...
... The variety of cells grouped together in the brain. These tissues contain millions of nerve cells (neurons) as well as cells that hold the shape of the neurons, supply nutrition, digest parts of dead neurons, and provide insulation. ...
Document
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
... Not really part but… The brain is well protected Bony skull 3 protective sheets of tissue • Space in the brain is filled with fluid: – Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) – Acts as a shock absorber ...
Brain Structure and Functioning in Relation to Outdoor Space
... Bonner 1998). They have also shown ...
... Bonner 1998). They have also shown ...
Study Guide
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
... The individual nerve cell is called a neuron. Impulses going to a nerve cell travel along feelers called dendrites. Impulses leaving a nerve cell travel along feelers called axons. Involuntary responses are performed without our brain becoming involved. Voluntary responses are performed when you wan ...
Neuroanatomy - UCSD Cognitive Science
... • Constitute 20-50% of the volume in most brain areas • Originate from radial glial cells – migration/guidance • Source for CAMs (N-CAM, laminin, fibronectin), growth factors, and cytokines (signaling proteins involved in immune function) • Regulate neurotransmitter uptake/inactivation (contain ...
... • Constitute 20-50% of the volume in most brain areas • Originate from radial glial cells – migration/guidance • Source for CAMs (N-CAM, laminin, fibronectin), growth factors, and cytokines (signaling proteins involved in immune function) • Regulate neurotransmitter uptake/inactivation (contain ...
Nervous System
... cerebrum, interprets input from the senses, controls movement, and carries out complex mental processes such as learning and remembering. Cerebellum: Coordinates the actions of your muscles and helps you keep your balance. Brain stem: Lies between the cerebellum and the spinal cord, controls your bo ...
... cerebrum, interprets input from the senses, controls movement, and carries out complex mental processes such as learning and remembering. Cerebellum: Coordinates the actions of your muscles and helps you keep your balance. Brain stem: Lies between the cerebellum and the spinal cord, controls your bo ...
Etiopathogenesis of Alzem - Nursing Powerpoint Presentations
... dementia in adult life and is associated with the selective damage of brain regions and neural circuits critical for memory and ...
... dementia in adult life and is associated with the selective damage of brain regions and neural circuits critical for memory and ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.