Check Yourself
... 2. Opiate-like substance found in the brain 4. Nervous system controlling heart, pupils of the eye, etc. 6. Chemical that affects a living organism 7. Powerful stimulant derived from a South American plant 10. An signal travels along the axon. 13. Drug that makes you drowsy, drunk, uncoordinated 14. ...
... 2. Opiate-like substance found in the brain 4. Nervous system controlling heart, pupils of the eye, etc. 6. Chemical that affects a living organism 7. Powerful stimulant derived from a South American plant 10. An signal travels along the axon. 13. Drug that makes you drowsy, drunk, uncoordinated 14. ...
Ch.02
... Reticular Formation a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal. ...
... Reticular Formation a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal. ...
BOLD fMRI - BIAC – Duke
... • Blood Oxyenation Level Dependent Contrast – Deoxyhemoglobin is paramagnetic, oxyhemoglobin is less so. – Magnetic susceptibility of blood increases linearly with increasing oxygenation ...
... • Blood Oxyenation Level Dependent Contrast – Deoxyhemoglobin is paramagnetic, oxyhemoglobin is less so. – Magnetic susceptibility of blood increases linearly with increasing oxygenation ...
Neuroimaging Tutorial
... Psy 531 Affects and Emotions A brief tutorial on neurimaging techniques fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common technique in use. PET (positron emission tomography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), as well as several newer techniques, are also used. Each technique has its st ...
... Psy 531 Affects and Emotions A brief tutorial on neurimaging techniques fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common technique in use. PET (positron emission tomography) and MEG (magnetoencephalography), as well as several newer techniques, are also used. Each technique has its st ...
Crossword Puzzle
... 19. technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of brain structures 21. neural impulse generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon's membrane 22. these cells of the brain guide neural connections and provide nu ...
... 19. technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of brain structures 21. neural impulse generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon's membrane 22. these cells of the brain guide neural connections and provide nu ...
PPT Guide Brain Development
... Brain growth and development There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ...
... Brain growth and development There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ...
RESPONSE TO THREAT SURVIVAL MECHANISM The challenges
... pales, sweats Sweat glands cool overheated muscles underneath. Skin whitens as blood is diverted to muscles reducing bleeding from surface ...
... pales, sweats Sweat glands cool overheated muscles underneath. Skin whitens as blood is diverted to muscles reducing bleeding from surface ...
Feedback and feedforward control of blood flow
... regulated by the by-products of neuronal metabolism. In this feedback model, functionally specific changes in blood flow are initiated when active neurons release substances that diffuse through the extracellular space and reach nearby3eblood vessels. These vasoactive substances cause the vessels to ...
... regulated by the by-products of neuronal metabolism. In this feedback model, functionally specific changes in blood flow are initiated when active neurons release substances that diffuse through the extracellular space and reach nearby3eblood vessels. These vasoactive substances cause the vessels to ...
INC-IEM Neuroengineering Seminar - 13-11-04
... Abstract: To date, brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) have sought to interface the brain with the external world using intrinsic neuronal signals as input commands for controlling external devices, or device-generated electrical signals to mimic sensory inputs to the nervous system. A new generation of ...
... Abstract: To date, brain-machine interfaces (BMIs) have sought to interface the brain with the external world using intrinsic neuronal signals as input commands for controlling external devices, or device-generated electrical signals to mimic sensory inputs to the nervous system. A new generation of ...
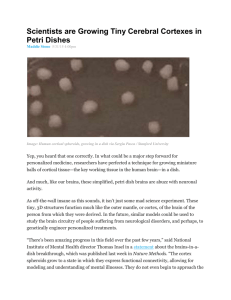
Scientists are Growing Tiny Cerebral Cortexes in Petri
... As described in their paper, Sergiu Pasca of Stanford University and his colleagues have developed a new, streamlined method for inducing pluripotent stem cells to form cortexlike “organoids.” These tiny balls of brain tissue include neurons supported by a cortexlike network of glial cells. This re ...
... As described in their paper, Sergiu Pasca of Stanford University and his colleagues have developed a new, streamlined method for inducing pluripotent stem cells to form cortexlike “organoids.” These tiny balls of brain tissue include neurons supported by a cortexlike network of glial cells. This re ...
Chapter 4
... resolution than CT and can visualize smaller brain lesions -PET: uses radioactive material to assess regional brain glucose and to secure images brain function (use in schizophrenia, depression and OCD) -SPECT: similar to PET, poor resolution, less cost -fMRI: relies on magnetic properties , use is ...
... resolution than CT and can visualize smaller brain lesions -PET: uses radioactive material to assess regional brain glucose and to secure images brain function (use in schizophrenia, depression and OCD) -SPECT: similar to PET, poor resolution, less cost -fMRI: relies on magnetic properties , use is ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... Event related potentials (ERPs) are changes in the pattern of electrical function in response to an event ...
... Event related potentials (ERPs) are changes in the pattern of electrical function in response to an event ...
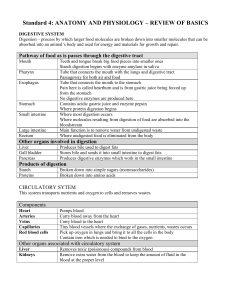
Standard 4: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY – REVIEW OF BASICS
... Where air enters body Moistens inhaled air Filters dust and particles from inhaled air Tube that connects the mouth with the lungs and digestive tract Passageway for both air and food Voice box – contains the vocal cords needed to make sounds Connects the pharynx with the lungs Also called the windp ...
... Where air enters body Moistens inhaled air Filters dust and particles from inhaled air Tube that connects the mouth with the lungs and digestive tract Passageway for both air and food Voice box – contains the vocal cords needed to make sounds Connects the pharynx with the lungs Also called the windp ...
Ch. 3 Discovering Psy Behaving Brain Video
... 4. All behavior begins with the actions of the neurons. First the a. _____________ - gathers & receives information from other neurons b. _____________ - neuron’s cell body c. Axon - ______________________________________________________ d. _____________ _____________ - where the impulses end up and ...
... 4. All behavior begins with the actions of the neurons. First the a. _____________ - gathers & receives information from other neurons b. _____________ - neuron’s cell body c. Axon - ______________________________________________________ d. _____________ _____________ - where the impulses end up and ...
7-9_BrainDev_ValaczkaiR
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.