SBI 4U Homeostasis 3
... cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Maintains homeostasis Hypothalamus and medulla oblongata control the autonomic nervous system, which has neurons that are bundled together with somatic system neurons in the cranial and spinal nerves. Has two divisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic. ...
... cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Maintains homeostasis Hypothalamus and medulla oblongata control the autonomic nervous system, which has neurons that are bundled together with somatic system neurons in the cranial and spinal nerves. Has two divisions: sympathetic and parasympathetic. ...
Anatomy and Physiology Notes
... • Found throughout the body • Hypothalamus and pituitary glands control the activity of many others • Specific for specific receptors • Function in positive feedback and negative feedback (thermostatic control) • Ex. of negative feedback – insulin and glucagon controlling blood sugar (glucose) level ...
... • Found throughout the body • Hypothalamus and pituitary glands control the activity of many others • Specific for specific receptors • Function in positive feedback and negative feedback (thermostatic control) • Ex. of negative feedback – insulin and glucagon controlling blood sugar (glucose) level ...
Parts of a Neuron…… Neuronal Communication….
... • These RF pulses are usually applied through a coil. MRI machines come with many different coils designed for different parts of the body: knees, shoulders, wrists, heads, necks and so on. These coils usually conform to the contour of the body part being imaged, or at least reside very close to it ...
... • These RF pulses are usually applied through a coil. MRI machines come with many different coils designed for different parts of the body: knees, shoulders, wrists, heads, necks and so on. These coils usually conform to the contour of the body part being imaged, or at least reside very close to it ...
Chapter 2 - bobcat
... MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that does not use xrays. The process involves passing a strong magnetic field through the head. The magnetic field used is 30,000 + times that of the earth's magnetic field. It's effect on the body, however, is harmless and temporary. The MRI scanner can detect ...
... MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that does not use xrays. The process involves passing a strong magnetic field through the head. The magnetic field used is 30,000 + times that of the earth's magnetic field. It's effect on the body, however, is harmless and temporary. The MRI scanner can detect ...
PSY550 Research and Ingestion
... acids, and fatty acids are derived from glycogen, protein, and adipose tissue during this phase. ...
... acids, and fatty acids are derived from glycogen, protein, and adipose tissue during this phase. ...
Interbrain and Brainstem
... Controls Breathing. • Medulla Oblongata = The lowest part of the brain stem – Merges into the spinal cord – Contains important control centers ...
... Controls Breathing. • Medulla Oblongata = The lowest part of the brain stem – Merges into the spinal cord – Contains important control centers ...
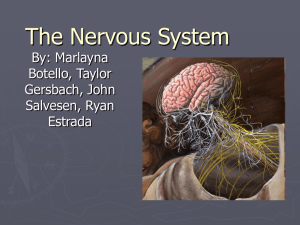
the nervous system
... How does it do it? • Cells carry messages from one part of the body to another • The messages in the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses • The cells that transmit the impulses are called neurons – Made of: • Dendrite • Axon • Myelin Sheath ...
... How does it do it? • Cells carry messages from one part of the body to another • The messages in the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses • The cells that transmit the impulses are called neurons – Made of: • Dendrite • Axon • Myelin Sheath ...
Ch 3 Biopsychology & the Foundations of Neuroscience
... O 14."Fight-or-flight" behavior is associated with ...
... O 14."Fight-or-flight" behavior is associated with ...
The Nervous System - Kirchner-WHS
... system is the function of everything. ► It sends signals notify the brain to react to the situation. ► Reflexes, movement, muscles, everything! ...
... system is the function of everything. ► It sends signals notify the brain to react to the situation. ► Reflexes, movement, muscles, everything! ...
Human Physiology
... Brain-controls nervous system, maintains normal function of the body, contains 100 billion neurons ...
... Brain-controls nervous system, maintains normal function of the body, contains 100 billion neurons ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... C) Mixed: Sensory & motor functions are unrelated (i.e. sense taste but control facial expression) ...
... C) Mixed: Sensory & motor functions are unrelated (i.e. sense taste but control facial expression) ...
The Nervous System
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
Document
... sensory inputs, to the Hypothalamus which elevates Harry's Heart Rate (HR) and Respiration and reduces his Digestive activity and Sexual desires. ...
... sensory inputs, to the Hypothalamus which elevates Harry's Heart Rate (HR) and Respiration and reduces his Digestive activity and Sexual desires. ...
Note 11
... - Hormones are produced by ductless gland (known as endocrine gland) and secreted into the blood capillary (its secretion will increase when there is a specific stimulation) - Blood carries the hormones around the body - Specific target organ(s) take(s) up the specific hormones, other organs are NOT ...
... - Hormones are produced by ductless gland (known as endocrine gland) and secreted into the blood capillary (its secretion will increase when there is a specific stimulation) - Blood carries the hormones around the body - Specific target organ(s) take(s) up the specific hormones, other organs are NOT ...
Nervous System
... Visual & auditory sensory input passes through the midbrain before being relayed to the higher brain centers Coordinates movements of the head related to vision and hearing (e.g. turning towards sound or ...
... Visual & auditory sensory input passes through the midbrain before being relayed to the higher brain centers Coordinates movements of the head related to vision and hearing (e.g. turning towards sound or ...
X-Ray imaging Used in many different ways in medical diagnosis. A
... the tracer and a computer converts this energy into 3D pictures – A physician can then look at cross-sectional images of the body organ from any angle in order to detect any functional problems ...
... the tracer and a computer converts this energy into 3D pictures – A physician can then look at cross-sectional images of the body organ from any angle in order to detect any functional problems ...
Nervous System
... FRONTAL LOBE: In charge of speech, movement, emotions, problem solving, memory OCCIPITAL LOBE: In charge of vision PARIETAL LOBE: In charge of touch, temperature and pain TEMPORAL LOBE: In charge of hearing ...
... FRONTAL LOBE: In charge of speech, movement, emotions, problem solving, memory OCCIPITAL LOBE: In charge of vision PARIETAL LOBE: In charge of touch, temperature and pain TEMPORAL LOBE: In charge of hearing ...
Wilson Language Training 10th Annual Conference Providence
... these new digital media will have the same effect. It’s critical that we understand (digital media’s) benefits and its unintended consequences. There are implications for both of those for schools.” --Connie Yowell, MacArthur Foundation, Education Week, ...
... these new digital media will have the same effect. It’s critical that we understand (digital media’s) benefits and its unintended consequences. There are implications for both of those for schools.” --Connie Yowell, MacArthur Foundation, Education Week, ...
1. 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter
... Roger Sperry received the Nobel Prize in physiology and medicine in 1981 for his experiments on split brain patients that provided strong evidence for lateralization of speech processing in the brain. Sperry's experiments showed, that the left hemisphere is responsible for the formation of speech wh ...
... Roger Sperry received the Nobel Prize in physiology and medicine in 1981 for his experiments on split brain patients that provided strong evidence for lateralization of speech processing in the brain. Sperry's experiments showed, that the left hemisphere is responsible for the formation of speech wh ...
circ and homeo
... • The capillaries, which are tiny blood vessels connecting arteries and veins, are in contact with extra cellular fluid surrounding each individual cell. • In these microscopic vessels, blood performs its ultimate homeostatic function. Nutrients and other essential materials pass from capillary blo ...
... • The capillaries, which are tiny blood vessels connecting arteries and veins, are in contact with extra cellular fluid surrounding each individual cell. • In these microscopic vessels, blood performs its ultimate homeostatic function. Nutrients and other essential materials pass from capillary blo ...
AP 1st Q Round 1
... the participant is aware of the condition to which the participant is assigned. ...
... the participant is aware of the condition to which the participant is assigned. ...
Flyer - Energy Kinesiology Association
... Hormone effects on our brain, including adolescence and menopause Emotional, short and long term stress effects on Glial Cell Neurotransmission Control of which neurons fire and their speed providing brain synchrony - the basis of Brain Integration ..... plus much more!! ...
... Hormone effects on our brain, including adolescence and menopause Emotional, short and long term stress effects on Glial Cell Neurotransmission Control of which neurons fire and their speed providing brain synchrony - the basis of Brain Integration ..... plus much more!! ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.