1244509Health Nervous System 2012
... The energy used by the brain is enough to light a 25 watt bulb. The weight of the average adult brain weights about 3 pounds. ...
... The energy used by the brain is enough to light a 25 watt bulb. The weight of the average adult brain weights about 3 pounds. ...
Chapter 23
... 2. Due to reorganization 3. Right hemisphere damage causes similar deficits to adults. ...
... 2. Due to reorganization 3. Right hemisphere damage causes similar deficits to adults. ...
Ch 10 Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity (pt2)
... May be possible to reduce brain damage by blocking neural degeneration Apoptosis inhibitor proteins Nerve growth factor Estrogren ▪ Potentially explains why several brain disorders are less common in women ...
... May be possible to reduce brain damage by blocking neural degeneration Apoptosis inhibitor proteins Nerve growth factor Estrogren ▪ Potentially explains why several brain disorders are less common in women ...
Nervous System - KidsHealth in the Classroom
... cerebellum, balance or coordination brain stem, breathing or circulation or digestion hypothalamus, body temperature or appetite or sleep pituitary gland, growth or metabolism ...
... cerebellum, balance or coordination brain stem, breathing or circulation or digestion hypothalamus, body temperature or appetite or sleep pituitary gland, growth or metabolism ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
Body Systems - St. Ambrose School
... • Gland that serves 3 functions – Produces insulin which regulates blood sugar levels – Produces enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats – Produces sodium bicarbonate, which neutralizes stomach acid ...
... • Gland that serves 3 functions – Produces insulin which regulates blood sugar levels – Produces enzymes that break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats – Produces sodium bicarbonate, which neutralizes stomach acid ...
Nervous_System - Ms. Kingery`s Class
... --a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy ...
... --a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy ...
Nervous System
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite • The chemical signal gets transdu ...
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite • The chemical signal gets transdu ...
The Promise and Peril of Tomorrow`s Neuroscience
... The chapter book group discussed The Future of the Brain by Steven Rose at its July 6 meeting. Rose is a Professor of Biology and Director of the Brain and Behavior Research Group at the Open University in the UK and a Visiting Professor in the Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology at Univ ...
... The chapter book group discussed The Future of the Brain by Steven Rose at its July 6 meeting. Rose is a Professor of Biology and Director of the Brain and Behavior Research Group at the Open University in the UK and a Visiting Professor in the Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology at Univ ...
AChE inhibitor
... With aging, normal adult gait changes to: •Hesitant •broad based •small stepped •Stooped posture •Diminished arm swings •Turns performed en bloc With Parkinson’s, there is also: •Rigidity •Tremors (at rest) •Akinesia (loss of power of movement) •Bradykinesia (slowed movement) Pathology of Parkinson ...
... With aging, normal adult gait changes to: •Hesitant •broad based •small stepped •Stooped posture •Diminished arm swings •Turns performed en bloc With Parkinson’s, there is also: •Rigidity •Tremors (at rest) •Akinesia (loss of power of movement) •Bradykinesia (slowed movement) Pathology of Parkinson ...
Chapter 2, section 2
... • Cycle of events in which information from one step controls or affects a previous ...
... • Cycle of events in which information from one step controls or affects a previous ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... glands and organs. Sympathetic NS arouses a person. Parasympathetic NS conserves energy and calms. ...
... glands and organs. Sympathetic NS arouses a person. Parasympathetic NS conserves energy and calms. ...
Chapter 18: Neurologic Emergencies
... pressure, pulse rate, and respiratory rate and pattern. The hypothalamus and pituitary control the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine from the endocrine system. The cerebellum allows unconscious management of complex motor activity. • Nerve cells, or neurons, transmit signals along their axon ...
... pressure, pulse rate, and respiratory rate and pattern. The hypothalamus and pituitary control the release of epinephrine and norepinephrine from the endocrine system. The cerebellum allows unconscious management of complex motor activity. • Nerve cells, or neurons, transmit signals along their axon ...
The nervous system
... Although the brain is only about 2% of the total body weight in humans, it receives 15-20% of the body's blood supply. Because brain cells will die if the supply of blood which carries oxygen is stopped, the brain has top priority for the blood. Even if other organs need blood, the body attempts to ...
... Although the brain is only about 2% of the total body weight in humans, it receives 15-20% of the body's blood supply. Because brain cells will die if the supply of blood which carries oxygen is stopped, the brain has top priority for the blood. Even if other organs need blood, the body attempts to ...
Left Brain
... "While one of those who were assisting me touched lightly, and by chance, the point of his scalpel to the internal crural nerves of the frog, suddenly all the muscles of its limbs were seen to be so contracted that they seemed to have fallen into tonic convulsions. “ ...
... "While one of those who were assisting me touched lightly, and by chance, the point of his scalpel to the internal crural nerves of the frog, suddenly all the muscles of its limbs were seen to be so contracted that they seemed to have fallen into tonic convulsions. “ ...
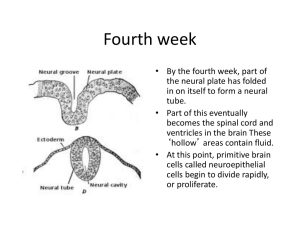
Fourth week
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
notes - Other Places you want to go
... Corpus callosum – allows the two hemispheres of the brain to communicate with each other Brain stem – controls basic functions like breathing, heart rate and the pressure which is used to pump blood Hypothalamus – (in addition to controlling pituitary gland) regulates thirst, hunger and body t ...
... Corpus callosum – allows the two hemispheres of the brain to communicate with each other Brain stem – controls basic functions like breathing, heart rate and the pressure which is used to pump blood Hypothalamus – (in addition to controlling pituitary gland) regulates thirst, hunger and body t ...
FinalStudyGuide
... What is the % of red blood cells in a sample called? What is erythropoietin & when is it released? Study features/characteristics of WBC, what are they properly called, their primary functions, conditions that arise when there are too many, too few, etc. What are thrombocytes? Who was Karl ...
... What is the % of red blood cells in a sample called? What is erythropoietin & when is it released? Study features/characteristics of WBC, what are they properly called, their primary functions, conditions that arise when there are too many, too few, etc. What are thrombocytes? Who was Karl ...
Studying the Living Human Brain
... Animal studies and clinical observations are useful, but often, such as when we need to diagnose or treat illness, we want to know what is happening inside the brain of a living human. For this we have: EEG: Electroencephalogram MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging ...
... Animal studies and clinical observations are useful, but often, such as when we need to diagnose or treat illness, we want to know what is happening inside the brain of a living human. For this we have: EEG: Electroencephalogram MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging ...
Chapter 2: Brain Development
... • Most embryonic cells are pluripotent stem cells • A variety of chemicals signal cells to turn into specialized cells • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: ...
... • Most embryonic cells are pluripotent stem cells • A variety of chemicals signal cells to turn into specialized cells • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.