Test Question 1 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive
... AW: Signal strength represents H+ concentration. Signal frequency is determined by the specific local magnetic field strength. With frequency encoding or phase encoding the spatial origin of the signal can be determined in a 2-dimensional plane It is also possible to measure increased local neural a ...
... AW: Signal strength represents H+ concentration. Signal frequency is determined by the specific local magnetic field strength. With frequency encoding or phase encoding the spatial origin of the signal can be determined in a 2-dimensional plane It is also possible to measure increased local neural a ...
Sensory Disorders
... 1. Gliomas- tumors that arise from glial cells & infiltrate the brain. May be benign to malignant. ...
... 1. Gliomas- tumors that arise from glial cells & infiltrate the brain. May be benign to malignant. ...
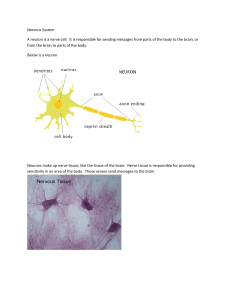
Nervous System A neuron is a nerve cell. It is responsible for
... signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. The brain is also responsible for thinking, dreaming, learning and more. ...
... signals that make the organs of our bodies function properly. The brain is why we blink, breathe and our hearts beat without thinking about it or being able to really stop it for very long. The brain is also responsible for thinking, dreaming, learning and more. ...
Nervous System Disorders and Homeostatic Imbalances
... • Also known as Lou Gehrig’s Disease • A relatively rare neurological disorder • A syndrome marked by muscular weakness and atrophy with spasticity and hyperflexion due to degeneration of the motor neurons of the spinal cord, medulla, and cortex • A degenerative disease • No known cure ...
... • Also known as Lou Gehrig’s Disease • A relatively rare neurological disorder • A syndrome marked by muscular weakness and atrophy with spasticity and hyperflexion due to degeneration of the motor neurons of the spinal cord, medulla, and cortex • A degenerative disease • No known cure ...
Normal Edema
... • Not all cells in the CNS are ‘equal’: while some disease processes affect some groups of cells more than others (‘selective vulnerability’), other disease processes could affect other areas more. • Not all areas in the brain are equal: most areas in the brain have specific functions: a same diseas ...
... • Not all cells in the CNS are ‘equal’: while some disease processes affect some groups of cells more than others (‘selective vulnerability’), other disease processes could affect other areas more. • Not all areas in the brain are equal: most areas in the brain have specific functions: a same diseas ...
How Does the Brain Work?
... The primitive brainstem regulates balance, coordination and life-sustaining processes such as breathing and heartbeat. Throughout the brain, neurons communicate with one another through interlocking circuits. When a neuron is stimulated, it generates a tiny electrical current, which passes down a fi ...
... The primitive brainstem regulates balance, coordination and life-sustaining processes such as breathing and heartbeat. Throughout the brain, neurons communicate with one another through interlocking circuits. When a neuron is stimulated, it generates a tiny electrical current, which passes down a fi ...
Neurons
... Generalizing from laboratory animals to human How can be such complex system investigated if we make a hole in the center of it ...
... Generalizing from laboratory animals to human How can be such complex system investigated if we make a hole in the center of it ...
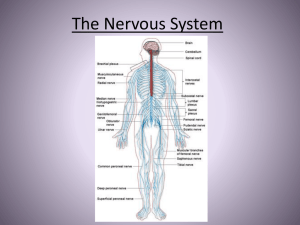
The Nervous System
... • Aka the “little brain” • Responsible for coordination of motor functions • Also involved in language (although poorly understood) Brain Stem • Two parts: pons and medulla oblongata • Mediates flow between body and brain Medulla ...
... • Aka the “little brain” • Responsible for coordination of motor functions • Also involved in language (although poorly understood) Brain Stem • Two parts: pons and medulla oblongata • Mediates flow between body and brain Medulla ...
46 Chapter Review: Fill-in-the
... deficiency of it is associated with Parkinson's disease, and anoversensitivity to it is associated with some cases of schizophrenia. 10. The control voluntary body mo;'ements, speech production, and such functions as thinking, motivation, planning for the future, impulse control, and emotional respo ...
... deficiency of it is associated with Parkinson's disease, and anoversensitivity to it is associated with some cases of schizophrenia. 10. The control voluntary body mo;'ements, speech production, and such functions as thinking, motivation, planning for the future, impulse control, and emotional respo ...
Final Exam - UF Psychology
... X b. is likely to mate with one of those males in adulthood O c. is more likely to show male-typical sexual behavior in adulthood than a female that was located between two females. X d. will be highly emotional as an adult as a result of the stress from being between two males as a fetus. X e. will ...
... X b. is likely to mate with one of those males in adulthood O c. is more likely to show male-typical sexual behavior in adulthood than a female that was located between two females. X d. will be highly emotional as an adult as a result of the stress from being between two males as a fetus. X e. will ...
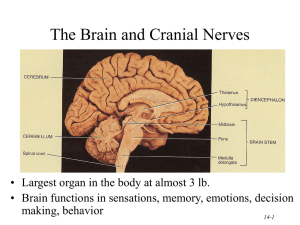
14-1
... Blood Supply to Brain • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanent injury • at that time, lysosome release enzymes ...
... Blood Supply to Brain • Uses 20% of our bodies oxygen & glucose needs – blood flow to an area increases with activity in that area – deprivation of O2 for 4 min does permanent injury • at that time, lysosome release enzymes ...
Neurological Diseases ppt
... CSF is examined for color, blood cells, bacteria, malignant cells, and glucose ...
... CSF is examined for color, blood cells, bacteria, malignant cells, and glucose ...
White blood cells play important roles in protecting us from infections
... White blood cells play important roles in protecting us from infections. On the other hand, neurons in the brain send signals that mediate memory formation or control our body movement. Thus, blood cells are entirely different population from neurons, and two cell types have no functional relationsh ...
... White blood cells play important roles in protecting us from infections. On the other hand, neurons in the brain send signals that mediate memory formation or control our body movement. Thus, blood cells are entirely different population from neurons, and two cell types have no functional relationsh ...
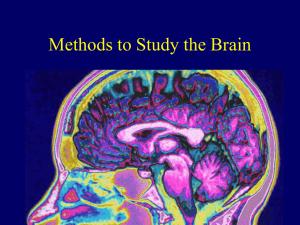
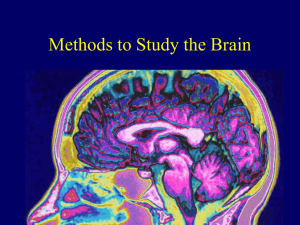
Module 11: Methods to Study the Brain
... • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
... • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
Module 11: Methods to Study the Brain
... • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
... • Takes a series of cross-sectional photographs, which are then put together to form a three-dimensional image. ...
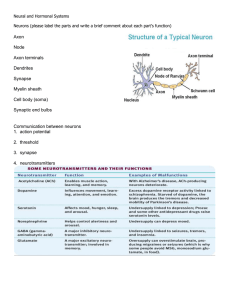
Neural and Hormonal Systems Neurons (please label the parts and
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
... hemispheres of the brains. This is used as a form of treatment for epileptic seizures. ...
specimen jar craft - National Wildlife Federation
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
studyingbrainpost
... • Experience and Learning result in a direct event in the nervous system • Every brain is wired differently ...
... • Experience and Learning result in a direct event in the nervous system • Every brain is wired differently ...
Haemodynamic response
In haemodynamics, the body must respond to physical activities, external temperature, and other factors by homeostatically adjusting its blood flow to deliver nutrients such as oxygen and glucose to stressed tissues and allow them to function. Haemodynamic response (HR) allows the rapid delivery of blood to active neuronal tissues. Since higher processes in the brain occur almost constantly, cerebral blood flow is essential for the maintenance of neurons, astrocytes, and other cells of the brain.