Pharmacology - The reward pathway
... The cortex, and particularly the prefrontal cortex, is associated with thinking, and planning, and deciding. It gives us a sense of recent events through working memory. Working memory is the memory that you're using to remember what I said at the beginning of the sentence. And that is, working memo ...
... The cortex, and particularly the prefrontal cortex, is associated with thinking, and planning, and deciding. It gives us a sense of recent events through working memory. Working memory is the memory that you're using to remember what I said at the beginning of the sentence. And that is, working memo ...
MCB 163: Mammalian Neuroanatomy
... independence of use. 11. ANTERIOR THALAMIC NUCLEI These nuclei are related to the limbic system and receive projections from the amygdala, and in turn project to the frontal lobes and especially the lateral prefrontal cortex. This circuit appears to be important for modulating emotionality and for s ...
... independence of use. 11. ANTERIOR THALAMIC NUCLEI These nuclei are related to the limbic system and receive projections from the amygdala, and in turn project to the frontal lobes and especially the lateral prefrontal cortex. This circuit appears to be important for modulating emotionality and for s ...
Fourth week
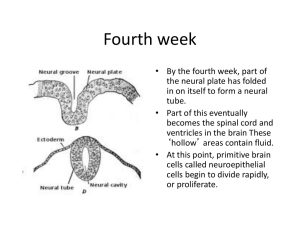
... undergoes the most complicated changes. • The forebrain divides into two distinct structures: the diencephalon and telencephalon. • The diencephalon develops into the thalamus and hypothalamus, which will affect everything from emotions to sensory perception. ...
... undergoes the most complicated changes. • The forebrain divides into two distinct structures: the diencephalon and telencephalon. • The diencephalon develops into the thalamus and hypothalamus, which will affect everything from emotions to sensory perception. ...
A Guided Tour of the Brain
... › Largest lobe › Primary motor cortex › Involved in planning, initiating, and executing voluntary movements Association Areas › Located on all lobes › Combine sensory and motor information › Coordinate interaction among different brain areas ...
... › Largest lobe › Primary motor cortex › Involved in planning, initiating, and executing voluntary movements Association Areas › Located on all lobes › Combine sensory and motor information › Coordinate interaction among different brain areas ...
Overview of Addiction Related Brain Regions Nucleus Accumbens
... individual's hippocampus grow is yet to be elucidated. A study on rats at Indiana University suggested that the sexual dimorphism in the hippocampus morphology is tied to a sexual dimorphism in repeated maze performance. Males seem to be better at contexualizing their whereabouts because they have m ...
... individual's hippocampus grow is yet to be elucidated. A study on rats at Indiana University suggested that the sexual dimorphism in the hippocampus morphology is tied to a sexual dimorphism in repeated maze performance. Males seem to be better at contexualizing their whereabouts because they have m ...
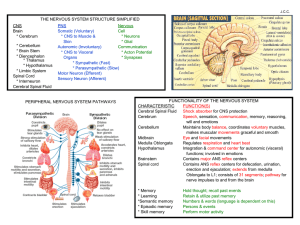
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
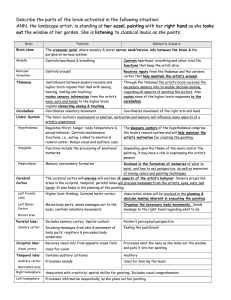
... Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Co ...
... Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Co ...
Slides
... rostrally or “towards” the head end): telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon and myelencephalon ...
... rostrally or “towards” the head end): telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon and myelencephalon ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Olfactory System, Amygdala and
... Figure 23-21 Major outputs from the basolateral (blue), central (red), and medial (green) nuclei of the amygdala (Am). These take three routes: (1) the stria terminalis, which reaches the septal nuclei (S) and hypothalamus (Hy); (2) the ventral amygdalofugal pathway (see Fig. 23-20B and C) to the hy ...
... Figure 23-21 Major outputs from the basolateral (blue), central (red), and medial (green) nuclei of the amygdala (Am). These take three routes: (1) the stria terminalis, which reaches the septal nuclei (S) and hypothalamus (Hy); (2) the ventral amygdalofugal pathway (see Fig. 23-20B and C) to the hy ...
Chapt13 Lecture 13ed Pt 3
... • It joins primitive emotions (i.e., fear, pleasure) with higher functions such as reasoning. • The _____________ can cause strong emotional reactions to situations but conscious thought can override and direct our behavior. • Includes • Amygdala – imparts emotional overtones • Hippocampus – importa ...
... • It joins primitive emotions (i.e., fear, pleasure) with higher functions such as reasoning. • The _____________ can cause strong emotional reactions to situations but conscious thought can override and direct our behavior. • Includes • Amygdala – imparts emotional overtones • Hippocampus – importa ...
Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation
... The limbic system’s involvement in emotion, motivation and memory will influence many aspects of a artistic experience ...
... The limbic system’s involvement in emotion, motivation and memory will influence many aspects of a artistic experience ...
Brain Structures and their Functions
... with higher brain function such as thought and action. The cerebral cortex is divided into four sections, called "lobes": the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe. Here is a visual representation of the cortex: ...
... with higher brain function such as thought and action. The cerebral cortex is divided into four sections, called "lobes": the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe. Here is a visual representation of the cortex: ...
Cranial nerve of smell, plus olfactory pathway
... secondary cortical olfactory areas, and their relationship to limbic system ...
... secondary cortical olfactory areas, and their relationship to limbic system ...
Barry Jacobs presentation
... • Is the mind a manifestation of brain function? If not, what is it? • If it is, then it is the manifestation of physico-chemical components. How is this different than a rock, a computer? Do computers think? Do they have free will, consciousness, and emotion? • Could we build a machine with the sam ...
... • Is the mind a manifestation of brain function? If not, what is it? • If it is, then it is the manifestation of physico-chemical components. How is this different than a rock, a computer? Do computers think? Do they have free will, consciousness, and emotion? • Could we build a machine with the sam ...
Brain Basics
... the cortex (except for olfaction); receives and organizes sensory information from the sensory organs Regulates sleep and wakefulness (during sleep the thalamus is closed. i.e., does not take input from sensory organs). ...
... the cortex (except for olfaction); receives and organizes sensory information from the sensory organs Regulates sleep and wakefulness (during sleep the thalamus is closed. i.e., does not take input from sensory organs). ...
Crossword Puzzle
... 1. located on the sides of the brain, these lobes contain the auditory areas, which receive information from the ears 2. situated between the frontal and occipital lobes, these lobes contain the sensory cortex 5. extension of a neuron that sends impulses to other nerve cells or to muscles or glands ...
... 1. located on the sides of the brain, these lobes contain the auditory areas, which receive information from the ears 2. situated between the frontal and occipital lobes, these lobes contain the sensory cortex 5. extension of a neuron that sends impulses to other nerve cells or to muscles or glands ...
Biological Basis of Emotions - California Training Institute
... There have been many theories on how human emotions are formed. We have arrived at the point where most researchers believe that emotion is not a function of any specific brain center but of a circuit that involves four basic structures, interconnected through several nervous bundle ...
... There have been many theories on how human emotions are formed. We have arrived at the point where most researchers believe that emotion is not a function of any specific brain center but of a circuit that involves four basic structures, interconnected through several nervous bundle ...
Thalamus and Limbic System
... Located anterior to the interventricular septum Main connections: ...
... Located anterior to the interventricular septum Main connections: ...
Brain abnormalities in murders indicated by positron emission
... Independent measures design (between-subjects) Quasi or (natural experiment) Paired match design Independent variable: murder or not Dependent: Results of the PET scans. Exp. Group- 41 subjects (39 males and 2 females) referred to the imaging centre for legal reason. Con. group- 41 non murders paire ...
... Independent measures design (between-subjects) Quasi or (natural experiment) Paired match design Independent variable: murder or not Dependent: Results of the PET scans. Exp. Group- 41 subjects (39 males and 2 females) referred to the imaging centre for legal reason. Con. group- 41 non murders paire ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Outer layers of cortex – gray matter Underlying myelinated axons and glial cells – white matter Clusters of related neurons – called nuclei: ...
... Outer layers of cortex – gray matter Underlying myelinated axons and glial cells – white matter Clusters of related neurons – called nuclei: ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.