Nature 411, 189 - 193 (2001)
... ganglia. These large subcortical structures that form the core of the cerebral hemispheres directly participate in the control of psychomotor behavior. Neuroanatomical methods combined with transmitter localization procedures were used to study the chemical organization of the forebrain in each majo ...
... ganglia. These large subcortical structures that form the core of the cerebral hemispheres directly participate in the control of psychomotor behavior. Neuroanatomical methods combined with transmitter localization procedures were used to study the chemical organization of the forebrain in each majo ...
Hypothalamus and Limbic System, Lecture 2 Emotion and reward
... as defined by Broca. The limbic lobe comprises a ring of “primitive” cortex around the brainstem, including the cingulate cortex, the parahippocampal gyrus, and the hippocampal formation. ...
... as defined by Broca. The limbic lobe comprises a ring of “primitive” cortex around the brainstem, including the cingulate cortex, the parahippocampal gyrus, and the hippocampal formation. ...
Hypothalamus and Limbic System, Lecture 2
... as defined by Broca. The limbic lobe comprises a ring of “primitive” cortex around the brainstem, including the cingulate cortex, the parahippocampal gyrus, and the hippocampal formation. ...
... as defined by Broca. The limbic lobe comprises a ring of “primitive” cortex around the brainstem, including the cingulate cortex, the parahippocampal gyrus, and the hippocampal formation. ...
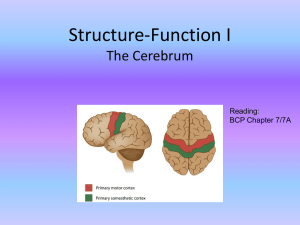
Structure-Function I
... subthalamus (diencephalon) and substantia nigra (mesencephalon). The basal ganglia plays a role in the selection of which of several motor actions to execute at any given time. Damage to the basal ganglia can lead to Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease. ...
... subthalamus (diencephalon) and substantia nigra (mesencephalon). The basal ganglia plays a role in the selection of which of several motor actions to execute at any given time. Damage to the basal ganglia can lead to Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease. ...
Chap2
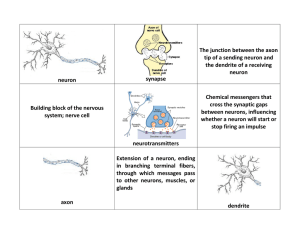
... structure of neurons that leads to increased likelihood of firing. Review of neural structure: ...
... structure of neurons that leads to increased likelihood of firing. Review of neural structure: ...
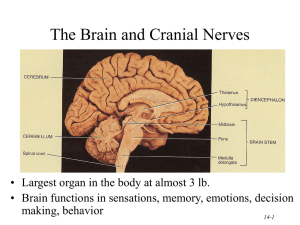
the brain: anatomical regions
... Similar to plasma be/c it is derived from plasma Made in the 3rd and 4th ventricle by the CHOROID PLEXUS There are fenestrated capillaries there; the fluid spreads into the ...
... Similar to plasma be/c it is derived from plasma Made in the 3rd and 4th ventricle by the CHOROID PLEXUS There are fenestrated capillaries there; the fluid spreads into the ...
PSYC550 Emotions and Memory
... • central nucleus (CE) – The region of the amygdala that receives information from the basal, lateral, and accessory basal nuclei and sends projections to a wide variety of regions in the brain; involved in emotional responses. ...
... • central nucleus (CE) – The region of the amygdala that receives information from the basal, lateral, and accessory basal nuclei and sends projections to a wide variety of regions in the brain; involved in emotional responses. ...
LECTURE23.EmotionDriveDrugs
... We (and rats) tend to eat more calories of flavorful food than bland diet Sexual behavior is drive towards pleasure fulfillment Stimuli that are pleasurable are believed to signal “pleasure” by activating certain midbrain dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) that project to the n ...
... We (and rats) tend to eat more calories of flavorful food than bland diet Sexual behavior is drive towards pleasure fulfillment Stimuli that are pleasurable are believed to signal “pleasure” by activating certain midbrain dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) that project to the n ...
The limbic system
... well as to the posterior cingulate and retrosplenial cortices and the amygdala [Figure 3].[10] Circuits of amygdala Amygdala serves to integrate information processing between prefrontal / temporal association cortices and the hypothalamus. The amygdala has two major output pathways: Dorsal route vi ...
... well as to the posterior cingulate and retrosplenial cortices and the amygdala [Figure 3].[10] Circuits of amygdala Amygdala serves to integrate information processing between prefrontal / temporal association cortices and the hypothalamus. The amygdala has two major output pathways: Dorsal route vi ...
{ How Neurosciences help us to understand some (psycho)therapeutic processes
... Vital to cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, decision-making, empathy, and emotion. ACC is involved in the processing of the affective dimension of pain responsible for rendering new memories permanent. ...
... Vital to cognitive functions, such as reward anticipation, decision-making, empathy, and emotion. ACC is involved in the processing of the affective dimension of pain responsible for rendering new memories permanent. ...
Ch38-Nervous_system
... • What we perceive as “mind” (thought, will, selfperception) does produce evidence of brain activity in brain scans. • That “brain” influences “mind” is well-established; but some evidence shows “mind” can influence “brain”; as cognitive therapy for depression can physically change the brain. • Neur ...
... • What we perceive as “mind” (thought, will, selfperception) does produce evidence of brain activity in brain scans. • That “brain” influences “mind” is well-established; but some evidence shows “mind” can influence “brain”; as cognitive therapy for depression can physically change the brain. • Neur ...
olfaction and limbic system
... Corpus amygdaloideum, hippocampus (diagonal band of Брока) Orbitofrontal cortex, hypothalamus, midbrain (medial forebrain bundle) ...
... Corpus amygdaloideum, hippocampus (diagonal band of Брока) Orbitofrontal cortex, hypothalamus, midbrain (medial forebrain bundle) ...
Secrets of the Teen Brain
... • Practicing piano: thickens neurons that control the fingers. • Study of London cab drivers: found larger hippocampus: structure involved in memory. ...
... • Practicing piano: thickens neurons that control the fingers. • Study of London cab drivers: found larger hippocampus: structure involved in memory. ...
The Great Brain Drain Review - Reeths
... nerve cell is called an action potential. There are 3 parts to this impulse: depolarization (when sodium ions rush into the cells), repolarization (when potassium ions rush out), and the refractory period (when the ions are being pumped back to where they started). The neural impulse will only be se ...
... nerve cell is called an action potential. There are 3 parts to this impulse: depolarization (when sodium ions rush into the cells), repolarization (when potassium ions rush out), and the refractory period (when the ions are being pumped back to where they started). The neural impulse will only be se ...
biological persp
... All that is psychological is first physiologicalreductionist! All behavior has a cause – deterministic! Psychology should investigate the brain, neurochemistry and genetics ...
... All that is psychological is first physiologicalreductionist! All behavior has a cause – deterministic! Psychology should investigate the brain, neurochemistry and genetics ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s A) dopamine B) GABA C) serotonin D) acetylcholine ...
... in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s A) dopamine B) GABA C) serotonin D) acetylcholine ...
the brain
... occipital bone • Is the visual cortex – Receives, integrates and processes visual information – Clinically referred to as Brodmann area 17 ...
... occipital bone • Is the visual cortex – Receives, integrates and processes visual information – Clinically referred to as Brodmann area 17 ...
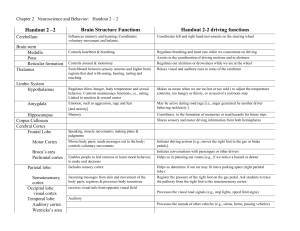
Handout 2 –2 Brain Structure Functions Handout 2-2 driving
... Regulates our alertness or drowsiness while we are at the wheel ...
... Regulates our alertness or drowsiness while we are at the wheel ...
The Great Brain Drain Review
... unconscious thoughts and behaviors. The sympathetic nervous system controls the fight-or-flight response. Examples of things this nervous system might stimulate include pupils dilating, heartbeat increasing, breathing rate increasing, slowed digestion, adrenaline release. The part of the brainstem t ...
... unconscious thoughts and behaviors. The sympathetic nervous system controls the fight-or-flight response. Examples of things this nervous system might stimulate include pupils dilating, heartbeat increasing, breathing rate increasing, slowed digestion, adrenaline release. The part of the brainstem t ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.