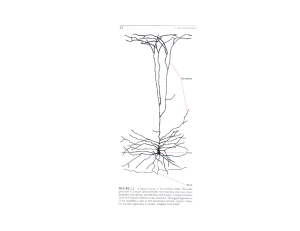
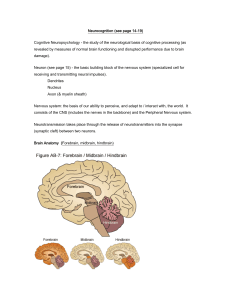
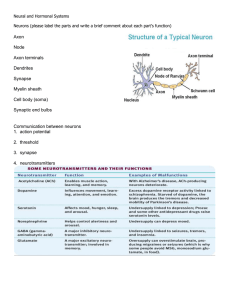
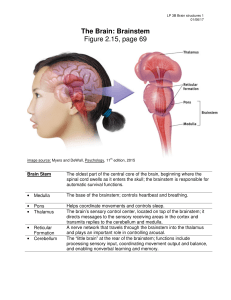
Nervous system slides
... ¾ Several cerebellum and brainstem centers control sleep and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytic ...
... ¾ Several cerebellum and brainstem centers control sleep and arousal, such as the reticular system that filters sensory input sent to the cortex. ¾The two hemispheres of the brain are specialized for different functions; the left hemisphere contains processes supporting speech, language, & analytic ...
Chapter 8: Sensation and Perception
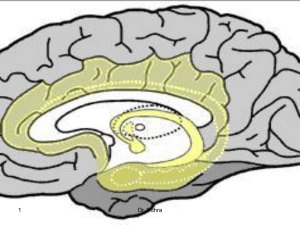
... Limbic System: Doughnut-shaped neural system Located below the cerebral hemispheres ...
... Limbic System: Doughnut-shaped neural system Located below the cerebral hemispheres ...
Chapter 15 Study Questions key
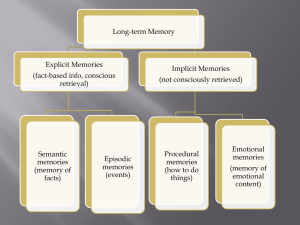
... 7. Why is it difficult to develop an animal model of episodic memory? Since episodic memory supports conscious recollection in humans, it is hard to tell if the particular tasks researchers use really measure episodic memory in animals. 8. What are the two strategies used to study the brain regions ...
... 7. Why is it difficult to develop an animal model of episodic memory? Since episodic memory supports conscious recollection in humans, it is hard to tell if the particular tasks researchers use really measure episodic memory in animals. 8. What are the two strategies used to study the brain regions ...
Learning - Dot Point 2.
... secondary motor areas of the frontal lobes, as well as from the somatosensory cortex, to integrate and smooth bodily movements. – Neural Pathways are transferred to the Basal Ganglia and new neural activity is generally activated once a response becomes very well learned and no longer requires much ...
... secondary motor areas of the frontal lobes, as well as from the somatosensory cortex, to integrate and smooth bodily movements. – Neural Pathways are transferred to the Basal Ganglia and new neural activity is generally activated once a response becomes very well learned and no longer requires much ...
Emotion: Cellular Level
... Learning Emotional Responses Emotions can be defined as 'states elicited by reinforcing stimuli' (Rolls 1986), whereby the association (innately, through conditioning or learning) of reinforcer stimuli with a behavior is responsible for its emotional coloring. At the cellular level, learning has bee ...
... Learning Emotional Responses Emotions can be defined as 'states elicited by reinforcing stimuli' (Rolls 1986), whereby the association (innately, through conditioning or learning) of reinforcer stimuli with a behavior is responsible for its emotional coloring. At the cellular level, learning has bee ...
Lewis FT 1923 The significance of the term hippocampus. J Comp
... description extant. It has left its readers in doubt whether the elevations of cerebral substance were being compared with fish or beast, and no one could be sure which end was the head." Lewis FT 1923 The significance of the term hippocampus. J Comp Neurol 35: 213 ...
... description extant. It has left its readers in doubt whether the elevations of cerebral substance were being compared with fish or beast, and no one could be sure which end was the head." Lewis FT 1923 The significance of the term hippocampus. J Comp Neurol 35: 213 ...
Spatial Memory - American Psychological Association
... features) or remember which direction (left, right) they turned. Neuroscience: Psychologists can study which brain areas are activated when spatial tasks are solved. In laboratory animals, they may record electrical signals from neurons or measure the release of chemicals in the brain. In humans, br ...
... features) or remember which direction (left, right) they turned. Neuroscience: Psychologists can study which brain areas are activated when spatial tasks are solved. In laboratory animals, they may record electrical signals from neurons or measure the release of chemicals in the brain. In humans, br ...
Neurology of Attachment: Wiring for Self-Care & Empathy
... and reorganization, losing overall gray matter (neurons) ...
... and reorganization, losing overall gray matter (neurons) ...
Older Brain Structures
... Limbic System: Doughnut-shaped neural system Located below the cerebral hemispheres ...
... Limbic System: Doughnut-shaped neural system Located below the cerebral hemispheres ...
LO: Explain how biological factors may affect one cognitive process.
... MRI scanning showed damage to Clive’s hippocampus and some of the frontal regions. This indicates that retrograde amnesia can be tied to the hippocampus ALSO ...
... MRI scanning showed damage to Clive’s hippocampus and some of the frontal regions. This indicates that retrograde amnesia can be tied to the hippocampus ALSO ...
Chapter 12 Central Nervous System – Brain
... spinal cord connect “appropriate” motor responses to stimuli also: learning memory Central Nervous System ...
... spinal cord connect “appropriate” motor responses to stimuli also: learning memory Central Nervous System ...
phys Learning Objectives Chapter 58 [10-31
... Hippocampus is easily hyperexcitable. The result is focal epileptic seizure during which, the person experiences various psychomotor effects (olfactory, auditory, tactile, and other hallucinations) even though the person has not lost consciousness and knows these hallucinations to be unreal. - The r ...
... Hippocampus is easily hyperexcitable. The result is focal epileptic seizure during which, the person experiences various psychomotor effects (olfactory, auditory, tactile, and other hallucinations) even though the person has not lost consciousness and knows these hallucinations to be unreal. - The r ...
CS 160 * Comparative Cognition * Spring 02
... - Superior Colliculus = Processes visual info (esp re: location of stimuli) & integrate w/motor output - e.g. “Blindsight” Human w/damage to higher visual areas is “blind” but can point to moving stim. - Inferior Colliculus = Processes auditory info (esp location), & integrate with motor output - To ...
... - Superior Colliculus = Processes visual info (esp re: location of stimuli) & integrate w/motor output - e.g. “Blindsight” Human w/damage to higher visual areas is “blind” but can point to moving stim. - Inferior Colliculus = Processes auditory info (esp location), & integrate with motor output - To ...
20-Limbic
... cross to the opposite side through small hippocampal commissure. The body of the fornix divides into two columns & enter the hypothalamus where the majority of the fibers terminate in the mammillary body. The mammillary body in turn projects to the anterior nuclear group of the thalamus via mammilot ...
... cross to the opposite side through small hippocampal commissure. The body of the fornix divides into two columns & enter the hypothalamus where the majority of the fibers terminate in the mammillary body. The mammillary body in turn projects to the anterior nuclear group of the thalamus via mammilot ...
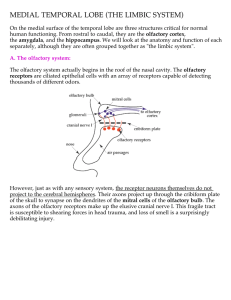
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
... visual, auditory, and somatosensory cortices are the main inputs to the amygdala. Outputs: the amygdala must be able to control the autonomic system, to provoke such an instant sympathetic response. The main outputs of the amygdala are to the hypothalamus and brainstem autonomic centers, including t ...
... visual, auditory, and somatosensory cortices are the main inputs to the amygdala. Outputs: the amygdala must be able to control the autonomic system, to provoke such an instant sympathetic response. The main outputs of the amygdala are to the hypothalamus and brainstem autonomic centers, including t ...
Reward” and “Punishment” Function of the Limbic System
... thinking type) into long-term memory (consolidation).Thus removal of a portions of the hippocampi as treatment for epilepsy, lead to anterograde amnesia. These people can recall most previously learned memories satisfactorily. They are capable of short-term memory for seconds up to a minute or two, ...
... thinking type) into long-term memory (consolidation).Thus removal of a portions of the hippocampi as treatment for epilepsy, lead to anterograde amnesia. These people can recall most previously learned memories satisfactorily. They are capable of short-term memory for seconds up to a minute or two, ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.