9 Functions of the Middle Prefrontal Cortex
... ongoing stimuli, the delay of reaction, selection from a variety of possible options and the initiation of action. ...
... ongoing stimuli, the delay of reaction, selection from a variety of possible options and the initiation of action. ...
Ch. 2 Practice
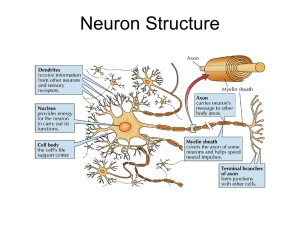
... 1. The type of neurons that communicate information from the environment to the central nervous system are: a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Mirror neurons d. Interneurons ...
... 1. The type of neurons that communicate information from the environment to the central nervous system are: a. Sensory neurons b. Motor neurons c. Mirror neurons d. Interneurons ...
Chapter 2
... – Pons: involved in respiration, sleep regulation, dreaming – Medulla: involved in life support functions such as respiration and heart rate – Reticular activating system is an arousal system within the brainstem ...
... – Pons: involved in respiration, sleep regulation, dreaming – Medulla: involved in life support functions such as respiration and heart rate – Reticular activating system is an arousal system within the brainstem ...
the brain: anatomical regions
... CEREBRUM is the largest portion of the brain Cerebellum is the second largest portion of the brain. Its function is for balance. ...
... CEREBRUM is the largest portion of the brain Cerebellum is the second largest portion of the brain. Its function is for balance. ...
Physiological Nature
... with emotion formation and processing, learning, and memory – Also, executive control needed to suppress inappropriate unconscious priming is known to involve the anterior cingulate gyrus Previous experiences that influence behavior ...
... with emotion formation and processing, learning, and memory – Also, executive control needed to suppress inappropriate unconscious priming is known to involve the anterior cingulate gyrus Previous experiences that influence behavior ...
SPHS 4050, Neurological bases, PP 03a
... (diencephalon), pons, medulla and midbrain (brain stem) and corpus callosum and commissures (which form connections between hemispheres) ...
... (diencephalon), pons, medulla and midbrain (brain stem) and corpus callosum and commissures (which form connections between hemispheres) ...
Learning and Memory Learning is defined as the acquisition of new
... in the brain in a different way. By studying people with damage to different parts of the brain, scientists have learned more about how the brain organizes and stores information, but much remains a mystery. Memories seem to be synthesized from many pieces of information that are stored in several p ...
... in the brain in a different way. By studying people with damage to different parts of the brain, scientists have learned more about how the brain organizes and stores information, but much remains a mystery. Memories seem to be synthesized from many pieces of information that are stored in several p ...
Slides on brain development
... Exposure to excessive stress hormones is bad for brain development. Early symptoms of PTSD The brain can become incapable of producing ...
... Exposure to excessive stress hormones is bad for brain development. Early symptoms of PTSD The brain can become incapable of producing ...
UsabilityPs3
... navigates a path. When various rats paused on completion of a run, the place neurons fired in reverse order from the firing that had occurred during navigation. This reverse replay occurred more frequently after walking through new mazes than familiar ones, implying that the technique plays a role i ...
... navigates a path. When various rats paused on completion of a run, the place neurons fired in reverse order from the firing that had occurred during navigation. This reverse replay occurred more frequently after walking through new mazes than familiar ones, implying that the technique plays a role i ...
UsabilityPs3
... navigates a path. When various rats paused on completion of a run, the place neurons fired in reverse order from the firing that had occurred during navigation. This reverse replay occurred more frequently after walking through new mazes than familiar ones, implying that the technique plays a role i ...
... navigates a path. When various rats paused on completion of a run, the place neurons fired in reverse order from the firing that had occurred during navigation. This reverse replay occurred more frequently after walking through new mazes than familiar ones, implying that the technique plays a role i ...
Evolution and The Brain - Falcon Science
... areas concerned with movement and thinking. The frontal lobe plans is also an integral part of personality. Parietal lobe – higher processing of sensory information from other brain areas and the spinal cord. Deals with direction, and orientation in a 3-dimensional space. *Proprioception – having a ...
... areas concerned with movement and thinking. The frontal lobe plans is also an integral part of personality. Parietal lobe – higher processing of sensory information from other brain areas and the spinal cord. Deals with direction, and orientation in a 3-dimensional space. *Proprioception – having a ...
Neuron Note #3 - WordPress.com
... which signals from your eyes were sent to the area of the brain that processes sound, and signals from the ears were sent to the area of the brain that processes vision, which part of the brain would most likely be ...
... which signals from your eyes were sent to the area of the brain that processes sound, and signals from the ears were sent to the area of the brain that processes vision, which part of the brain would most likely be ...
11/10/16 Memory Part 2 Reinforcement learning (12.2) • Involves a
... o Memory items: a pattern of synapses (between excitatory cells) o Different kinds of memory, different kinds of learning → different brain structures The hippocampus: short term memory o Basic anatomy: the tri-synaptic circuit o Long-term potentiation o Long-term depression o Rat hippocampus (12.4) ...
... o Memory items: a pattern of synapses (between excitatory cells) o Different kinds of memory, different kinds of learning → different brain structures The hippocampus: short term memory o Basic anatomy: the tri-synaptic circuit o Long-term potentiation o Long-term depression o Rat hippocampus (12.4) ...
History of Psychology - Western Washington University
... • Midbrain – Species-typical movement patterns ...
... • Midbrain – Species-typical movement patterns ...
CAST
... • The hippocampus is one of the important brain areas that are connected with emotional expression and cognition function, and it is also an area that is very susceptible to stress and aging. • The hippocampus is one of the important brain areas that is connected with emotional expression and cogni ...
... • The hippocampus is one of the important brain areas that are connected with emotional expression and cognition function, and it is also an area that is very susceptible to stress and aging. • The hippocampus is one of the important brain areas that is connected with emotional expression and cogni ...
The human brain
... The secret of the brain lies in the vast number of neurons (tens of billions) and the complicated way they are connected. ...
... The secret of the brain lies in the vast number of neurons (tens of billions) and the complicated way they are connected. ...
Chapter 2: Biopsychology Study Guide
... information from short-term to long-term memory B. "central switching station" – relays incoming sensory information (except olfactory) to the brain C. balance, smooth movement, and posture D. emotional expression, particularly the emotional component of behavior, memory, and motivation E. controls ...
... information from short-term to long-term memory B. "central switching station" – relays incoming sensory information (except olfactory) to the brain C. balance, smooth movement, and posture D. emotional expression, particularly the emotional component of behavior, memory, and motivation E. controls ...
The Structures of the Brain
... structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebrum, associated with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus. ...
... structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebrum, associated with emotions such as fear, aggression and drives for food and sex. It includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus. ...
nervous_system_-_cns_and_pns_part_2_-_2015
... Cerebrum is the forebrain • Contains two hemispheres for coordinating sensory and motor information • Speech, reasoning, memory, personality, may be located on one side only ...
... Cerebrum is the forebrain • Contains two hemispheres for coordinating sensory and motor information • Speech, reasoning, memory, personality, may be located on one side only ...
1050927abstract
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
... intrinsic excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. In addition, silent cells show long-lasting activity in respond to past experience of encountering novel objects. Such reverberating activity is reminiscent of engram cell activity that reflects storage of the memory. Using two-photon imaging ...
Slide 1
... grid cells and more localized sensory input (e.g. vision, smell). Investigate the role of network topology and synaptic learning rules in forming memorized sequences (i.e. navigational routes). Model the effect of changes in the environment (e.g size, features) on hippocampal cell activity, and conn ...
... grid cells and more localized sensory input (e.g. vision, smell). Investigate the role of network topology and synaptic learning rules in forming memorized sequences (i.e. navigational routes). Model the effect of changes in the environment (e.g size, features) on hippocampal cell activity, and conn ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.