File
... 10. The three main components of a neuron are the cell body, dendrites, and axon. What are the functions of each component? Answer: Cell body- control center (nucleus & cytoplasm). Axons- extends from cell body & produces nerve terminals. Dendrite- receives messages from other neurons. ...
... 10. The three main components of a neuron are the cell body, dendrites, and axon. What are the functions of each component? Answer: Cell body- control center (nucleus & cytoplasm). Axons- extends from cell body & produces nerve terminals. Dendrite- receives messages from other neurons. ...
Brain Advanced 2
... Reticular Formation •Widespread connections •Arousal of the brain as a whole •Reticular activating system (RAS) •Maintains consciousness and alertness •Functions in sleep and arousal from sleep ...
... Reticular Formation •Widespread connections •Arousal of the brain as a whole •Reticular activating system (RAS) •Maintains consciousness and alertness •Functions in sleep and arousal from sleep ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... Reticular Formation •Widespread connections •Arousal of the brain as a whole •Reticular activating system (RAS) •Maintains consciousness and alertness •Functions in sleep and arousal from sleep ...
... Reticular Formation •Widespread connections •Arousal of the brain as a whole •Reticular activating system (RAS) •Maintains consciousness and alertness •Functions in sleep and arousal from sleep ...
W10 Brain Development
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
Module 7 - The Brain
... If damaged, the person could perform basic movements but would lose fine coordination skills. ...
... If damaged, the person could perform basic movements but would lose fine coordination skills. ...
Resting state functional connectivity MRI inisoflurane
... • In specific brain regions SA and MEC had an opposite effect on functional connectivity: intrinsic BOLD signal co-fluctuations were reduced and enhanced by SA and MEC, respectively. • These results provide support for the application of rsfcMRI in isoflurane-anesthetized rat brain to investigate no ...
... • In specific brain regions SA and MEC had an opposite effect on functional connectivity: intrinsic BOLD signal co-fluctuations were reduced and enhanced by SA and MEC, respectively. • These results provide support for the application of rsfcMRI in isoflurane-anesthetized rat brain to investigate no ...
Studying the Brain
... “relay station” for all the info that travels to and from the cortex Hypothalamus Controls hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior Controls the body’s reaction to temperature Cerebral Cortex Outer layer of the forebrain ...
... “relay station” for all the info that travels to and from the cortex Hypothalamus Controls hunger, thirst, and sexual behavior Controls the body’s reaction to temperature Cerebral Cortex Outer layer of the forebrain ...
CNS STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS
... perhaps (in association with the limbic system) with emotions, they contain the motor cortex and Broca’s area (left hemisphere only). The temporal lobes are concerned with hearing, containing the auditory cortex and, in the left hemisphere where the lobe borders the parietal lobe, Wernicke’s area. T ...
... perhaps (in association with the limbic system) with emotions, they contain the motor cortex and Broca’s area (left hemisphere only). The temporal lobes are concerned with hearing, containing the auditory cortex and, in the left hemisphere where the lobe borders the parietal lobe, Wernicke’s area. T ...
1. What are some major differences between
... The reptilian brain is the oldest layer of the brain and is composed of the brainstem (medulla, pons, cerebellum, midbrain, globus pallidus, and olfactory bulbs) (see page 370 and Figure 13.1). These are the structures that dominate in the brains of snakes and lizards, which is why it referred to as ...
... The reptilian brain is the oldest layer of the brain and is composed of the brainstem (medulla, pons, cerebellum, midbrain, globus pallidus, and olfactory bulbs) (see page 370 and Figure 13.1). These are the structures that dominate in the brains of snakes and lizards, which is why it referred to as ...
Chapter 2
... Master gland Produces hormones influencing the secretions of all other endocrine glands Produces hormones that influences growth Attached to hypothalamus ...
... Master gland Produces hormones influencing the secretions of all other endocrine glands Produces hormones that influences growth Attached to hypothalamus ...
Neurotransmitters
... attention, sleep and wakefulness, and control of reflexes; Pons – regulates states of arousal, including sleep and dreaming. Cerebellum – balance, smooth movement, and posture Thalamus – "central switching station" – relays incoming sensory information (except olfactory) to the brain Hypothalamus – ...
... attention, sleep and wakefulness, and control of reflexes; Pons – regulates states of arousal, including sleep and dreaming. Cerebellum – balance, smooth movement, and posture Thalamus – "central switching station" – relays incoming sensory information (except olfactory) to the brain Hypothalamus – ...
Neurochemistry of executive functions
... This and noradrenergic systems part of the ascending reticular activating system ...
... This and noradrenergic systems part of the ascending reticular activating system ...
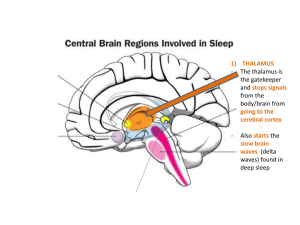
Sleep Brain Labelling
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
Memory
... change (e.g., shape of terminal button, number of receptors) • This causes memories to be now be stored in the long term ...
... change (e.g., shape of terminal button, number of receptors) • This causes memories to be now be stored in the long term ...
Brain Plasticity and Emotional Regulation
... What is Brain Plasticity? Term is in vogue, but what do we really mean? Pliable and changeable. It’s really been several “Decades of the Brain”. Dalai Lama has held numerous conferences in India to discuss breakthroughs in Neuroscience. The brain isn’t fully formed (especially, PFC) until t ...
... What is Brain Plasticity? Term is in vogue, but what do we really mean? Pliable and changeable. It’s really been several “Decades of the Brain”. Dalai Lama has held numerous conferences in India to discuss breakthroughs in Neuroscience. The brain isn’t fully formed (especially, PFC) until t ...
Hippocampus+and+Neurons+Final+Draft
... (synapses) coupled with this organ’s ability to control every function in the human body make this organ a never-ending source of research. I narrowed this project to the hippocampus and neurons. There were so many interesting things that I learned about while doing this project. For example the hip ...
... (synapses) coupled with this organ’s ability to control every function in the human body make this organ a never-ending source of research. I narrowed this project to the hippocampus and neurons. There were so many interesting things that I learned about while doing this project. For example the hip ...
myers Chapter 02 review game
... important in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s ...
... important in memory. Depletion of it is found in those with Alzheimer’s ...
Nervous System
... A group of neural pathways that connects parts of the thalmus & hypolthalmus & inner portions of the cerebrum “border” – to describe structures that bordered the basal regions of the cerebrum – but has come to describe all neuronal structures that control emotional behavior and motivational drives L ...
... A group of neural pathways that connects parts of the thalmus & hypolthalmus & inner portions of the cerebrum “border” – to describe structures that bordered the basal regions of the cerebrum – but has come to describe all neuronal structures that control emotional behavior and motivational drives L ...
The Brain Summary Notes
... The Brain The following is a list of the tools and techniques used to help gather information on the brain: 1. Lesions The surgical destruction or removal of brain tissue. 2. Electroencephalogram (EEG) A machine that measures brain electric activity. 3. Computed Tomograph (CT or CAT Scan) This appar ...
... The Brain The following is a list of the tools and techniques used to help gather information on the brain: 1. Lesions The surgical destruction or removal of brain tissue. 2. Electroencephalogram (EEG) A machine that measures brain electric activity. 3. Computed Tomograph (CT or CAT Scan) This appar ...
Memory
... • Semantic memory linked to the limbic cortex. • Consolidation of episodic memory mediated by the hippocampus. • Procedural memory function associated with basal ganglia and motor cortex. ...
... • Semantic memory linked to the limbic cortex. • Consolidation of episodic memory mediated by the hippocampus. • Procedural memory function associated with basal ganglia and motor cortex. ...
“Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to
... which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that information or those abilities are stored. It is important to note from the outset that there are certainly different kinds of memory, such as procedural memory (remembering how to do someth ...
... which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that information or those abilities are stored. It is important to note from the outset that there are certainly different kinds of memory, such as procedural memory (remembering how to do someth ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.