brain drain answers
... unconscious thoughts and behaviors. The sympathetic nervous system controls the fight-or-flight response. Examples of things this nervous system might stimulate include pupils dilating, heartbeat increasing, breathing rate increasing, slowed digestion, adrenaline release. The part of the brainstem t ...
... unconscious thoughts and behaviors. The sympathetic nervous system controls the fight-or-flight response. Examples of things this nervous system might stimulate include pupils dilating, heartbeat increasing, breathing rate increasing, slowed digestion, adrenaline release. The part of the brainstem t ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... – it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and ...
... – it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and ...
Brain Powerpoint
... Limbic System • Limbic system produces emotions in response to stimuli such as sex hormones, stress hormones, hunger hormones, body senses, and information from the frontal lobe – Essentially a parallel consciousness – Animals with no frontal lobe activity (including infants) behave solely on limbi ...
... Limbic System • Limbic system produces emotions in response to stimuli such as sex hormones, stress hormones, hunger hormones, body senses, and information from the frontal lobe – Essentially a parallel consciousness – Animals with no frontal lobe activity (including infants) behave solely on limbi ...
Document
... The Limbic System The limbic system connects us to our emotions and motivations. Most of these emotions and motivations are related to survival. ...
... The Limbic System The limbic system connects us to our emotions and motivations. Most of these emotions and motivations are related to survival. ...
Physiology Ch 58 p711-720 [4-25
... 3. over the top of corpus callosum onto medial aspect cerebral hemisphere in cingulate gyrus 4. passing behind corpus callosum into ventromedial surface of temporal love to the parahippocampal gyrus and uncus -on the medial/ventral surface of each hemisphere there is a paleocortex, surrounding group ...
... 3. over the top of corpus callosum onto medial aspect cerebral hemisphere in cingulate gyrus 4. passing behind corpus callosum into ventromedial surface of temporal love to the parahippocampal gyrus and uncus -on the medial/ventral surface of each hemisphere there is a paleocortex, surrounding group ...
Justin Smith - USD Biology
... • NPSR mRNA- expressed in stress related areas – Amygdala – BNST – Hypothalamus – Raphe Nucleus – Ventral tegmental area ...
... • NPSR mRNA- expressed in stress related areas – Amygdala – BNST – Hypothalamus – Raphe Nucleus – Ventral tegmental area ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... Medulla – control breathing, regulate reflexes Cerebellum – movement, motor coordination Pons – governs sleep and arousal Midbrain Relay between hindbrain and forebrain Integrating sensory info. Reticular Formation - Regulates arousal, attention, sleep/wakefulness, pain perception Forebrain - ...
... Medulla – control breathing, regulate reflexes Cerebellum – movement, motor coordination Pons – governs sleep and arousal Midbrain Relay between hindbrain and forebrain Integrating sensory info. Reticular Formation - Regulates arousal, attention, sleep/wakefulness, pain perception Forebrain - ...
100 - Bloomfield Central School
... balance and muscle movements, such as when you are playing a sport of instrument. ...
... balance and muscle movements, such as when you are playing a sport of instrument. ...
Parieto-prefrontal pathway
... (thought) Why is the hippocampus connected into the parieto-medial temporal pathway? •Much of the processing done by the parieto-medial temporal pathway is focused on navigation and relating ourselves to our environment. •The hippocampus creates cognitive maps, which reduce the cognitive load requi ...
... (thought) Why is the hippocampus connected into the parieto-medial temporal pathway? •Much of the processing done by the parieto-medial temporal pathway is focused on navigation and relating ourselves to our environment. •The hippocampus creates cognitive maps, which reduce the cognitive load requi ...
THE DOGMA OF AN AGING BRAIN
... AGING: LONG-TERM MEMORY Explicit memory – Retention of previously acquired skills & reflexes. Implicit memory – Conscious memory of facts & events. ...
... AGING: LONG-TERM MEMORY Explicit memory – Retention of previously acquired skills & reflexes. Implicit memory – Conscious memory of facts & events. ...
a PowerPoint Presentation of Module 24
... recall how we acquired the fear. The basal ganglia, next to the thalamus, controls movement, and forms and stores procedural memory and motor skills. We can learn to ride a bicycle even if we can’t recall having the lesson. ...
... recall how we acquired the fear. The basal ganglia, next to the thalamus, controls movement, and forms and stores procedural memory and motor skills. We can learn to ride a bicycle even if we can’t recall having the lesson. ...
HSTMemoryLecture - Psychology
... Recap: The Neural Basis of Memory • Computational models, genetics, and neurophysiology all complement the study of human and animal behavior in the contemporary investigation of memory. ...
... Recap: The Neural Basis of Memory • Computational models, genetics, and neurophysiology all complement the study of human and animal behavior in the contemporary investigation of memory. ...
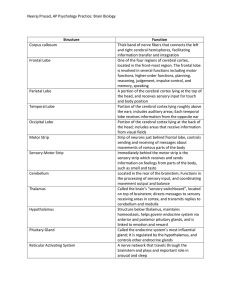
Neeraj Prasad, AP Psychology Practice: Brain Biology Structure
... Located at the base of the brainstem; Controls many essential involuntary functions such as heartbeat and breathing Region of frontal lobe that contains motor neurons involved in the control of speech Region of the frontal lobe that contains motor neurons involved in the comprehension of speech A fa ...
... Located at the base of the brainstem; Controls many essential involuntary functions such as heartbeat and breathing Region of frontal lobe that contains motor neurons involved in the control of speech Region of the frontal lobe that contains motor neurons involved in the comprehension of speech A fa ...
Slide ()
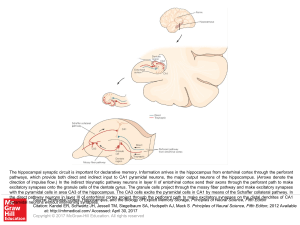
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
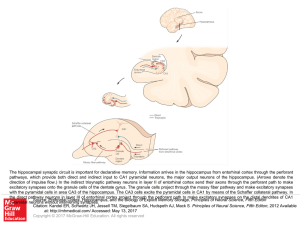
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Behavioural and electrophysiological studies of learning, memory and long-term potentiation.
... Our laboratory has adopted a novel approach to address this long‐standing problem in cognitive neurobiology. We are studying olfactory conditioning in rats by training them to associate the pairing of an odour and direct electrical stimulation of the perforant path to the dentate gyr ...
... Our laboratory has adopted a novel approach to address this long‐standing problem in cognitive neurobiology. We are studying olfactory conditioning in rats by training them to associate the pairing of an odour and direct electrical stimulation of the perforant path to the dentate gyr ...
action potential
... •Network of neurons in the brainstem (and thalamus) •Sleep and arousal •Attention ...
... •Network of neurons in the brainstem (and thalamus) •Sleep and arousal •Attention ...
biological psychologists endorphins neuron morphine dendrite
... 9. What does it mean to be "right-brained" or "left-brained"? 10. Why do psychologists say "everything psychological is simultaneously biological"? What does this statement mean? ...
... 9. What does it mean to be "right-brained" or "left-brained"? 10. Why do psychologists say "everything psychological is simultaneously biological"? What does this statement mean? ...
Brain Structure - Updated 14
... amygdala, and hippocampus all deal with basic drives, emotions, and memory • Hippocampus Memory processing • Amygdala Aggression (fight) and fear (flight) ...
... amygdala, and hippocampus all deal with basic drives, emotions, and memory • Hippocampus Memory processing • Amygdala Aggression (fight) and fear (flight) ...
Unit 3 Cerqueira guide
... “the distinction is no longer clear.” Hormones, adrenal glands, pituitary, testes/ovaries. The role of hormones on sex and gender (“is biology destiny?”) Titchener’s brain! “The brain is what the mind does.” Brain imaging devices: EEG, PET, MRI, fMRI. Hindbrain structures: brainstem, medulla, reticu ...
... “the distinction is no longer clear.” Hormones, adrenal glands, pituitary, testes/ovaries. The role of hormones on sex and gender (“is biology destiny?”) Titchener’s brain! “The brain is what the mind does.” Brain imaging devices: EEG, PET, MRI, fMRI. Hindbrain structures: brainstem, medulla, reticu ...
Neurons
... MRI + tracking blood flow in the brain the more active brain area is the more blood flows to it produce picture of brain activity measure pattern of electrical activity through electrodes attached to the scalp ...
... MRI + tracking blood flow in the brain the more active brain area is the more blood flows to it produce picture of brain activity measure pattern of electrical activity through electrodes attached to the scalp ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.