File
... • Locate examples of each rock type on a map of Ireland. • Understand the formation & main characteristics of two types of rock from each group. • Answer an essay style exam question, explaining in detail the formation of one rock type. ...
... • Locate examples of each rock type on a map of Ireland. • Understand the formation & main characteristics of two types of rock from each group. • Answer an essay style exam question, explaining in detail the formation of one rock type. ...
Earth
... 1. Igneous Rocks (Fact: Igneous means “fiery”) a. How they form: When magma reaches the surface, it becomes lava. b. This hot, molten rock cools and hardens to form igneous rock. c. Characteristics: Igneous rocks vary in size, shape, color, and texture. Examples: basalt, pumice, obsidian ...
... 1. Igneous Rocks (Fact: Igneous means “fiery”) a. How they form: When magma reaches the surface, it becomes lava. b. This hot, molten rock cools and hardens to form igneous rock. c. Characteristics: Igneous rocks vary in size, shape, color, and texture. Examples: basalt, pumice, obsidian ...
nandi central joint examinations – 2009
... Original Rock Metamorphic Rock Granite Gneiss Augite Horn blende Limestone Marble b) i) Name at least three rocks types that are found in Western Kenya. - Granite, Gneisss, Sandstone, Mudstone 1x3= 3mks c) Describe the formation of mechanically formed sedimentary rocks 5mks Pre – existing rocks are ...
... Original Rock Metamorphic Rock Granite Gneiss Augite Horn blende Limestone Marble b) i) Name at least three rocks types that are found in Western Kenya. - Granite, Gneisss, Sandstone, Mudstone 1x3= 3mks c) Describe the formation of mechanically formed sedimentary rocks 5mks Pre – existing rocks are ...
Science 1st 9 weeks
... SPI 0307.Inq.1 Select an investigation that could be used to answer a specific question. 3. WCE.SC.1: Maintain a science notebook that includes: observations, data, diagrams and explanations to analyze and communicate scientific findings (observation, data, diagrams, explanations, conclusions and re ...
... SPI 0307.Inq.1 Select an investigation that could be used to answer a specific question. 3. WCE.SC.1: Maintain a science notebook that includes: observations, data, diagrams and explanations to analyze and communicate scientific findings (observation, data, diagrams, explanations, conclusions and re ...
Standard III, Objective 1, Indicator A
... D. the water has evaporated out of Jar A but not Jar B 17. Where in nature might similar processes occur? A. in a farmers field B. on a mountain top C. under a forest D. on a river bottom 18. What inference can be made from this experiment? A. jars allow some gravel to shrink and other gravel to gro ...
... D. the water has evaporated out of Jar A but not Jar B 17. Where in nature might similar processes occur? A. in a farmers field B. on a mountain top C. under a forest D. on a river bottom 18. What inference can be made from this experiment? A. jars allow some gravel to shrink and other gravel to gro ...
Chapter 15
... When facies changes are combined with either regression or transgression the formation of lithostratigraphic units that cut across time lines is almost inevitable (see Figure 15.2C for example). As described in the section entitled “Gaps in the Record” we need to forget the concept that the stratigr ...
... When facies changes are combined with either regression or transgression the formation of lithostratigraphic units that cut across time lines is almost inevitable (see Figure 15.2C for example). As described in the section entitled “Gaps in the Record” we need to forget the concept that the stratigr ...
On the recognition of volcanic material in sedimentary rocks by
... The other components may show a similar uniformity as the zircons. but owing to the fact that the frequency of occurrence of the other trans~ parent components is only rarely so great as of zircon, their features are less conspicuous. This uniformity still increases the tendency of volcanic sediment ...
... The other components may show a similar uniformity as the zircons. but owing to the fact that the frequency of occurrence of the other trans~ parent components is only rarely so great as of zircon, their features are less conspicuous. This uniformity still increases the tendency of volcanic sediment ...
Name: 1 GEOL 104 Dinosaurs: A Natural History Geology
... Part I: Environments of Deposition Geologists can use various clues in sedimentary rocks to interpret their environment of deposition: that is, the type of conditions that were present when they were laid down. Some aspects of the environment of deposition are revealed by the type of sedimentary roc ...
... Part I: Environments of Deposition Geologists can use various clues in sedimentary rocks to interpret their environment of deposition: that is, the type of conditions that were present when they were laid down. Some aspects of the environment of deposition are revealed by the type of sedimentary roc ...
Geology Basics - San Diego Mesa College
... weight of the now quite cool oceanic crust sinking into the mantle helps drive plate tectonics. (458) In these subduction zones, a deep-sea trench forms off-shore of the continent, where one the oceanic plate along with sea floor sediments and some sea water sinks beneath the continental plate. Wate ...
... weight of the now quite cool oceanic crust sinking into the mantle helps drive plate tectonics. (458) In these subduction zones, a deep-sea trench forms off-shore of the continent, where one the oceanic plate along with sea floor sediments and some sea water sinks beneath the continental plate. Wate ...
Desert Rock Formations [Kompatibilis mód]
... Rock formations • The term 'rock formation' can also refer to specific sedimentary strata or other rock unit in stratigraphic and petrologic studies. • A rock structure can be created in any rock type or combination ...
... Rock formations • The term 'rock formation' can also refer to specific sedimentary strata or other rock unit in stratigraphic and petrologic studies. • A rock structure can be created in any rock type or combination ...
Desert Rock Formation
... Rock formations • The term 'rock formation' can also refer to specific sedimentary strata or other rock unit in stratigraphic and petrologic studies. • A rock structure can be created in any rock type or combination ...
... Rock formations • The term 'rock formation' can also refer to specific sedimentary strata or other rock unit in stratigraphic and petrologic studies. • A rock structure can be created in any rock type or combination ...
Introduction to Metamorphic Rock Forms
... Metamorphic Rock Forms Metamorphic rocks are formed from sedimentary or igneous rocks with physical or chemical alterations caused by heat, pressure, or the infiltration of other materials. Metamorphic rocks can be classified as either foliated or nonfoliated; foliation refers to the rock flaking or ...
... Metamorphic Rock Forms Metamorphic rocks are formed from sedimentary or igneous rocks with physical or chemical alterations caused by heat, pressure, or the infiltration of other materials. Metamorphic rocks can be classified as either foliated or nonfoliated; foliation refers to the rock flaking or ...
Topic 10: GEOLOGY of SYDNEY REGION
... just become abundant on earth, and accumulated into thick peat-like layers which with burial were progressively transformed into black coal. The Greta Seam, long mined at Cessnock and Kurri, is up to 11m thick, and occurs within sediments deposited in fresh water producing coals low in sulphur. The ...
... just become abundant on earth, and accumulated into thick peat-like layers which with burial were progressively transformed into black coal. The Greta Seam, long mined at Cessnock and Kurri, is up to 11m thick, and occurs within sediments deposited in fresh water producing coals low in sulphur. The ...
3-6 The Rock Cycle - Ms Dudek`s Website
... Rock in which the composition and texture of the rock have been changed by heat and pressure is call _____________ rock. metamorphic ...
... Rock in which the composition and texture of the rock have been changed by heat and pressure is call _____________ rock. metamorphic ...
rock-cycle-inro-ppt
... Rock in which the composition and texture of the rock have been changed by heat and pressure is call _____________ rock. metamorphic ...
... Rock in which the composition and texture of the rock have been changed by heat and pressure is call _____________ rock. metamorphic ...
Rocks - Macmillan Learning
... Three types of rocks Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Igneous rocks make up most of the earth sedimentary rocks make up most of the surface. ...
... Three types of rocks Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic Igneous rocks make up most of the earth sedimentary rocks make up most of the surface. ...
5.2 Sandstones
... Clast-supported conglomerate: gravel-size grains touch and form a supporting framework. Matrix-supported conglomerate: gravel-size grains do not touch and are supported in a mud/sand matrix. This type of conglomerate may be referred to as diamictites. Note: Other meaning for diamictites: poorly sor ...
... Clast-supported conglomerate: gravel-size grains touch and form a supporting framework. Matrix-supported conglomerate: gravel-size grains do not touch and are supported in a mud/sand matrix. This type of conglomerate may be referred to as diamictites. Note: Other meaning for diamictites: poorly sor ...
Stratigraphic Principles
... is loose, unconsolidated (not cemented together into a solid rock), soil or sediments, eroded, deposited, and reshaped by water in some form in a non-marine setting. ...
... is loose, unconsolidated (not cemented together into a solid rock), soil or sediments, eroded, deposited, and reshaped by water in some form in a non-marine setting. ...
Name: Date: Earth and Environmental FINAL Study Guide What is a
... 3. Differentiate between fracture and cleavage. Give an example of a mineral for each one. ...
... 3. Differentiate between fracture and cleavage. Give an example of a mineral for each one. ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... Ions may move between minerals to create minerals of different chemical composition. Hornfels, with its alternating bands of dark and light crystals, is a good example of how minerals rearrange themselves during metamorphism. Hornfels is shown in the table for the "Metamorphic Rock Classification" c ...
... Ions may move between minerals to create minerals of different chemical composition. Hornfels, with its alternating bands of dark and light crystals, is a good example of how minerals rearrange themselves during metamorphism. Hornfels is shown in the table for the "Metamorphic Rock Classification" c ...
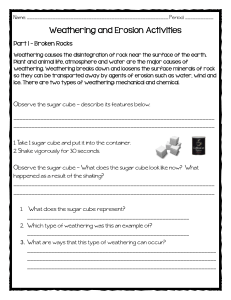
Weathering and Erosion Activities
... 1. What landform / feature is created as a result of the water? _______________________________________________________ 2. What was carried by the water to the bottom of the pan? _______________________________________________________ 3. What process is this an example of? _________________________ ...
... 1. What landform / feature is created as a result of the water? _______________________________________________________ 2. What was carried by the water to the bottom of the pan? _______________________________________________________ 3. What process is this an example of? _________________________ ...
Rock and Rock Materials
... • Most abundant minerals are silicates • Basic building block is the silica tetrahedra • Rock properties determined by properties of component materials (minerals) • Three main classes of rocks – Igneous: Formed from molten material – Sedimentary: Clastic, chemical, organic, combinations – Metamorph ...
... • Most abundant minerals are silicates • Basic building block is the silica tetrahedra • Rock properties determined by properties of component materials (minerals) • Three main classes of rocks – Igneous: Formed from molten material – Sedimentary: Clastic, chemical, organic, combinations – Metamorph ...
Moon Rocks - DouglasSpaceWeek
... Digging at a rate of one foot per minute, it would take you 87 years to tunnel all the way through Earth. ...
... Digging at a rate of one foot per minute, it would take you 87 years to tunnel all the way through Earth. ...
Changes on the earth*s surface
... C. Chemical Weathering – alters a rock’s chemical makeup by changing the minerals that form the rock or combining them with new chemicals 1. can change one rock into a completely different type of rock 2. many caves are formed when acidic water seeps into cracks of rocks 3. acid rain – chemicals in ...
... C. Chemical Weathering – alters a rock’s chemical makeup by changing the minerals that form the rock or combining them with new chemicals 1. can change one rock into a completely different type of rock 2. many caves are formed when acidic water seeps into cracks of rocks 3. acid rain – chemicals in ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.








![Desert Rock Formations [Kompatibilis mód]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005971893_1-51504e6f57ddffd75c531227a72a6428-300x300.png)