Chapter 21 Planet Earth
... What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes occur at plate boundaries and release energy as seismic waves. Focus is the area along a fault at which the first motion of an earthquake occurs. Epicenter is the point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s focus ...
... What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes occur at plate boundaries and release energy as seismic waves. Focus is the area along a fault at which the first motion of an earthquake occurs. Epicenter is the point on Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s focus ...
Slide 1
... Minerals are divided into two groups based on the elements they are made of: 1 Minerals that contain the elements silicon and oxygen are called silicate minerals. 2 The nonsilicate minerals do not contain a combination of the elements silicon and oxygen. Minerals in this group are made up of other e ...
... Minerals are divided into two groups based on the elements they are made of: 1 Minerals that contain the elements silicon and oxygen are called silicate minerals. 2 The nonsilicate minerals do not contain a combination of the elements silicon and oxygen. Minerals in this group are made up of other e ...
Cell Biology Review Game
... b. The rock has a vesicular texture. c. The rock contains fragments of other rocks. d. The rock shows distorted and stretched pebbles. ...
... b. The rock has a vesicular texture. c. The rock contains fragments of other rocks. d. The rock shows distorted and stretched pebbles. ...
Bal Bharati Public School Class – 7 Subject
... 2. What are endogenic and enogenic forces? The forces which act in the interior of the earth, are called endogenic forces. The forces which act on the surface of the earth are called enogenic forces. 3. What is a volcano ? A volcano is a vent in the earth’s crust through which the molten material er ...
... 2. What are endogenic and enogenic forces? The forces which act in the interior of the earth, are called endogenic forces. The forces which act on the surface of the earth are called enogenic forces. 3. What is a volcano ? A volcano is a vent in the earth’s crust through which the molten material er ...
chemical composition and origin of the shock metamorphic rocks of
... and these are presented in the following paragraphs: 1) The first rock group is characterized by a porphyritic appearance. The rocks are dark gray in hand specimens and contain rare angular fragments of light granitic rocks. The texture is porphyritic with plagioclase as phenocrysts in the fine-grai ...
... and these are presented in the following paragraphs: 1) The first rock group is characterized by a porphyritic appearance. The rocks are dark gray in hand specimens and contain rare angular fragments of light granitic rocks. The texture is porphyritic with plagioclase as phenocrysts in the fine-grai ...
GY343 Petrology
... Terms continued • Pumice: frothy volcanic glass, usually has density less than water • Scoria: extrusive volcanic rock that is composed of > 50% vesicles (void space) • Tuff: fine grained, fragmented volcanic rock that results from the eruption of viscous magma; usually the major component of ash fl ...
... Terms continued • Pumice: frothy volcanic glass, usually has density less than water • Scoria: extrusive volcanic rock that is composed of > 50% vesicles (void space) • Tuff: fine grained, fragmented volcanic rock that results from the eruption of viscous magma; usually the major component of ash fl ...
Igneous Rocks
... minerals that cool and crystallize our of magma. Minerals are compounds of chemical elements. There are 6 types of minerals that are common in igneous ...
... minerals that cool and crystallize our of magma. Minerals are compounds of chemical elements. There are 6 types of minerals that are common in igneous ...
The Process of Erosion and Deposition of Sediments Power Point
... • Downward movement of rock and sediment down a slope due to the pull of gravity • The process is quite slow and almost impossible to see until the land mass is no longer able to support itself and falls or slides down a slope. • Examples: landslide, slump, mass wasting, ...
... • Downward movement of rock and sediment down a slope due to the pull of gravity • The process is quite slow and almost impossible to see until the land mass is no longer able to support itself and falls or slides down a slope. • Examples: landslide, slump, mass wasting, ...
UNIT 5 PLANET EARTH
... Intrusive rock- rock formed very deep and slowly in Earth’s crust Lava- when magma breaks through Earth’s crust from an volcanic eruption Extrusive rock- rock formed when lava cools on Earth’s surface Sedimentary rock- formed from sediment (loose bits of rock, minerals, and plant and animal remains) ...
... Intrusive rock- rock formed very deep and slowly in Earth’s crust Lava- when magma breaks through Earth’s crust from an volcanic eruption Extrusive rock- rock formed when lava cools on Earth’s surface Sedimentary rock- formed from sediment (loose bits of rock, minerals, and plant and animal remains) ...
E.S. SOL Facts
... 42. Examples of clastic sedimentary rocks include conglomerate, breccia, sandstone and shale. 43. Limestone is formed either organically or chemically. 44. Virginia resources include limestone, coal, and gravel. 45. Renewable resources can be replaced by nature at a rate close to the rate at which ...
... 42. Examples of clastic sedimentary rocks include conglomerate, breccia, sandstone and shale. 43. Limestone is formed either organically or chemically. 44. Virginia resources include limestone, coal, and gravel. 45. Renewable resources can be replaced by nature at a rate close to the rate at which ...
Minerals and Rocks Notes
... Mineral Identification Mineral identification refers to the way to tell one mineral from another. The _______________ is the most obvious but one of the least reliable methods for identifying a mineral. ___________________ is a measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched. The _____________ hard ...
... Mineral Identification Mineral identification refers to the way to tell one mineral from another. The _______________ is the most obvious but one of the least reliable methods for identifying a mineral. ___________________ is a measure of how easily a mineral can be scratched. The _____________ hard ...
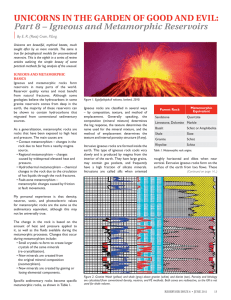
Igneous and Metamorphic Reservoirs
... the rock near the intrusion. Extrusives only heat the rock below them, and may not cause much alteration due to rapid cooling. Extrusives can be buried by later sedimentation, and are difficult to distinguish from intrusives, except by their chemical composition and grain size. The mineral compositi ...
... the rock near the intrusion. Extrusives only heat the rock below them, and may not cause much alteration due to rapid cooling. Extrusives can be buried by later sedimentation, and are difficult to distinguish from intrusives, except by their chemical composition and grain size. The mineral compositi ...
lesson 4 rock cycleplus - science
... Schist and mica are formed when mudstone is subjected to very high temperatures and pressure. Again, they contain layers, which is typical of many (but not all) metamorphic rocks. ...
... Schist and mica are formed when mudstone is subjected to very high temperatures and pressure. Again, they contain layers, which is typical of many (but not all) metamorphic rocks. ...
What cause a Valley to form?
... It moves rocks above ground where it is exposed to wind and rain. ...
... It moves rocks above ground where it is exposed to wind and rain. ...
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY
... distinguish the major classes of rocks and explain their origin understand the various processes of physical and chemical weathering and be able to recognize them in the field explain the different agents of erosion and recognize the landforms they leave on the earth’s surface write an essay on one ...
... distinguish the major classes of rocks and explain their origin understand the various processes of physical and chemical weathering and be able to recognize them in the field explain the different agents of erosion and recognize the landforms they leave on the earth’s surface write an essay on one ...
Rocks
... from magma that is a mixture of both mafic and felsic minerals, therefore its minerals have characteristics of both granites and basalts. 9. Porphyritic textures refer to igneous rocks that have VARIOUS sized minerals, like a chocolate chip cookie. This happens when the magma _______________________ ...
... from magma that is a mixture of both mafic and felsic minerals, therefore its minerals have characteristics of both granites and basalts. 9. Porphyritic textures refer to igneous rocks that have VARIOUS sized minerals, like a chocolate chip cookie. This happens when the magma _______________________ ...
Earth Science Quiz-1 Please answer the following multiple choice
... 35. As the rate of cooling increases, the size of the crystals that form ________. A) increases B) decreases C) is not affected D) none of these 36. Which one of the following is an igneous rock? A) limestone B) rhyolite C) slate D) shale 37. Intrusive rocks ________. A) are generally fine-grained ...
... 35. As the rate of cooling increases, the size of the crystals that form ________. A) increases B) decreases C) is not affected D) none of these 36. Which one of the following is an igneous rock? A) limestone B) rhyolite C) slate D) shale 37. Intrusive rocks ________. A) are generally fine-grained ...
Earth Science Quiz-1 Please answer the following multiple choice
... 35. As the rate of cooling increases, the size of the crystals that form ________. A) increases B) decreases C) is not affected D) none of these 36. Which one of the following is an igneous rock? A) limestone B) rhyolite C) slate D) shale 37. Intrusive rocks ________. A) are generally fine-grained ...
... 35. As the rate of cooling increases, the size of the crystals that form ________. A) increases B) decreases C) is not affected D) none of these 36. Which one of the following is an igneous rock? A) limestone B) rhyolite C) slate D) shale 37. Intrusive rocks ________. A) are generally fine-grained ...
Earth Science Quiz-1 –Main Campus Quiz
... 41. As the rate of cooling increases, the size of the crystals that form ________. A) increases B) decreases C) is not affected D) none of these 42. Which one of the following is an igneous rock? A) limestone B) rhyolite C) slate D) shale 43. Intrusive rocks ________. A) are generally fine-grained B ...
... 41. As the rate of cooling increases, the size of the crystals that form ________. A) increases B) decreases C) is not affected D) none of these 42. Which one of the following is an igneous rock? A) limestone B) rhyolite C) slate D) shale 43. Intrusive rocks ________. A) are generally fine-grained B ...
study guide part 2
... 1. What are the parts of animals most likely to be preserved? -Hard parts such as bones, shells, or teeth 2. What is the isotope scientist use to find out how old a fossil is ? -Carbon-14 or C-14 3. Law of Superposition states -the oldest rocks are at the bottom, and youngest rocks are near the surf ...
... 1. What are the parts of animals most likely to be preserved? -Hard parts such as bones, shells, or teeth 2. What is the isotope scientist use to find out how old a fossil is ? -Carbon-14 or C-14 3. Law of Superposition states -the oldest rocks are at the bottom, and youngest rocks are near the surf ...
Chemical Sedimentary Rocks
... formed from cemented sediment grains that are fragments of preexisting rocks. The rock fragments can be either identifiable pieces of rock, such as pebbles of granite or shale, or individual mineral grains, such as sand-sized quartz and feldspar crystals loosened from rocks by weathering and erosion ...
... formed from cemented sediment grains that are fragments of preexisting rocks. The rock fragments can be either identifiable pieces of rock, such as pebbles of granite or shale, or individual mineral grains, such as sand-sized quartz and feldspar crystals loosened from rocks by weathering and erosion ...
Name: 1 GEOL 104 Dinosaurs: A Natural History Geology
... Part I: Environments of Deposition Geologists can use various clues in sedimentary rocks to interpret their environment of deposition: that is, the type of conditions that were present when they were laid down. ...
... Part I: Environments of Deposition Geologists can use various clues in sedimentary rocks to interpret their environment of deposition: that is, the type of conditions that were present when they were laid down. ...
Planet Earth - Manasquan Public Schools
... -Minerals: are natural, inorganic solid compounds with a definite chemical composition and internal structure. 3500 known minerals in Earth’s crust Rocks and minerals classified by texture, hardness, color, and density. ...
... -Minerals: are natural, inorganic solid compounds with a definite chemical composition and internal structure. 3500 known minerals in Earth’s crust Rocks and minerals classified by texture, hardness, color, and density. ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.