argo and other tidal structures around the milky way
... sample was limited to −25◦ < b < +25◦ , in order to avoid the Magellanic Clouds. The solar position is X = −8 kpc, Y = 0 kpc. A number of known structures can be seen in these plots: The Monoceros stream, Sagittarius, the TriAnd and Perseus systems (Rocha-Pinto et al. 2004). The large southern hemis ...
... sample was limited to −25◦ < b < +25◦ , in order to avoid the Magellanic Clouds. The solar position is X = −8 kpc, Y = 0 kpc. A number of known structures can be seen in these plots: The Monoceros stream, Sagittarius, the TriAnd and Perseus systems (Rocha-Pinto et al. 2004). The large southern hemis ...
Surveying the Stars
... • What is the significance of the main sequence? — Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram. — A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high mass: luminous and blue; low mass: faint and red). ...
... • What is the significance of the main sequence? — Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram. — A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high mass: luminous and blue; low mass: faint and red). ...
Chapter 19 Stars Galaxies and the Universe
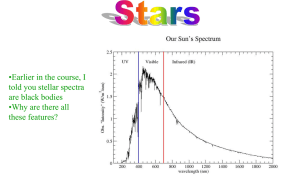
... make up a spectrum, including red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. Scientists use a machine called a spectrograph to break up a star’s light into a spectrum. Each element has a particular pattern of lines that appear in an emission spectrum. The emission spectrum shows scientists wh ...
... make up a spectrum, including red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. Scientists use a machine called a spectrograph to break up a star’s light into a spectrum. Each element has a particular pattern of lines that appear in an emission spectrum. The emission spectrum shows scientists wh ...
PHYS3380_110415_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... periodic table, except the more unstable ones. Type II Cepheids not as opaque as type I • energy escapes more easily • less luminous for same period of pulsation ...
... periodic table, except the more unstable ones. Type II Cepheids not as opaque as type I • energy escapes more easily • less luminous for same period of pulsation ...
1. setting the scene 2. the cosmic dark ages and the first stars
... Our knowledge of the process by which gas turns into stars is still sketchy. One thing we do know is that stars are not all of the same mass – when a cloud of gas cools and condenses to form a cluster of stars, some stars will be as heavy as our Sun, while others will be less massive and yet others ...
... Our knowledge of the process by which gas turns into stars is still sketchy. One thing we do know is that stars are not all of the same mass – when a cloud of gas cools and condenses to form a cluster of stars, some stars will be as heavy as our Sun, while others will be less massive and yet others ...
3D maps of the local interstellar medium: searching for the imprints
... 1998). Interestingly, their study shows that the GRB rate exhibits three peaks at ∼ -70, -180 and -340 Myrs, all three due to encounters with the massive cluster 47 Tuc. The most recent peak indeed corresponds to the time period of the well known KT extinction. The range of distances of closest appr ...
... 1998). Interestingly, their study shows that the GRB rate exhibits three peaks at ∼ -70, -180 and -340 Myrs, all three due to encounters with the massive cluster 47 Tuc. The most recent peak indeed corresponds to the time period of the well known KT extinction. The range of distances of closest appr ...
- MNASSA Page
... axy, but on the other hand it is not very can be seen lurking in the nebulosity. Star centrally placed. The inner core consists splinters dot the surface of this outstanding of stars that are very hot and large, their object like dewdrops on frosted glass. combined radiation being responsible for it ...
... axy, but on the other hand it is not very can be seen lurking in the nebulosity. Star centrally placed. The inner core consists splinters dot the surface of this outstanding of stars that are very hot and large, their object like dewdrops on frosted glass. combined radiation being responsible for it ...
The Interstellar Medium White Paper
... Hydrogen is the dominant constituent in gas clouds, found as H and H2 in the atomic and molecular clouds. However, while hydrogen can readily be detected through its 21cm HI line, this does not provide a ready distinction as to whether the emitting gas comes from the cold neutral or warm neutral pha ...
... Hydrogen is the dominant constituent in gas clouds, found as H and H2 in the atomic and molecular clouds. However, while hydrogen can readily be detected through its 21cm HI line, this does not provide a ready distinction as to whether the emitting gas comes from the cold neutral or warm neutral pha ...
Milky Way
... •The halo •At the center of our galaxy lies a complex region •Globular •Fast star formation clusters •Recent supernovae remnants •Hot gas •Fast motion •Density of stars is very high here •Intense radio sources can penetrate the gas and dust ...
... •The halo •At the center of our galaxy lies a complex region •Globular •Fast star formation clusters •Recent supernovae remnants •Hot gas •Fast motion •Density of stars is very high here •Intense radio sources can penetrate the gas and dust ...
WFIRST-2.4: What Every Astronomer Should Know
... reaches an AB-magnitude depth similar to what LSST achieves in each of its g, r, and i filters. The cumulative imaging depth in the WFIRST-2.4 supernova survey fields, which will be observed many times over a 2-year interval, reaches 0.5 – 2.5 magnitudes fainter than the HLS (see Table 1). Figure 3 ...
... reaches an AB-magnitude depth similar to what LSST achieves in each of its g, r, and i filters. The cumulative imaging depth in the WFIRST-2.4 supernova survey fields, which will be observed many times over a 2-year interval, reaches 0.5 – 2.5 magnitudes fainter than the HLS (see Table 1). Figure 3 ...
2_ISM - UCT Astronomy Department
... density of smoke would be such that objects would disappear in haze at distance of much less than 1m!!! ...
... density of smoke would be such that objects would disappear in haze at distance of much less than 1m!!! ...
AGN surveys to study galaxy evolution along cosmic times
... of galaxies. We also know that they are deeply connected, as shown by the so-called Magorrian relation (Magorrian et al. 1998). We want to know the full cosmic history of energy generation by stars (star formation) and AGNs (black hole accretion). These energy production rates correspond to built up ...
... of galaxies. We also know that they are deeply connected, as shown by the so-called Magorrian relation (Magorrian et al. 1998). We want to know the full cosmic history of energy generation by stars (star formation) and AGNs (black hole accretion). These energy production rates correspond to built up ...
PoS(EVN 2014)058 - Proceeding of science
... The aim of this project is to exploit the high-resolution capability and tremendous sensitivity of eMERLIN to assemble the most substantial radio dataset of an important massive stellar population within our Galaxy. COBRaS will produce extensive radio mapping of the OB rich stellar cluster at both C ...
... The aim of this project is to exploit the high-resolution capability and tremendous sensitivity of eMERLIN to assemble the most substantial radio dataset of an important massive stellar population within our Galaxy. COBRaS will produce extensive radio mapping of the OB rich stellar cluster at both C ...
Lecture1-1
... The actual measured data (left) and constructed models (model) are compared on the Dn(4000), HdA index plane. The solid lines in the left panels are tracks of burst star formation model and the points are “continuus” star formation model. ...
... The actual measured data (left) and constructed models (model) are compared on the Dn(4000), HdA index plane. The solid lines in the left panels are tracks of burst star formation model and the points are “continuus” star formation model. ...
First firm spectral classification of an early-B pre-main
... The optical to near-infrared (300−2500 nm) spectrum of the candidate massive young stellar object (YSO) B275, embedded in the star-forming region M 17, has been observed with X-shooter on the ESO Very Large Telescope. The spectrum includes both photospheric absorption lines and emission features (H ...
... The optical to near-infrared (300−2500 nm) spectrum of the candidate massive young stellar object (YSO) B275, embedded in the star-forming region M 17, has been observed with X-shooter on the ESO Very Large Telescope. The spectrum includes both photospheric absorption lines and emission features (H ...
Recipe for a Star
... of mostly helium, then another shell of mostly hydrogen (see figure 5.19). The helium fusion in the core continues until helium is all used up in making carbon. Most of the red giants’s mass remains concentrated in the dense carbon core. These red giants are not hot enough to start carbon fusion. Th ...
... of mostly helium, then another shell of mostly hydrogen (see figure 5.19). The helium fusion in the core continues until helium is all used up in making carbon. Most of the red giants’s mass remains concentrated in the dense carbon core. These red giants are not hot enough to start carbon fusion. Th ...
Physics- HSC- Module 9.7 Astrophysics
... The wonders of the Universe are revealed through technological advances based on tested principles of physics. Our understanding of the cosmos draws upon models, theories and laws in our endeavour to seek explanations for the myriad of observations made by various instruments at many different wavel ...
... The wonders of the Universe are revealed through technological advances based on tested principles of physics. Our understanding of the cosmos draws upon models, theories and laws in our endeavour to seek explanations for the myriad of observations made by various instruments at many different wavel ...
B LOG - Science Centre
... pulling a plough and three mourners standing beside a funeral pyre. The names of the stars come from Arabic phrases indicating the different meanings. The stars Merak, Phad, Megrez, Alioth, Mizar and Alcor are approximately the same distance from Earth (80 lightyears) moving together as a large star ...
... pulling a plough and three mourners standing beside a funeral pyre. The names of the stars come from Arabic phrases indicating the different meanings. The stars Merak, Phad, Megrez, Alioth, Mizar and Alcor are approximately the same distance from Earth (80 lightyears) moving together as a large star ...
Rotation in the ZAMS: Be and Bn stars
... Figure 3a shows the apparent V=7 magnitude limited counts of dwarf Be stars relative to dwarf B stars. There is an apparent lack of dwarf Be stars cooler than spectral type B7. This could be due to genuine Be stars whose discs are minute and/or too cool for the Hα emission be detectable and/or, to f ...
... Figure 3a shows the apparent V=7 magnitude limited counts of dwarf Be stars relative to dwarf B stars. There is an apparent lack of dwarf Be stars cooler than spectral type B7. This could be due to genuine Be stars whose discs are minute and/or too cool for the Hα emission be detectable and/or, to f ...
April 2015 - Southern Astronomical Society
... returned from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the ESA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has found dark matter does not slow down when it collides with itself. This is significant as it shows the ghostly substance interacts with itself less than previously thought, narrowing down the options of what this ...
... returned from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and the ESA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has found dark matter does not slow down when it collides with itself. This is significant as it shows the ghostly substance interacts with itself less than previously thought, narrowing down the options of what this ...
FROM MOLECULAR CLOUDS TO STARS 1 Star formation and the
... Region 1a) contains the first generation of stars, formed 12 Myr ago: the parental cloud is completely disrupted and the stars appear free from circumstellar material, but still grouped in a cluster that demonstrates their common origin. Region 1b) where star formation is going on since ~ 7 Myr: on ...
... Region 1a) contains the first generation of stars, formed 12 Myr ago: the parental cloud is completely disrupted and the stars appear free from circumstellar material, but still grouped in a cluster that demonstrates their common origin. Region 1b) where star formation is going on since ~ 7 Myr: on ...
Survey of Astrophysics A110 The Milky Way Galaxy
... Outside the bulge is the pancake-like (or pinwheel-like) structure called the Galactic disk. It is very thin (its thickness is 2% of its diameter) and it exhibits concentrations of stars in a spiral pattern. The disk contains interstellar gas and dust, and young stars (Population I), with the younge ...
... Outside the bulge is the pancake-like (or pinwheel-like) structure called the Galactic disk. It is very thin (its thickness is 2% of its diameter) and it exhibits concentrations of stars in a spiral pattern. The disk contains interstellar gas and dust, and young stars (Population I), with the younge ...
Part2
... important differences, but this is a good place to start): an exponential decline with a scale length ~0.2 to 0.25 times the optical radius. o The exponential decline is a mix of filling factor (e.g., arms vs empty space) and decline in the peak integrated intensity (arms get fainter). o The local s ...
... important differences, but this is a good place to start): an exponential decline with a scale length ~0.2 to 0.25 times the optical radius. o The exponential decline is a mix of filling factor (e.g., arms vs empty space) and decline in the peak integrated intensity (arms get fainter). o The local s ...
AMNH_colloquium_2May07_v7b
... O star X-ray emission line profiles are broadened, shifted, and asymmetric as the wind-shock scenario predicts But the degree of asymmetry requires significantly lower wind optical depths than are expected in these stars Clumping and the associated porosity can, in principle, alleviate this problem, ...
... O star X-ray emission line profiles are broadened, shifted, and asymmetric as the wind-shock scenario predicts But the degree of asymmetry requires significantly lower wind optical depths than are expected in these stars Clumping and the associated porosity can, in principle, alleviate this problem, ...
Pattern recognition of star constellations for spacecraft
... A: The Angular Distance to First Neighboring Star; B: The Angular Distance to Second Neighboring Star; C: The Angle between the 1. and 2. Neighboring Stars neighboring star- star- second neighboring star). As presumed the dispersion of angles between two neighboring stars is nearly uncorrelated as F ...
... A: The Angular Distance to First Neighboring Star; B: The Angular Distance to Second Neighboring Star; C: The Angle between the 1. and 2. Neighboring Stars neighboring star- star- second neighboring star). As presumed the dispersion of angles between two neighboring stars is nearly uncorrelated as F ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.