Slide 1
... details of core collision outcomes. Accretion (low-mass end) introduces variability. If a large number of variables determines the stellar mass and enter multiplicatively, by fragmentation (Larson 1973, Elmegreen & Mathieu 1983, Zinnecker 1984) or accretion rate (Adams & Fatuzzo 1996), 5-30 collisio ...
... details of core collision outcomes. Accretion (low-mass end) introduces variability. If a large number of variables determines the stellar mass and enter multiplicatively, by fragmentation (Larson 1973, Elmegreen & Mathieu 1983, Zinnecker 1984) or accretion rate (Adams & Fatuzzo 1996), 5-30 collisio ...
PC3692: Physics of Stellar Structure (and Evolution)
... Fig. 7.— HR diagram for 41453 nearby stars with accurate distance measured by the Hipparcos satellite. The horizontal axis is the V − I colour index, while the vertical axis is the absolute magnitude in the Hipparcos passband. The I-band is a filter centred around 8000Å. One striking feature is the ...
... Fig. 7.— HR diagram for 41453 nearby stars with accurate distance measured by the Hipparcos satellite. The horizontal axis is the V − I colour index, while the vertical axis is the absolute magnitude in the Hipparcos passband. The I-band is a filter centred around 8000Å. One striking feature is the ...
Stellarium01 Starter Part A B Doc - ASTR101
... What constellation is at the Zenith at “Current Time” tonight? ___________________ How many constellations are in the sky at “Current Time” tonight? (count them!) _________ Open the Search window (CTRL-F or F3, or FN-F3 in some) to help you find the following ...
... What constellation is at the Zenith at “Current Time” tonight? ___________________ How many constellations are in the sky at “Current Time” tonight? (count them!) _________ Open the Search window (CTRL-F or F3, or FN-F3 in some) to help you find the following ...
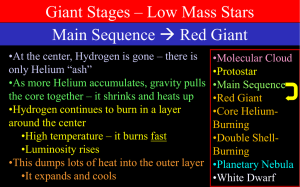
Giant Stars
... •At 100 million K, three Heliums can join to make carbon plus a little energy 3He C + Energy •With a little higher temperature, they can add one more to make oxygen C + He O + Energy •These processes produce far less energy than hydrogen burning ...
... •At 100 million K, three Heliums can join to make carbon plus a little energy 3He C + Energy •With a little higher temperature, they can add one more to make oxygen C + He O + Energy •These processes produce far less energy than hydrogen burning ...
The Cosmic Perspective Star Stuff
... The binary star Algol has a 3.7 solar mass main sequence star and a 0.8 solar mass red giant. How could that be? a) In this system, the lower mass star must have evolved faster than the higher mass one. b) The red giant might be made of some different elements, so it evolved faster. c) The lower ...
... The binary star Algol has a 3.7 solar mass main sequence star and a 0.8 solar mass red giant. How could that be? a) In this system, the lower mass star must have evolved faster than the higher mass one. b) The red giant might be made of some different elements, so it evolved faster. c) The lower ...
Document
... Are the dots outside the band 0s ? Certainly they aren’t 0s with pt between 5 and 6GeV/c but they are 0 candidates for other pt bins. Is the asymmetry cut efficient here? It is obvious NO. ...
... Are the dots outside the band 0s ? Certainly they aren’t 0s with pt between 5 and 6GeV/c but they are 0 candidates for other pt bins. Is the asymmetry cut efficient here? It is obvious NO. ...
Image Analysis of Planetary Nebula NGC 6543 South Carolina State University
... tipped at various angles creating a display with two-sided symmetry. Beside the discovery of a glowing bubble of hot gas, scientists noticed an unexpected X-ray bright central star, which is an O-type star, within the structure of the planetary nebula. NGC 6543 is 8th magnitude and located almost ex ...
... tipped at various angles creating a display with two-sided symmetry. Beside the discovery of a glowing bubble of hot gas, scientists noticed an unexpected X-ray bright central star, which is an O-type star, within the structure of the planetary nebula. NGC 6543 is 8th magnitude and located almost ex ...
Lecture notes 18: Galaxies and galaxy clusters
... Figure 5: Galaxy Cluster CL0024+1654 serving as a gravitational lens. The Hubble Space Telescope has captured a striking image of the galaxy cluster which lies some 1.5 Gpc away in the constellation Pisces. The oblong, blue objects on the outskirts of the cluster are all in fact a mirage of the same ...
... Figure 5: Galaxy Cluster CL0024+1654 serving as a gravitational lens. The Hubble Space Telescope has captured a striking image of the galaxy cluster which lies some 1.5 Gpc away in the constellation Pisces. The oblong, blue objects on the outskirts of the cluster are all in fact a mirage of the same ...
HR DIAGRAM (Page 1) - McDonald Observatory
... Looking up into the night sky, you see thousands of stars at varying distances from Earth. The luminosity and temperature of each star varies as well. These are the reasons behind the wide range of apparent magnitudes of stars. Imagine being able to magically pull or push each star (including the su ...
... Looking up into the night sky, you see thousands of stars at varying distances from Earth. The luminosity and temperature of each star varies as well. These are the reasons behind the wide range of apparent magnitudes of stars. Imagine being able to magically pull or push each star (including the su ...
Formation of z~6 Quasars from Hierarchical Galaxy Mergers
... For the purpose of this paper, the simulations used WMAP1 values because WMAP3 predicts lower halo masses and longer formation time. Although they do compare results using WMAP3. ...
... For the purpose of this paper, the simulations used WMAP1 values because WMAP3 predicts lower halo masses and longer formation time. Although they do compare results using WMAP3. ...
Abstract - UChicago High Energy Physics
... Neutrinos shape the physical phenomena surrounding compact object mergers, from the dynamics of the disk or hypermassive-neutron star itself [1–4], to the energetic jets, e.g. [5] that may from them. Neutrinos also play an important role in the nucleosynthesis that takes place in and around disks [6 ...
... Neutrinos shape the physical phenomena surrounding compact object mergers, from the dynamics of the disk or hypermassive-neutron star itself [1–4], to the energetic jets, e.g. [5] that may from them. Neutrinos also play an important role in the nucleosynthesis that takes place in and around disks [6 ...
Constellation
... harvest in the fall. But in some regions, there is not much difference between the seasons. Since different constellations are visible at different times of the year, you can use them to tell what month it is. For example, Scorpius is only visible in the northern hemisphere's evening sky in the summ ...
... harvest in the fall. But in some regions, there is not much difference between the seasons. Since different constellations are visible at different times of the year, you can use them to tell what month it is. For example, Scorpius is only visible in the northern hemisphere's evening sky in the summ ...
27B Star Life Cycle and the HR Diagram
... d. Which stars on your graph are located in the area associated with white dwarf stars? ...
... d. Which stars on your graph are located in the area associated with white dwarf stars? ...
Neistein_dekel60
... The history of one galaxy We follow all the particles, and check which got heated/cooled/SF/accreted ...
... The history of one galaxy We follow all the particles, and check which got heated/cooled/SF/accreted ...
J: Chapter 4: Stars and Galaxies
... How do scientists determine distance to stars from the solar system that Earth is part of? One way is to measure its parallax—the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. Extend your arm and look at your thumb first with your left eye closed and then with ...
... How do scientists determine distance to stars from the solar system that Earth is part of? One way is to measure its parallax—the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. Extend your arm and look at your thumb first with your left eye closed and then with ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Massive stars use fuel faster and exist for only a few million years • Small stars use fuel slowly and exist for perhaps hundreds of billions of years • 90 percent of a star’s life is in the main-sequence ...
... • Massive stars use fuel faster and exist for only a few million years • Small stars use fuel slowly and exist for perhaps hundreds of billions of years • 90 percent of a star’s life is in the main-sequence ...
The masses of stars
... neutron stars, about 1.4 million km for our Sun, and up the largest known star at just under two billion km); of mass (from about a tenth the mass of our Sun to around 100 times greater); of age (some still being formed, while others are perhaps eleven billion years old); of chemical composition (so ...
... neutron stars, about 1.4 million km for our Sun, and up the largest known star at just under two billion km); of mass (from about a tenth the mass of our Sun to around 100 times greater); of age (some still being formed, while others are perhaps eleven billion years old); of chemical composition (so ...
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter:
... • Hot, X-ray emitting gas is observed to be insufficient • Warm, 104 K ionized gas emits by bremstrahlung. If in hydrostatic equilibrium, central regions would be dense enough to be easily observed. • Molecular gas must be H2; large quantities would be ionized and observed near the galactic plane; i ...
... • Hot, X-ray emitting gas is observed to be insufficient • Warm, 104 K ionized gas emits by bremstrahlung. If in hydrostatic equilibrium, central regions would be dense enough to be easily observed. • Molecular gas must be H2; large quantities would be ionized and observed near the galactic plane; i ...
Interpolation of Magnitude.
... Variable and comparison stars Look at the example below. The variable is shown between the four focus lines. The magnitudes of the comparison (“comp”) stars are shown on the chart next to the stars (64,51,91, etc.). ...
... Variable and comparison stars Look at the example below. The variable is shown between the four focus lines. The magnitudes of the comparison (“comp”) stars are shown on the chart next to the stars (64,51,91, etc.). ...
PDF
... today. His “tuning fork” diagram (figure 1) differentiates ellipticals from unbarred and barred spirals, further classified according to the tightness and fine structure of their spiral arms which appears to correlate with the fraction of light present in the central bulge. Intermediate to the spira ...
... today. His “tuning fork” diagram (figure 1) differentiates ellipticals from unbarred and barred spirals, further classified according to the tightness and fine structure of their spiral arms which appears to correlate with the fraction of light present in the central bulge. Intermediate to the spira ...
Canis Majoris
... Canis Majoris is the largest star that has so far been discovered. When viewed from earth it’s very tiny, which means it has a very small apparent magnitude. Canis Majoris is so large that you could fit about seven quadrillion earths inside of it. To put this into perspective, if earth were the size ...
... Canis Majoris is the largest star that has so far been discovered. When viewed from earth it’s very tiny, which means it has a very small apparent magnitude. Canis Majoris is so large that you could fit about seven quadrillion earths inside of it. To put this into perspective, if earth were the size ...
What To See Telescope(Jul-Sept) v1 - One
... The guide assumes you are at least somewhat familiar with the set-up and operation of your telescope. If your telescope has a larger aperture than 4 inches, then you will see more detail in most objects. Sights that benefit from larger-aperture telescopes, and descriptions of what you will see with ...
... The guide assumes you are at least somewhat familiar with the set-up and operation of your telescope. If your telescope has a larger aperture than 4 inches, then you will see more detail in most objects. Sights that benefit from larger-aperture telescopes, and descriptions of what you will see with ...
Estimating the mass and star formation rate in galaxies
... total quantity of dust between the observed and the emitting source. Since dust is formed during the late stages of stellar evolution regions such as nuclei of galaxies, where many generations of stars are actively forming or have formed, evolved and “died” are often enshrouded by ...
... total quantity of dust between the observed and the emitting source. Since dust is formed during the late stages of stellar evolution regions such as nuclei of galaxies, where many generations of stars are actively forming or have formed, evolved and “died” are often enshrouded by ...
Star Birth - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... The Variable Star Phase Horizontal Branch Stars (Helium Burning Star) • After helium core burning begins, a stars core returns to an ideal gas and its surface becomes hotter and smaller - settling into moving across the H-R diagram with roughly a constant luminosity passing into a yellow giant stage ...
... The Variable Star Phase Horizontal Branch Stars (Helium Burning Star) • After helium core burning begins, a stars core returns to an ideal gas and its surface becomes hotter and smaller - settling into moving across the H-R diagram with roughly a constant luminosity passing into a yellow giant stage ...
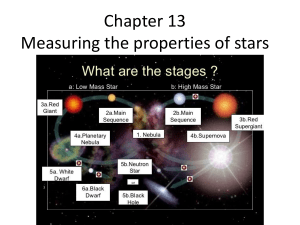
Chapter 13 Measuring the properties of stars
... The amount of energy emitted by a star each second is the ____ and is measured in ____. A. Apparent brightness; degrees K B. Temperature; degrees K C. Apparent brightness; Watts D. Luminosity; Watts ...
... The amount of energy emitted by a star each second is the ____ and is measured in ____. A. Apparent brightness; degrees K B. Temperature; degrees K C. Apparent brightness; Watts D. Luminosity; Watts ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.