Encyclopedia of Optical Engineering Stellar Evolution
... that these stars are blown apart from within. 3. Mass distribution—The cluster of stars that is formed contains many more low-mass stars than intermediate mass ones. Likewise, there are more intermediate mass objects than high-mass stars. As stellar mass increases, the number of stars per that mass ...
... that these stars are blown apart from within. 3. Mass distribution—The cluster of stars that is formed contains many more low-mass stars than intermediate mass ones. Likewise, there are more intermediate mass objects than high-mass stars. As stellar mass increases, the number of stars per that mass ...
NGC 1808 - Rencontres de Moriond
... by the active source: + The contribution to soft X-rays might be non-negligible, but is is any case below 30%. + The contribution to hard X-rays is negligible. + The SSC could produce only around 1/50 of the ionizing photons producing the observed emission line spectrum, and no more than 1/10 of the ...
... by the active source: + The contribution to soft X-rays might be non-negligible, but is is any case below 30%. + The contribution to hard X-rays is negligible. + The SSC could produce only around 1/50 of the ionizing photons producing the observed emission line spectrum, and no more than 1/10 of the ...
LET THE STARS GET IN YOUR EYES SKY MOTIONS
... Astronomy, like anything, takes practice. To learn your way around the sky, it is best to get as far away from lights as possible and to observe when the Moon is not present in the sky. Lights and the Moon vastly diminish how much you are able to see. It takes your eyes about 20 to 30 minutes to ful ...
... Astronomy, like anything, takes practice. To learn your way around the sky, it is best to get as far away from lights as possible and to observe when the Moon is not present in the sky. Lights and the Moon vastly diminish how much you are able to see. It takes your eyes about 20 to 30 minutes to ful ...
objects in telescope are farther than they appear
... be detected, such sky conditions and the sensitivity of the human eye.10 This detection limit means that the apparent star diameters Galileo sees will be smaller than twice the Airy Disk radius (Figure 2). What's more, dimmer stars will appear to have smaller diameters than brighter stars (Figure 3) ...
... be detected, such sky conditions and the sensitivity of the human eye.10 This detection limit means that the apparent star diameters Galileo sees will be smaller than twice the Airy Disk radius (Figure 2). What's more, dimmer stars will appear to have smaller diameters than brighter stars (Figure 3) ...
PPS
... discovery that light can be split into its component colours in this way. The spectrum can then be photographed and studied in detail. The positions and strengths of the lines in the spectrum can also be determined electronically, using suitable detectors attached directly to the telescopes or desig ...
... discovery that light can be split into its component colours in this way. The spectrum can then be photographed and studied in detail. The positions and strengths of the lines in the spectrum can also be determined electronically, using suitable detectors attached directly to the telescopes or desig ...
The Bigger Picture
... `astrometrists’ are trying to measure a tiny motion of the centroid as it moves back and forth every six months. The lack of parallax apparent to the unaided eye was used as a proof that the Earth did not revolve around the Sun. ...
... `astrometrists’ are trying to measure a tiny motion of the centroid as it moves back and forth every six months. The lack of parallax apparent to the unaided eye was used as a proof that the Earth did not revolve around the Sun. ...
Evolution of a Planetary System
... 1. Data. Have a student or teams of students use a calculator to average the results from the various groups. Ask the students for the conclusions that they can draw from this experiment. Go over the questions on the data sheet. The students will find that the A-type star is hottest (gives off the m ...
... 1. Data. Have a student or teams of students use a calculator to average the results from the various groups. Ask the students for the conclusions that they can draw from this experiment. Go over the questions on the data sheet. The students will find that the A-type star is hottest (gives off the m ...
The 2008 RBSE Journal - National Optical Astronomy Observatory
... A Double Radio Source Associated with a Galactic Nucleus (DRAGN) is a radio source that is produced by jets produced by active galactic nucleus that is not in the Milky Way. This happens when an accretion disk forms around a black hole and spins, converts gravitational and rotational energy into exc ...
... A Double Radio Source Associated with a Galactic Nucleus (DRAGN) is a radio source that is produced by jets produced by active galactic nucleus that is not in the Milky Way. This happens when an accretion disk forms around a black hole and spins, converts gravitational and rotational energy into exc ...
JWST_eye - University of Arizona
... and Rigel in Orion have much different colors. The color of Betelgeuse is ________. The color of Rigel is ________. The color of stars in the Pleiades is ______. JWST is designed to sense “infrared” colors of light about 3-30 times redder than the limit of the human eye. Infrared light penetrates in ...
... and Rigel in Orion have much different colors. The color of Betelgeuse is ________. The color of Rigel is ________. The color of stars in the Pleiades is ______. JWST is designed to sense “infrared” colors of light about 3-30 times redder than the limit of the human eye. Infrared light penetrates in ...
Geoscience Astronomy Formative on Stellar Evolution and
... 25. Which of the following indicates that the universe is expanding? a. red shift of distant galaxies b. red shift of the galaxies in the Local Group c. blue shift of distant galaxies d. blue shift of the Milky Way 26. According to the big bang theory, the universe began about ____. a. 4.5 billion y ...
... 25. Which of the following indicates that the universe is expanding? a. red shift of distant galaxies b. red shift of the galaxies in the Local Group c. blue shift of distant galaxies d. blue shift of the Milky Way 26. According to the big bang theory, the universe began about ____. a. 4.5 billion y ...
Chapter 25 - Haiku Learning
... stars orbit each other. These pairs of stars, pulled toward each other by gravity, are called binary stars. More than 50 percent of the stars in the universe may occur in pairs or multiples. Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate—its mass. The mass of a body ...
... stars orbit each other. These pairs of stars, pulled toward each other by gravity, are called binary stars. More than 50 percent of the stars in the universe may occur in pairs or multiples. Binary stars are used to determine the star property most difficult to calculate—its mass. The mass of a body ...
Is the central binary system of the planetary nebula Henize 2
... line belonging to the primary star, and a narrow emission line coming from the compact dense nebula reported by Rodríguez et al. (2001), or which originates even much closer to the star from the wind itself. In this alternative explanation both emission and absorption lines change with orbital phase ...
... line belonging to the primary star, and a narrow emission line coming from the compact dense nebula reported by Rodríguez et al. (2001), or which originates even much closer to the star from the wind itself. In this alternative explanation both emission and absorption lines change with orbital phase ...
EF Eri: Its White Dwarf Primary and L Dwarf Secondary
... --> Polar or AM Herculis type. These contain no accretion disk. ...
... --> Polar or AM Herculis type. These contain no accretion disk. ...
OUR COSMIC NEIGHBORS Story of the Stars
... to stone anyone who looked upon her. Perseus cut off her head and from the blood which dripped into the sea a white winged horse was born. After mounting the horse, which became known as Pegasus, Perseus was flying home when he came upon the predicament of the fair Andromeda and hastened to rescue h ...
... to stone anyone who looked upon her. Perseus cut off her head and from the blood which dripped into the sea a white winged horse was born. After mounting the horse, which became known as Pegasus, Perseus was flying home when he came upon the predicament of the fair Andromeda and hastened to rescue h ...
MHD_of_Accretion_Disks
... Observing the formation and evolution of circumstellar disks is crucial for understanding the star formation and planet-building processes. If a disk becomes sufficiently massive, compared to the central object that it surrounds, a gravitational instability in the system may cause the disk to accumu ...
... Observing the formation and evolution of circumstellar disks is crucial for understanding the star formation and planet-building processes. If a disk becomes sufficiently massive, compared to the central object that it surrounds, a gravitational instability in the system may cause the disk to accumu ...
Introduction
... changes in the years. In Peimbert & Torres-Peimbert (1987) PNe of Type I are re-defined as nebulae with He/H>0.125 or log(N/O) > −0.3. PNe are also divided according to their carbon over oxygen (C/O) ratio. If C/O> 1 the nebula is carbon-rich and if it is < 1, oxygenrich. ...
... changes in the years. In Peimbert & Torres-Peimbert (1987) PNe of Type I are re-defined as nebulae with He/H>0.125 or log(N/O) > −0.3. PNe are also divided according to their carbon over oxygen (C/O) ratio. If C/O> 1 the nebula is carbon-rich and if it is < 1, oxygenrich. ...
poster
... The emission from young stellar objects (YSOs) in the mid-IR is dominated by the inner rim of their circumstellar disks. We present an IR-monitoring survey in the direction of the Lynds 1688 (L1688) star forming region over four visibility windows spanning 1.6 years using the Spitzer space telescope ...
... The emission from young stellar objects (YSOs) in the mid-IR is dominated by the inner rim of their circumstellar disks. We present an IR-monitoring survey in the direction of the Lynds 1688 (L1688) star forming region over four visibility windows spanning 1.6 years using the Spitzer space telescope ...
Challenging our Understanding of Stellar Structure and Evolution
... What is the biggest star? What is the smallest star? How is the mass of a stellar nursery partitioned into various types of stars? and, What is the mass content of the Galaxy and how does it evolve? To answer these and other fundamental questions requires masses to 1% accuracy. Why 1%? Our knowledge ...
... What is the biggest star? What is the smallest star? How is the mass of a stellar nursery partitioned into various types of stars? and, What is the mass content of the Galaxy and how does it evolve? To answer these and other fundamental questions requires masses to 1% accuracy. Why 1%? Our knowledge ...
Plotting Variable Stars on the H
... strip on the H-R diagram as massive stars transition from the main sequence to the giant and supergiant branches. Polaris (α Ursae Minoris) is currently the star nearest to the north celestial pole and referred to as the North Star or Pole Star. Polaris is a multiple star system, consisting of Polar ...
... strip on the H-R diagram as massive stars transition from the main sequence to the giant and supergiant branches. Polaris (α Ursae Minoris) is currently the star nearest to the north celestial pole and referred to as the North Star or Pole Star. Polaris is a multiple star system, consisting of Polar ...
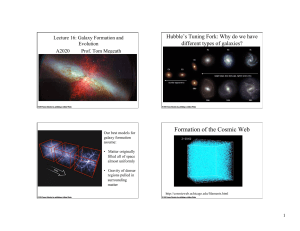
Lecture 16
... – Our best models for galaxy formation assume that gravity made galaxies out of regions of the early universe that were slightly denser than their surroundings. The gas collapsed to form galaxies. Galaxies continue to cannibalize smaller galaxies and draw in gas as the evolve. What determines the m ...
... – Our best models for galaxy formation assume that gravity made galaxies out of regions of the early universe that were slightly denser than their surroundings. The gas collapsed to form galaxies. Galaxies continue to cannibalize smaller galaxies and draw in gas as the evolve. What determines the m ...
Stars - gilbertmath.com
... every colour white many different many same all oragne and yellow colour depends on distance from our eye ...
... every colour white many different many same all oragne and yellow colour depends on distance from our eye ...
Magnitude. . . ?
... Among several “obtrusive medieval features” in astronomy there is one, which is simple to solve, but difficult to obey the chosen solution. I mean the ridiculous way of indicating, how bright the stars are. For two thousand years the stars had been just sorted into several classes. Only recently, in ...
... Among several “obtrusive medieval features” in astronomy there is one, which is simple to solve, but difficult to obey the chosen solution. I mean the ridiculous way of indicating, how bright the stars are. For two thousand years the stars had been just sorted into several classes. Only recently, in ...
Lecture 3
... • Imagine a star with a relatively cool (4000k) atmosphere. Temperature is just a measure of the average velocity of the atoms and molecules in a gas. For a relatively cool gas there are: (1) Few atomic collisions with enough energy to knock electrons up to the 1st excited state so the majority of t ...
... • Imagine a star with a relatively cool (4000k) atmosphere. Temperature is just a measure of the average velocity of the atoms and molecules in a gas. For a relatively cool gas there are: (1) Few atomic collisions with enough energy to knock electrons up to the 1st excited state so the majority of t ...
October 2012 - astronomy for beginners
... the Moon will be disappearing over the western horizon. Orion rises over the eastern horizon at about 10 o’clock. Hopefully if there is a clear sky and with no Moon the prospect for seeing some meteors from the shower is looking quite promising. It will be better fun to watch for meteors with a frie ...
... the Moon will be disappearing over the western horizon. Orion rises over the eastern horizon at about 10 o’clock. Hopefully if there is a clear sky and with no Moon the prospect for seeing some meteors from the shower is looking quite promising. It will be better fun to watch for meteors with a frie ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.