Stars - cayugascience
... explosion is directed not only outward, but also inward. This force causes the atoms in the star’s core to compress and collapse. When an atom collapses, it forms neutrons, particles that are at the centre of most atoms already. When the star’s core becomes little more than a ball of neutrons only a ...
... explosion is directed not only outward, but also inward. This force causes the atoms in the star’s core to compress and collapse. When an atom collapses, it forms neutrons, particles that are at the centre of most atoms already. When the star’s core becomes little more than a ball of neutrons only a ...
Lectures 19-20 The Milky Way Galaxy
... The Morphology of the Galaxy Structure of Thin and Thick Disks Galactic Disk has two major components, the thin disk, and the thick disk. Thin disk: composed of young stars, dust, and gas, with Hnthin = 350 pc (youngest stars found with scale height of 35-90 pc). Thick disk: older stars with a scal ...
... The Morphology of the Galaxy Structure of Thin and Thick Disks Galactic Disk has two major components, the thin disk, and the thick disk. Thin disk: composed of young stars, dust, and gas, with Hnthin = 350 pc (youngest stars found with scale height of 35-90 pc). Thick disk: older stars with a scal ...
Slide 1
... massive objects settle onto the main sequence, where they burned hydrogen into helium. After burning helium into carbon, stars run out of fuel and collapse into white dwarf stars, producing beautiful planetary nebulae in the process. ...
... massive objects settle onto the main sequence, where they burned hydrogen into helium. After burning helium into carbon, stars run out of fuel and collapse into white dwarf stars, producing beautiful planetary nebulae in the process. ...
Chap 16: Galaxies
... Starburst galaxies contain many young stars and recent supernovae, and are often very rich in gas and dust; bright in infrared: ultraluminous infrared galaxies ...
... Starburst galaxies contain many young stars and recent supernovae, and are often very rich in gas and dust; bright in infrared: ultraluminous infrared galaxies ...
THE HERTZSPRUNG-RUSSELL DIAGRAM
... HB starts out as a short stub just to the left of the RGB and gradually extends outwards, until in the cluster with lowest heavy element content (1% of the Sun’s, or 0.02% by mass) most of the HB stars are blue. (These diagrams are in terms of apparent magnitude, so the difference in the y-axis scal ...
... HB starts out as a short stub just to the left of the RGB and gradually extends outwards, until in the cluster with lowest heavy element content (1% of the Sun’s, or 0.02% by mass) most of the HB stars are blue. (These diagrams are in terms of apparent magnitude, so the difference in the y-axis scal ...
12 Introduction to Cepheid Variable Stars Exercise
... periods of 25 cepheid variables in the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. Miss Leavitt noted that when the cepheids were ordered by increasing period that the variable stars were also ordered by increasing brightness. Because both the Small Magellanic Cloud and the Large Magellanic Cloud are each a ...
... periods of 25 cepheid variables in the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds. Miss Leavitt noted that when the cepheids were ordered by increasing period that the variable stars were also ordered by increasing brightness. Because both the Small Magellanic Cloud and the Large Magellanic Cloud are each a ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1
... Polaris is almost exactly above the pole of Earth’s rotational axis, so Polaris moves only slightly around the pole during one rotation of Earth. ...
... Polaris is almost exactly above the pole of Earth’s rotational axis, so Polaris moves only slightly around the pole during one rotation of Earth. ...
Astronomy 160: Frontiers and Controversies in Astrophysics
... If the definition of the numerator on the right hand side of that equation changes, the denominator must also change by the same amount (to keep the parallax angle on the left hand side of the equation the same). A larger unit means that the numerical value measured is smaller (for example, 24 inche ...
... If the definition of the numerator on the right hand side of that equation changes, the denominator must also change by the same amount (to keep the parallax angle on the left hand side of the equation the same). A larger unit means that the numerical value measured is smaller (for example, 24 inche ...
Galaxies
... b. the barred spiral galaxies. c. the dwarf elliptical galaxies. d. the irregular galaxies. e. the giant elliptical galaxies. We should expect galaxies to collide fairly often because a. they are large with respect to their separation distances. b. galaxies contain large amounts of neutral hydrogen. ...
... b. the barred spiral galaxies. c. the dwarf elliptical galaxies. d. the irregular galaxies. e. the giant elliptical galaxies. We should expect galaxies to collide fairly often because a. they are large with respect to their separation distances. b. galaxies contain large amounts of neutral hydrogen. ...
Name: Astronomy Lab: The Hertzsprung-Russell (H
... Sometimes the student of astronomy starts to become overwhelmed trying to understand the many measurements and observations astronomers make. Data concerning distance, brightness, color, spectral class, mass, temperature, motion, etc. all seem to be gathered in an attempt to impress the student with ...
... Sometimes the student of astronomy starts to become overwhelmed trying to understand the many measurements and observations astronomers make. Data concerning distance, brightness, color, spectral class, mass, temperature, motion, etc. all seem to be gathered in an attempt to impress the student with ...
key for the HR Diagram Lab Handout
... quickly since their high temperatures will burn through the fusion fuel elements more quickly than the colder red stars. Blue stars will live approximately 100,000 years, while red stars can live up to 1,000,000,000,000 years. 3.) Explain how we know that there are red giants and supergiants on the ...
... quickly since their high temperatures will burn through the fusion fuel elements more quickly than the colder red stars. Blue stars will live approximately 100,000 years, while red stars can live up to 1,000,000,000,000 years. 3.) Explain how we know that there are red giants and supergiants on the ...
PDF format
... d) It depends on the standard candle: if they are Cepheid variables, they will still pulsate at the same rate no matter what distance they are from you. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... d) It depends on the standard candle: if they are Cepheid variables, they will still pulsate at the same rate no matter what distance they are from you. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
129 DYNAMICAL STREAMS IN THE SOLAR NEIGHBOURHOOD B
... Eggen’s hypothesis that they are cluster remnants with the results of a kinematic analysis of more than 6000 K and M giants in the solar neighbourhood. This analysis includes new radial velocity data from a large survey performed with the CORAVEL spectrometer, complemented by Hipparcos parallaxes an ...
... Eggen’s hypothesis that they are cluster remnants with the results of a kinematic analysis of more than 6000 K and M giants in the solar neighbourhood. This analysis includes new radial velocity data from a large survey performed with the CORAVEL spectrometer, complemented by Hipparcos parallaxes an ...
Notes
... Hydrogen layer thins further from mass loss and He burning shell Star evolves at constant luminosity (~104LSun), shrinking and heating up, until nuclear burning ceases Masses between 0.55 and 1+ solar masses (more massive are brighter) Outflowing winds seen in “P Cygni” profiles Hydrogen abundance l ...
... Hydrogen layer thins further from mass loss and He burning shell Star evolves at constant luminosity (~104LSun), shrinking and heating up, until nuclear burning ceases Masses between 0.55 and 1+ solar masses (more massive are brighter) Outflowing winds seen in “P Cygni” profiles Hydrogen abundance l ...
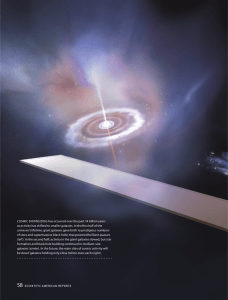
has occurred over the past 14 billion years COSMIC DOWNSIZING
... Madison and also holds an affiliate graduate faculty appointment at the University of Hawaii at Manoa. Barger earned her Ph.D. in astronomy in 1997 at the University of Cambridge, then did postdoctoral research at the University of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy. An observational cosmologist, she ha ...
... Madison and also holds an affiliate graduate faculty appointment at the University of Hawaii at Manoa. Barger earned her Ph.D. in astronomy in 1997 at the University of Cambridge, then did postdoctoral research at the University of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy. An observational cosmologist, she ha ...
HIGH RESOLTION SPH SIMULATIONS OF GALAXY CLUSTERS
... Spatial smoothing= 0.5 kpc Different feedback params. ...
... Spatial smoothing= 0.5 kpc Different feedback params. ...
The Life Cycle of A Star
... dwarfs are stable because the inward pull of gravity is balanced by the electrons in the core of the star repulsing each other. With no fuel left to burn, the hot star radiates its remaining heat into the coldness of space for many billions of years. In the end, it will just sit in space as a cold d ...
... dwarfs are stable because the inward pull of gravity is balanced by the electrons in the core of the star repulsing each other. With no fuel left to burn, the hot star radiates its remaining heat into the coldness of space for many billions of years. In the end, it will just sit in space as a cold d ...
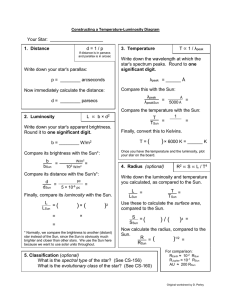
Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
Astron 104 Laboratory #9 Cepheid Variable Stars
... • The apparent magnitude of the star, which is a measure of how much light we receive on Earth (i.e., how bright do we measure the star to be). • The absolute magnitude of the star, which is a measure of how much light it is actually radiating into space (i.e, how bright it actually is). • The star’ ...
... • The apparent magnitude of the star, which is a measure of how much light we receive on Earth (i.e., how bright do we measure the star to be). • The absolute magnitude of the star, which is a measure of how much light it is actually radiating into space (i.e, how bright it actually is). • The star’ ...
First Light Sources at the End of the Dark Ages: Direct
... begun. Thus, near-infrared observations of these dwarfs could reveal strong Lyman ! and He II emission detectable by large ground-based telescopes, and possibly a rest-frame ultraviolet continuum observable from the ground and/or with the JWST. By 2016, the JWST and/or ground-based surveys will reg ...
... begun. Thus, near-infrared observations of these dwarfs could reveal strong Lyman ! and He II emission detectable by large ground-based telescopes, and possibly a rest-frame ultraviolet continuum observable from the ground and/or with the JWST. By 2016, the JWST and/or ground-based surveys will reg ...
color magnitude diagrams - AST 114, Astronomy Lab II for Spring
... b. Where on the main sequence (ie., what color) are the most massive stars found? ...
... b. Where on the main sequence (ie., what color) are the most massive stars found? ...
Galaxy Structure
... smaller group of three large and over 30 small galaxies, and is the second largest (after the Andromeda Galaxy M31) but perhaps the most massive member of this group. The Milky Way is most likely a BARRED SPIRAL GALAXY of Hubble type SBc. We are situated within the outer regions of its spiral disk, ...
... smaller group of three large and over 30 small galaxies, and is the second largest (after the Andromeda Galaxy M31) but perhaps the most massive member of this group. The Milky Way is most likely a BARRED SPIRAL GALAXY of Hubble type SBc. We are situated within the outer regions of its spiral disk, ...
Star Formation in Bok Globules - European Southern Observatory
... is a huge, faintly luminous H 1I region spread over more than 30 degrees of the southern sky. At a distance of roughly 450 pc this corresponds to a radius of about 125 pc, making the Gum Nebula one of the largest structures known in our galaxy. Near its center are several objects which tagether prod ...
... is a huge, faintly luminous H 1I region spread over more than 30 degrees of the southern sky. At a distance of roughly 450 pc this corresponds to a radius of about 125 pc, making the Gum Nebula one of the largest structures known in our galaxy. Near its center are several objects which tagether prod ...
Xiao Yang Xia
... (2) Star formation rate and accretion rate onto the central BH in IR QSOs at low redshift follow Mbulge- MBH relation, i.e., the ratio of the star formation rate and the accretion rate is about several hundred for IR QSOs, but decreases with the central black hole mass. This shows that the tight cor ...
... (2) Star formation rate and accretion rate onto the central BH in IR QSOs at low redshift follow Mbulge- MBH relation, i.e., the ratio of the star formation rate and the accretion rate is about several hundred for IR QSOs, but decreases with the central black hole mass. This shows that the tight cor ...
The Significance of Mega Stars
... by light during the course of one year. To gain an understanding of the enormous distances involved, we need only consider that Sirius —8½ light years away (amounting to some fifty trillion miles or eighty trillion kilometres)—is a close neighbor to our Sun in comparison with the greater distances o ...
... by light during the course of one year. To gain an understanding of the enormous distances involved, we need only consider that Sirius —8½ light years away (amounting to some fifty trillion miles or eighty trillion kilometres)—is a close neighbor to our Sun in comparison with the greater distances o ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.