Chapter 13 Measuring the properties of stars
... The amount of energy emitted by a star each second is the ____ and is measured in ____. A. Apparent brightness; degrees K B. Temperature; degrees K C. Apparent brightness; Watts D. Luminosity; Watts ...
... The amount of energy emitted by a star each second is the ____ and is measured in ____. A. Apparent brightness; degrees K B. Temperature; degrees K C. Apparent brightness; Watts D. Luminosity; Watts ...
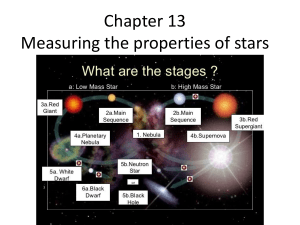
The Origin, Structure, and Evolution of the Stars
... easy to show that the sun must convert four and a half million tons of matter into energy every second to maintain its present brightness. In the deep interior of the sun this would require more than 500 million tons of hydrogen converted to helium each second. The Evolution of Stars How long can th ...
... easy to show that the sun must convert four and a half million tons of matter into energy every second to maintain its present brightness. In the deep interior of the sun this would require more than 500 million tons of hydrogen converted to helium each second. The Evolution of Stars How long can th ...
Astrophysical parameters of ten poorly studied open star clusters
... Open star clusters (OCs) are very important tools in studying the formation and evolution of the Galactic disk and the associated stellar evolution. The fundamental physical parameters of OCs, e.g. distance, reddening, age, and metallicity, are necessary for studying the Galactic disk. The Galactic, ...
... Open star clusters (OCs) are very important tools in studying the formation and evolution of the Galactic disk and the associated stellar evolution. The fundamental physical parameters of OCs, e.g. distance, reddening, age, and metallicity, are necessary for studying the Galactic disk. The Galactic, ...
Lecture21 - Michigan State University
... Gravity of a Black Hole • As long as you are a reasonable distance from the black hole, the black hole acts as is it mass is concentrated at the center (and it really is!) • Newton’s laws are in effect • The event horizon is small so ordinary distances (like 1 AU) are safe from a black hole of 1 to ...
... Gravity of a Black Hole • As long as you are a reasonable distance from the black hole, the black hole acts as is it mass is concentrated at the center (and it really is!) • Newton’s laws are in effect • The event horizon is small so ordinary distances (like 1 AU) are safe from a black hole of 1 to ...
First young loose association in the northern hemisphere?
... Once mixed in the ambient galactic plane stellar population, young stars are virtually indiscernible because neither their global photometric properties nor the presence of nearby gas can help to disentangle them from older ones. Nevertheless, in the RasTyc sample, we discovered 4 lithium-rich field ...
... Once mixed in the ambient galactic plane stellar population, young stars are virtually indiscernible because neither their global photometric properties nor the presence of nearby gas can help to disentangle them from older ones. Nevertheless, in the RasTyc sample, we discovered 4 lithium-rich field ...
Order of Magnitude Icebreaker
... ★ Start the project (with your team): ★ Two afternoons of team work ★ One afternoon to prepare a presentation ★ Present on Friday KAS16/MT ...
... ★ Start the project (with your team): ★ Two afternoons of team work ★ One afternoon to prepare a presentation ★ Present on Friday KAS16/MT ...
November - Hawaiian Astronomical Society
... In other exoplanet news, a planet that is probably composed largely of diamond has been found orbiting the star 55 Cancri (Rho 1 Cancri). The innermost of 5 planets in the system, it orbits in only 18 hours. Even more exciting, an Earth-sized planet has been found to orbit Alpha Centauri B. While it ...
... In other exoplanet news, a planet that is probably composed largely of diamond has been found orbiting the star 55 Cancri (Rho 1 Cancri). The innermost of 5 planets in the system, it orbits in only 18 hours. Even more exciting, an Earth-sized planet has been found to orbit Alpha Centauri B. While it ...
File - Mr. Catt`s Class
... 2. Astronomers once also thought the diagram represented an evolutionary sequence, but this interpretation has been discarded as old stars have been found in all three types. ...
... 2. Astronomers once also thought the diagram represented an evolutionary sequence, but this interpretation has been discarded as old stars have been found in all three types. ...
X-ray binaries
... and Magellanic Clouds LMXBs with NSs and BHs as accreting components. Donors can be WDs, or normal low-mass stars (main sequence or sub-giants). Many sources are found in globular clusters. Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an a ...
... and Magellanic Clouds LMXBs with NSs and BHs as accreting components. Donors can be WDs, or normal low-mass stars (main sequence or sub-giants). Many sources are found in globular clusters. Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an a ...
X-ray binaries
... and Magellanic Clouds LMXBs with NSs and BHs as accreting components. Donors can be WDs, or normal low-mass stars (main sequence or sub-giants). Many sources are found in globular clusters. Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an a ...
... and Magellanic Clouds LMXBs with NSs and BHs as accreting components. Donors can be WDs, or normal low-mass stars (main sequence or sub-giants). Many sources are found in globular clusters. Also there are more and more LMXBs found in more distant galaxies. In optics the emission is dominated by an a ...
Was a cloud-cloud collision the trigger of the recent star formation in
... Results. A configuration was found that reproduces many of the observed characteristics of Serpens, including some of the main features of the peculiar velocity field. The evolution of the velocity with position throughout the model is similar to the observed one and the column density and masses wi ...
... Results. A configuration was found that reproduces many of the observed characteristics of Serpens, including some of the main features of the peculiar velocity field. The evolution of the velocity with position throughout the model is similar to the observed one and the column density and masses wi ...
TOOLS IN ASTRONOMY SPECTROSCOPY
... 1. Know that starlight is often broken up into component wavelengths with diffraction gratings to produce stellar spectra. 2. Understand how stellar spectra are classified as A, B, C, D, E and so on, based on prominent characteristics. 3. Understand how stellar spectra are related to composition and ...
... 1. Know that starlight is often broken up into component wavelengths with diffraction gratings to produce stellar spectra. 2. Understand how stellar spectra are classified as A, B, C, D, E and so on, based on prominent characteristics. 3. Understand how stellar spectra are related to composition and ...
Calculate the Mass of the Milky Way Galaxy
... • During the uncertainties of the era, Hubble was able to observe galaxies at distances up to 7 million light years away. By doing so he was able to come up with Hubble's Law, which said that the further galaxies were away from earth the faster they moved away from our planet. Hubble's rule proved t ...
... • During the uncertainties of the era, Hubble was able to observe galaxies at distances up to 7 million light years away. By doing so he was able to come up with Hubble's Law, which said that the further galaxies were away from earth the faster they moved away from our planet. Hubble's rule proved t ...
PSF - ESO
... space. Because of the obvious definitions just given, not all parts of (b/a, c/a)-space can be occupied, but the same three stars - no matter how you shift, rotate, expand, contract, or flip the coordinate system - will always be projected to the same point in (b/a, c/a) space. One starts by sorting ...
... space. Because of the obvious definitions just given, not all parts of (b/a, c/a)-space can be occupied, but the same three stars - no matter how you shift, rotate, expand, contract, or flip the coordinate system - will always be projected to the same point in (b/a, c/a) space. One starts by sorting ...
ASTR3007/4007/6007, Class 1: Observing the Stars 23 February
... as well as absorption lines. Emission lines are like absorption lines in reverse: they are upward spikes in the spectrum, where there is much more light at a given frequency than you would get from a blackbody. Emission lines appear when there is an excess of a certain species of atoms and molecules ...
... as well as absorption lines. Emission lines are like absorption lines in reverse: they are upward spikes in the spectrum, where there is much more light at a given frequency than you would get from a blackbody. Emission lines appear when there is an excess of a certain species of atoms and molecules ...
The Evolution of Galaxy - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... Such x-ray images have led astronomers to conclude that clusters form from the merger of groups. The lumps in the main body of the Coma cluster presumably represent groups that have already been drawn in but have not yet been fully assimilated. Virgo seems to be in an even earlier stage of formation ...
... Such x-ray images have led astronomers to conclude that clusters form from the merger of groups. The lumps in the main body of the Coma cluster presumably represent groups that have already been drawn in but have not yet been fully assimilated. Virgo seems to be in an even earlier stage of formation ...
Bright versus Nearby Stars
... • The 269 Brightest stars are: – 381 light years away on average • Max Distance = 3400 light years – 75% are late stage giant stars – 25% are young hot (most probably B) stars. – Average absolute magnitude = -1.2 – Average luminosity = 300 solar luminosities. – Short lived stars or stars near the of ...
... • The 269 Brightest stars are: – 381 light years away on average • Max Distance = 3400 light years – 75% are late stage giant stars – 25% are young hot (most probably B) stars. – Average absolute magnitude = -1.2 – Average luminosity = 300 solar luminosities. – Short lived stars or stars near the of ...
A Comet-Hunter`s Legacy -
... interaction. M81's bright spiral arms are the site of star formation, partially caused by density waves raised by the most recent passage of M82, and the central portion of M82 is undergoing a starburst -- an explosively rapid surge of star formation and death -- which is violently blowing huge amou ...
... interaction. M81's bright spiral arms are the site of star formation, partially caused by density waves raised by the most recent passage of M82, and the central portion of M82 is undergoing a starburst -- an explosively rapid surge of star formation and death -- which is violently blowing huge amou ...
How to Plot the H-R Diagram and Use its Applications
... by increasing the luminosity of the star, the star may, in addition to the more visible light, infrared and ultraviolet light emit more, but the absolute magnitudes and appearance, standard visible light shining stars. Basically brightness of the stars by mass and stage of the life cycle of stars is ...
... by increasing the luminosity of the star, the star may, in addition to the more visible light, infrared and ultraviolet light emit more, but the absolute magnitudes and appearance, standard visible light shining stars. Basically brightness of the stars by mass and stage of the life cycle of stars is ...
WSN 42 (2016) 132-142
... by increasing the luminosity of the star, the star may, in addition to the more visible light, infrared and ultraviolet light emit more, but the absolute magnitudes and appearance, standard visible light shining stars. Basically brightness of the stars by mass and stage of the life cycle of stars is ...
... by increasing the luminosity of the star, the star may, in addition to the more visible light, infrared and ultraviolet light emit more, but the absolute magnitudes and appearance, standard visible light shining stars. Basically brightness of the stars by mass and stage of the life cycle of stars is ...
What Are the Faint X-ray Transients Near the Galactic Center?
... • Most bright, transient X-ray sources are accreting black holes and neutron stars. • When accretion occurs at low rates, the disk tends to be unstable, producing outbursts with LX>1037 erg s-1. ...
... • Most bright, transient X-ray sources are accreting black holes and neutron stars. • When accretion occurs at low rates, the disk tends to be unstable, producing outbursts with LX>1037 erg s-1. ...
Magnitudes lesson plan
... came from the Babylonians whose base number was six. The formal introduction of six magnitudes has been credited to Ptolemy (100-150 A.D.) who was a Greek/Egyptian astronomer. He simply advanced the ideas of Hipparchus by placing the twenty brightest stars he could see into magnitude one. All stars ...
... came from the Babylonians whose base number was six. The formal introduction of six magnitudes has been credited to Ptolemy (100-150 A.D.) who was a Greek/Egyptian astronomer. He simply advanced the ideas of Hipparchus by placing the twenty brightest stars he could see into magnitude one. All stars ...
Constellations Overview
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
... The most famous of all the constellations are the 12 that make up the Zodiac. All planets can be observed only in these 12 constellations as they pass across the sky during the course of their year. This is because the orbits of all the planets lie within ± 8º of the ecliptic. The Sun also moves t ...
Lecture 13 Local group chapter 4 of S+G
... γ-ray emission correlates with massive star forming regions and not with the gas distribution (simulated images if the γ-ray emission was distributed like the source) • Compactness of emission regions suggests little CR diffusion • 30 Doradus star forming region is a bright source of gamma rays and ...
... γ-ray emission correlates with massive star forming regions and not with the gas distribution (simulated images if the γ-ray emission was distributed like the source) • Compactness of emission regions suggests little CR diffusion • 30 Doradus star forming region is a bright source of gamma rays and ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.