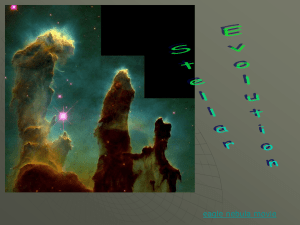
Characteristics of stars powerpoint
... • The distance that light travels in one year • It travels about 9.5 million million km • Travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second ...
... • The distance that light travels in one year • It travels about 9.5 million million km • Travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second ...
The Lifecycle of Stars
... to document the stages of a star’s lifecycle. Using the paper I provide, you will have to design and ...
... to document the stages of a star’s lifecycle. Using the paper I provide, you will have to design and ...
Stellar Evolution Slideshow
... Later in life, a star will eject the outer shell of Hydrogen, leaving the Helium behind in the core. This fast traveling Hydrogen gas is called a Planetary nebula ...
... Later in life, a star will eject the outer shell of Hydrogen, leaving the Helium behind in the core. This fast traveling Hydrogen gas is called a Planetary nebula ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... • Matter started to “_______” back together • This was due to __________ • The ________, _______ and __________ formed from these clumps of dust and gas • There are __________ of galaxies in the universe and each galaxy consists of __________ of stars ...
... • Matter started to “_______” back together • This was due to __________ • The ________, _______ and __________ formed from these clumps of dust and gas • There are __________ of galaxies in the universe and each galaxy consists of __________ of stars ...
Astronomy
... When a star suddenly increases in brightness (100x) in a few hrs/days, then dims back to original state. Gases from one binary star strike the other causing nuclear explosions which we see as light. Can occur several times ...
... When a star suddenly increases in brightness (100x) in a few hrs/days, then dims back to original state. Gases from one binary star strike the other causing nuclear explosions which we see as light. Can occur several times ...
HW 5 Solutions What are “black smokers?” Where in our solar
... 4. How did Edwin Hubble use Cepheid variables to determine the distance to the Andromeda spiral nebula? Describe his method. Cepheid variable stars are stars with changing luminosity. They grow brighter then dimmer in a repeating cycle that can be as short as a couple days or as long as an entire mo ...
... 4. How did Edwin Hubble use Cepheid variables to determine the distance to the Andromeda spiral nebula? Describe his method. Cepheid variable stars are stars with changing luminosity. They grow brighter then dimmer in a repeating cycle that can be as short as a couple days or as long as an entire mo ...
Messier Galaxies of #202541
... These stars have been plotted in figure 1. Notice that the dimmers stars have not been designated by their common names, but by their magnitudes. The decimal has been left out to avoid mistaking it for a dim star. 3. Begin the search using a methodical pattern. Since the constellations drift across ...
... These stars have been plotted in figure 1. Notice that the dimmers stars have not been designated by their common names, but by their magnitudes. The decimal has been left out to avoid mistaking it for a dim star. 3. Begin the search using a methodical pattern. Since the constellations drift across ...
The IC 348 surface density in the Perseus molecular cloud L. Cambrésy Observatoire de Strasbourg, France
... the cluster morphology cluster morphology ...
... the cluster morphology cluster morphology ...
6th Grade Science Chapter 19 Jeopardy Game
... b. A star does not change its’ size or temperature during its’ life. c. The shortest stage in a star’s life cycle is the main sequence. ...
... b. A star does not change its’ size or temperature during its’ life. c. The shortest stage in a star’s life cycle is the main sequence. ...
Stars and Sun
... Stars revolve around the center of galaxies once every 225 million years the Sun makes a revolution ...
... Stars revolve around the center of galaxies once every 225 million years the Sun makes a revolution ...
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
Sample exam 2
... 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power dial on the side of emission lamp and, just for fun, decide to turn up the power. The color of the helium lamp changes and you look through the spectroscop ...
... 13. Suppose you are looking at the emission spectrum of gaseous helium. You dutifully write down the wavelengths of emission. You notice a power dial on the side of emission lamp and, just for fun, decide to turn up the power. The color of the helium lamp changes and you look through the spectroscop ...
ASTRONOMY 313
... 2. Suppose that a white light flare is observed on the Sun, originating from a massive sunspot complex that was transiting the Earth-facing hemisphere of the Sun at the time. Roughly 60 hours later, during the evening hours, sky observers all over North America witness spectacular displays of the n ...
... 2. Suppose that a white light flare is observed on the Sun, originating from a massive sunspot complex that was transiting the Earth-facing hemisphere of the Sun at the time. Roughly 60 hours later, during the evening hours, sky observers all over North America witness spectacular displays of the n ...
Stars and Galaxies
... collection of stars, gas, and dust Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar Elliptical galaxies—large, three-dimensional ellipses; most ...
... collection of stars, gas, and dust Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar Elliptical galaxies—large, three-dimensional ellipses; most ...
Stars
... Apparent magnitude: brightness as seen from Earth Absolute magnitude: brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth ...
... Apparent magnitude: brightness as seen from Earth Absolute magnitude: brightness if it were a standard distance from Earth ...
Stars and Constellations
... • In order to be recognized as a star, it has to have two characteristics: – be self-bound by gravity, – it has to radiate energy. ...
... • In order to be recognized as a star, it has to have two characteristics: – be self-bound by gravity, – it has to radiate energy. ...
Study Guide for Stars and the Universe Test
... Extra Credit Questions for the Stars and the Universe Test 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away fro ...
... Extra Credit Questions for the Stars and the Universe Test 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away fro ...
Stellar Evolution and the HR Diagram Study Guide
... Which star will appear brighter in the night sky, a star with an apparent magnitude of 0 or a star with an apparent magnitude of +1? Star with apparent magnitude of 0 ...
... Which star will appear brighter in the night sky, a star with an apparent magnitude of 0 or a star with an apparent magnitude of +1? Star with apparent magnitude of 0 ...
galaxy
... • A galaxy is a system of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity. • Galaxies are large collections of stars….. millions and billions of stars • There are hundreds of billions of galaxies in the Universe • Millions to hundreds of billions of stars in each galaxy ...
... • A galaxy is a system of stars, dust, and gas held together by gravity. • Galaxies are large collections of stars….. millions and billions of stars • There are hundreds of billions of galaxies in the Universe • Millions to hundreds of billions of stars in each galaxy ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... • 4 hydrogen nuclei fuse to become 1 helium nucleus • Since the mass of 4 hydrogen nuclei is greater than the mass of 1 helium nucleus, the leftover mass (0.7%) is converted to energy by Einstein’s equation: E=mc2 ...
... • 4 hydrogen nuclei fuse to become 1 helium nucleus • Since the mass of 4 hydrogen nuclei is greater than the mass of 1 helium nucleus, the leftover mass (0.7%) is converted to energy by Einstein’s equation: E=mc2 ...
Review Guide
... 6. What type of galaxy contains only old stars? 7. What type of galaxy contains only young stars? 8. Besides their shape what other characteristic distinguishes the different types of galaxies from each other? 9. Why do distant galaxies appear redder than they should? 10. What are 2 pieces of eviden ...
... 6. What type of galaxy contains only old stars? 7. What type of galaxy contains only young stars? 8. Besides their shape what other characteristic distinguishes the different types of galaxies from each other? 9. Why do distant galaxies appear redder than they should? 10. What are 2 pieces of eviden ...
ASTRONOMY WEBQUEST…… EXPLORE THE UNIVERSE
... What are the possible end-products of a supernova? ...
... What are the possible end-products of a supernova? ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.