The Milky Way Galaxy
... • The Milky Way galaxy is home to 400 billion stars and our own Sun and Solar System. • It is a barred spiral galaxy. • Scientists think the centre of the galaxy contains a super massive black hole. • The Milky Way is full of dust, gas and stars. • The Milky Way, along with everything else, is ...
... • The Milky Way galaxy is home to 400 billion stars and our own Sun and Solar System. • It is a barred spiral galaxy. • Scientists think the centre of the galaxy contains a super massive black hole. • The Milky Way is full of dust, gas and stars. • The Milky Way, along with everything else, is ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #16
... 10-5. The star Zubenelgenubi (from Arabic for “scorpion’s southern claw”) has apparent magnitude 2.75 while the star Sulafat (Arabic for “tortoise”) has apparent magnitude 3.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Exp ...
... 10-5. The star Zubenelgenubi (from Arabic for “scorpion’s southern claw”) has apparent magnitude 2.75 while the star Sulafat (Arabic for “tortoise”) has apparent magnitude 3.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Exp ...
Sagittarius - columbusastronomy
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
... Constellation: Carina 2nd brightest star in the night sky Magnitude: -0.72 Type: supergiant, spectral type F Color: white to the naked eye Temperature: 7,350 K Distance: 310 light years RA: 6h 24m ...
1_Introduction
... The Galaxy has an entourage of star clusters that (on average) are at rest with respect to the Galaxy’s center. ...
... The Galaxy has an entourage of star clusters that (on average) are at rest with respect to the Galaxy’s center. ...
Astronomy Review revised Key
... yellow, 5000-6000 degrees C in temperature, average in brightness, main sequence, average star. ...
... yellow, 5000-6000 degrees C in temperature, average in brightness, main sequence, average star. ...
The Stars
... Stars are like the sun, some being smaller and some larger, but so far away that they look like points of light. By the end of the 5th grade, students should know that The sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a disk-shaped galaxy of stars, part of which can be seen as a glowing ba ...
... Stars are like the sun, some being smaller and some larger, but so far away that they look like points of light. By the end of the 5th grade, students should know that The sun is a medium-sized star located near the edge of a disk-shaped galaxy of stars, part of which can be seen as a glowing ba ...
Slide 1
... supernova is an exploding star that can become three times as bright as the sun. When a supernova occurs. All the dust particles, gas, and Dupree collect up. Creating a Nebula. These Nebulas can create many stars like our sun. Some stars can be brighter then others. This is an example of a Supernova ...
... supernova is an exploding star that can become three times as bright as the sun. When a supernova occurs. All the dust particles, gas, and Dupree collect up. Creating a Nebula. These Nebulas can create many stars like our sun. Some stars can be brighter then others. This is an example of a Supernova ...
ppt
... MW is a giant disk of stars. Kant also hypothesized that space was full of other, similar disks of stars (island universes). ...
... MW is a giant disk of stars. Kant also hypothesized that space was full of other, similar disks of stars (island universes). ...
The Evening Sky in February 2016
... distant star; 13 000 times brighter than the sun and 300 light years away. The Milky Way is brightest in the southeast toward Crux. It can be traced up the sky, fading where it is nearly overhead. It becomes very faint east or right of Orion. The Milky Way is our edgewise view of the galaxy, the pan ...
... distant star; 13 000 times brighter than the sun and 300 light years away. The Milky Way is brightest in the southeast toward Crux. It can be traced up the sky, fading where it is nearly overhead. It becomes very faint east or right of Orion. The Milky Way is our edgewise view of the galaxy, the pan ...
Cat`s EyE - Chandra X
... HOW: The spectacular filamentary structures in planetary nebulas come from the outer layers that have been shed by the dying star then sculpted by intense radiation from the hot central star (bright white dot in middle) that will eventually become a white dwarf. WHY: It is important to understand th ...
... HOW: The spectacular filamentary structures in planetary nebulas come from the outer layers that have been shed by the dying star then sculpted by intense radiation from the hot central star (bright white dot in middle) that will eventually become a white dwarf. WHY: It is important to understand th ...
What is a star`s life cycle?
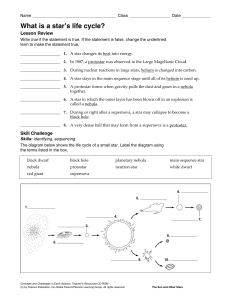
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
... ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During nuclear reactions in large stars, helium is changed into carbon. ____________________ 4. A star stays in the main seque ...
Great Astronomers of the 20th Century
... Jill Tarter • Joint appointment at UC Berkeley and SETI ...
... Jill Tarter • Joint appointment at UC Berkeley and SETI ...
Starry Night¨ Times - October 2008
... (40x) to find the object, and then try 100x and 200x. The name "planetary" is misleading, as these objects are not planets at all but stars at the end of their life cycle. However, they do look something like cloudy planets, and this fact confused earlier observers whose incorrect naming convention ...
... (40x) to find the object, and then try 100x and 200x. The name "planetary" is misleading, as these objects are not planets at all but stars at the end of their life cycle. However, they do look something like cloudy planets, and this fact confused earlier observers whose incorrect naming convention ...
The Hot-plate Model of a Star Model of Stars— 3 Oct
... • Definition of apparent magnitude – The magnitude of Vega is 0. – For every factor of 10 fainter, the magnitude is 2.5 greater. ...
... • Definition of apparent magnitude – The magnitude of Vega is 0. – For every factor of 10 fainter, the magnitude is 2.5 greater. ...
Document
... a. They show where too much light is absorbed by a star’s atmosphere. b. They show where less light is absorbed by a star’s atmosphere. c. They are the emission lines of an electrically charged element. d. They show where a star has black spots. _____ 10. What objects are formed from the materials i ...
... a. They show where too much light is absorbed by a star’s atmosphere. b. They show where less light is absorbed by a star’s atmosphere. c. They are the emission lines of an electrically charged element. d. They show where a star has black spots. _____ 10. What objects are formed from the materials i ...
Astronomy Campus Assessment
... Scientists measure the movement of distant galaxies to learn more about the origin of the universe. You researched scientific data that showed that light from a distant galaxy is red-shifted. How would you evaluate the data? A. It indicates that the expansion of the universe has stopped, and so it d ...
... Scientists measure the movement of distant galaxies to learn more about the origin of the universe. You researched scientific data that showed that light from a distant galaxy is red-shifted. How would you evaluate the data? A. It indicates that the expansion of the universe has stopped, and so it d ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
... formed iron, no more reactions can occur, and the core violently collapses in on itself Supernova ...
Starry Lives, Starry Skies
... · The Messier Catalog organized by type of object: http://www.seds.org/messier/objects.html · The Hubble Space Telescope pictures, organized by type of object: http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/browse/ · The National Observatory Image Gallery: http://www.noao.edu/image_gallery/ · The STA ...
... · The Messier Catalog organized by type of object: http://www.seds.org/messier/objects.html · The Hubble Space Telescope pictures, organized by type of object: http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/browse/ · The National Observatory Image Gallery: http://www.noao.edu/image_gallery/ · The STA ...
Stars
... characters from mythology. The formations appear at different times of the year. Each season earth can view a different sets of constellations. Also the earth views a different set of constellations on the northern and southern hemispheres. Like in August they have different sets of constellations t ...
... characters from mythology. The formations appear at different times of the year. Each season earth can view a different sets of constellations. Also the earth views a different set of constellations on the northern and southern hemispheres. Like in August they have different sets of constellations t ...
The Lives of Stars
... • Since a white dwarf has the same mass as the sun but only one millionth the volume, it is one million times as dense as the sun. A spoonful of material from a white dwarf has as much mass as a large truck. White dwarfs have no fuel, but they glow faintly from leftover energy. After billions of yea ...
... • Since a white dwarf has the same mass as the sun but only one millionth the volume, it is one million times as dense as the sun. A spoonful of material from a white dwarf has as much mass as a large truck. White dwarfs have no fuel, but they glow faintly from leftover energy. After billions of yea ...
Chapter14- Our Galaxy - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... These are just nebulae within the Milky Way! ...
... These are just nebulae within the Milky Way! ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.