Light from stars part II
... Apparent Magnitude mv (How bright stars appear) • Refined in the 19th Century when instruments became precise enough to accurately measure brightness • Modern scale is defined so that 6th magnitude stars are exactly 100 times brighter than 1st magnitude stars • This means stars that differ in magni ...
... Apparent Magnitude mv (How bright stars appear) • Refined in the 19th Century when instruments became precise enough to accurately measure brightness • Modern scale is defined so that 6th magnitude stars are exactly 100 times brighter than 1st magnitude stars • This means stars that differ in magni ...
01 - cloudfront.net
... Original content Copyright © Holt McDougal. All rights reserved. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. ...
... Original content Copyright © Holt McDougal. All rights reserved. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. ...
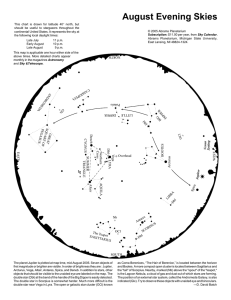
August Evening Skies
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
100 X size of Sun - East Penn School District
... • The scientific name for the twinkling of stars is stellar scintillation • Stars twinkle when we see them from the Earth's surface because we are viewing them through thick layers of turbulent (moving) air in the Earth's atmosphere. ...
... • The scientific name for the twinkling of stars is stellar scintillation • Stars twinkle when we see them from the Earth's surface because we are viewing them through thick layers of turbulent (moving) air in the Earth's atmosphere. ...
Stars
... appear brighter than those that are farther away • Absolute Magnitude: big stars are brighter than small stars. This is the ACTUAL brightness of the star – If all the stars were lined up equi-distant from Earth, we would be able to compare their actual brightness ...
... appear brighter than those that are farther away • Absolute Magnitude: big stars are brighter than small stars. This is the ACTUAL brightness of the star – If all the stars were lined up equi-distant from Earth, we would be able to compare their actual brightness ...
LT 5: I can describe how astronomers determine the composition
... All stars have dark-line spectra Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, scientists can determine the elements that make up a star by studying its spectrum ...
... All stars have dark-line spectra Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, scientists can determine the elements that make up a star by studying its spectrum ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Spring 2011
... 3. A binary star system contains one star of mass 0.8 M ⊙ and another of mass 2.2 M⊙ . They are in circular orbits and the distance between the centers of the stars is 1.5 AU. (a) What is the period P of the binary? Kepler’s third law is (M1 +M2 )P 2 = a3 . In this case M1 +M2 = 2.2+0.8 ...
... 3. A binary star system contains one star of mass 0.8 M ⊙ and another of mass 2.2 M⊙ . They are in circular orbits and the distance between the centers of the stars is 1.5 AU. (a) What is the period P of the binary? Kepler’s third law is (M1 +M2 )P 2 = a3 . In this case M1 +M2 = 2.2+0.8 ...
Stars and Galaxies - Earth Science: Astronomy
... Earth revolves around the Sun 4. Circumpolar constellations in the northern sky appear to circle around Polaris and are visible all year ...
... Earth revolves around the Sun 4. Circumpolar constellations in the northern sky appear to circle around Polaris and are visible all year ...
The Lives of Stars
... • White dwarfs are only about the size of Earth, but they have about as much mass as the sun. • Since a white dwarf has the same mass as the sun but only one millionth the volume, it is one million times as dense as the sun. A spoonful of material from a white dwarf has as much mass as a large truc ...
... • White dwarfs are only about the size of Earth, but they have about as much mass as the sun. • Since a white dwarf has the same mass as the sun but only one millionth the volume, it is one million times as dense as the sun. A spoonful of material from a white dwarf has as much mass as a large truc ...
Types of Stars - WordPress.com
... • 2 stars that orbit together (same orbit) • By measuring orbit size and time lapsed, it is possible to calculate “solar mass” • Sun = 1 solar mass ...
... • 2 stars that orbit together (same orbit) • By measuring orbit size and time lapsed, it is possible to calculate “solar mass” • Sun = 1 solar mass ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... • absolute magnitudemeasure of how bright the star would be if all stars were at the same distance from Earth – The more negative the number, the brighter the star ...
... • absolute magnitudemeasure of how bright the star would be if all stars were at the same distance from Earth – The more negative the number, the brighter the star ...
Mr - White Plains Public Schools
... diagram, a star like Earth’s Sun will eventually (1) explode in a supernova (2) become a black hole (3) change to a white dwarf (4) become a neutron star 2. Stars like Earth’s Sun ...
... diagram, a star like Earth’s Sun will eventually (1) explode in a supernova (2) become a black hole (3) change to a white dwarf (4) become a neutron star 2. Stars like Earth’s Sun ...
Stars - cmamath
... Describe the life cycle of stars and be able to diagram it. Make and use an H-R diagram. Define luminosity and magnitude. ...
... Describe the life cycle of stars and be able to diagram it. Make and use an H-R diagram. Define luminosity and magnitude. ...
Review 2
... Parts of Chapters 13-14-15: Main features of Uranus and Neptune and of the Galilean moons of Jupiter. Structure of a comet. The asteroid belt and the Oort cloud. Why do we have meteor showers during specific days of a year? Chapter 16: How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find ...
... Parts of Chapters 13-14-15: Main features of Uranus and Neptune and of the Galilean moons of Jupiter. Structure of a comet. The asteroid belt and the Oort cloud. Why do we have meteor showers during specific days of a year? Chapter 16: How do we use the atomic emission and absorption spectra to find ...