Chapter 1 Starts and Galaxies
... Binary star- member of a double star system Constellation- group of stars that form a pattern Nova- star that suddenly increases in brightness in just a few hours or days Nebula- massive cloud of dust and gas between the stars Galaxy- huge collection of stars Spiral Galaxy- galaxy that is shaped lik ...
... Binary star- member of a double star system Constellation- group of stars that form a pattern Nova- star that suddenly increases in brightness in just a few hours or days Nebula- massive cloud of dust and gas between the stars Galaxy- huge collection of stars Spiral Galaxy- galaxy that is shaped lik ...
Astronomy I Ex.2
... c) 100,000 AU. 2. H0 ' 70 secKm M pc What is the (approximate) age of the universe in Gyr? 3. Convert the following distances in cm to distances in AU: a) Approximate distance from the earth to the sun: 1.44 × 1013 cm b) Approximate distance from the earth to the next nearest star - Alpha Centauri: ...
... c) 100,000 AU. 2. H0 ' 70 secKm M pc What is the (approximate) age of the universe in Gyr? 3. Convert the following distances in cm to distances in AU: a) Approximate distance from the earth to the sun: 1.44 × 1013 cm b) Approximate distance from the earth to the next nearest star - Alpha Centauri: ...
Characteristics of Stars WS Questions 1-20
... Answer all of the following questions by rephrasing and using complete sentences. If you do not rephrase or use complete sentences, you will automatically lose half of the points ...
... Answer all of the following questions by rephrasing and using complete sentences. If you do not rephrase or use complete sentences, you will automatically lose half of the points ...
Surface Environments of the Planets o+ our Solar System
... In this exercise, you will also become more familiar with the various naming systems for stars. Remember, only the brightest stars which form our constellations have been given proper names. There are thousands of stars that have either Bayer Greek letter names, and even more that have Flamsteed num ...
... In this exercise, you will also become more familiar with the various naming systems for stars. Remember, only the brightest stars which form our constellations have been given proper names. There are thousands of stars that have either Bayer Greek letter names, and even more that have Flamsteed num ...
ASTRONOMY 313
... 6. When the Sun has swollen to full red-giant size (R 0.5 A.U. = 107.5 R), its luminosity will be about 2000 times greater than it is now (i.e. L/L = 2000). Assume that the size of the Earth’s orbit remains unchanged. a. Calculate the Sun’s angular diameter at that time as seen from the Earth. ...
... 6. When the Sun has swollen to full red-giant size (R 0.5 A.U. = 107.5 R), its luminosity will be about 2000 times greater than it is now (i.e. L/L = 2000). Assume that the size of the Earth’s orbit remains unchanged. a. Calculate the Sun’s angular diameter at that time as seen from the Earth. ...
ASTR100 Homework #5 Solutions Chapter 11 #29, 31 Due
... Also the more massive a white dwarf is, the smaller it is! This is because the more mass a white dwarf has, the more its electrons must squeeze together to maintain enough outward pressure to support the extra mass. There is a limit on the amount of mass a white dwarf can have, however. This limit i ...
... Also the more massive a white dwarf is, the smaller it is! This is because the more mass a white dwarf has, the more its electrons must squeeze together to maintain enough outward pressure to support the extra mass. There is a limit on the amount of mass a white dwarf can have, however. This limit i ...
Astronomy 360 Physics/Geology 360
... The point at which the line bends away from the main sequence straight line is the turnoff point. The star’s age is just a tiny bit less than the main sequence lifetime. To get the cluster’s age we therefore measure the age of the star at the turnoff point by calculating its main sequence lifetime f ...
... The point at which the line bends away from the main sequence straight line is the turnoff point. The star’s age is just a tiny bit less than the main sequence lifetime. To get the cluster’s age we therefore measure the age of the star at the turnoff point by calculating its main sequence lifetime f ...
File
... Stars can be arranged based on their luminosity (absolute magnitude) and temperature (spectral type) using a Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram ...
... Stars can be arranged based on their luminosity (absolute magnitude) and temperature (spectral type) using a Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram ...
Stars - White Plains Public Schools
... Luminosity is how bright a star is compared to the Sun if they were the same distance away. Stars are classified based on luminosity and temperature. Temperature affects the color of stars. Red = cool Blue = hot ...
... Luminosity is how bright a star is compared to the Sun if they were the same distance away. Stars are classified based on luminosity and temperature. Temperature affects the color of stars. Red = cool Blue = hot ...
labex7
... 4. From the absolute magnitude that you found for each star determine the star’s luminosity in solar units. (Hint – the absolute magnitude of the Sun is 4.84. Polaris has an absolute magnitude of -3.66. This means that Polaris is 4.84 - (-3.66) = 8.5 magnitudes brighter than the Sun. Use the magnitu ...
... 4. From the absolute magnitude that you found for each star determine the star’s luminosity in solar units. (Hint – the absolute magnitude of the Sun is 4.84. Polaris has an absolute magnitude of -3.66. This means that Polaris is 4.84 - (-3.66) = 8.5 magnitudes brighter than the Sun. Use the magnitu ...
F03HW09
... The luminosity is a measure of the total amount of energy emitted by a star in one second. The absolute visual magnitude is related to the portion of the total luminosity emitted only in the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Consequently, the absolute visual magnitude ignores energy i ...
... The luminosity is a measure of the total amount of energy emitted by a star in one second. The absolute visual magnitude is related to the portion of the total luminosity emitted only in the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Consequently, the absolute visual magnitude ignores energy i ...
the lab handout here
... How does the temperature and luminosity of the Sun compare to that of the other stars on the Main Sequence? ________________________________________________________ ...
... How does the temperature and luminosity of the Sun compare to that of the other stars on the Main Sequence? ________________________________________________________ ...
H-R Diagram - Faculty Website Listing
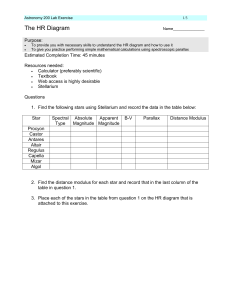
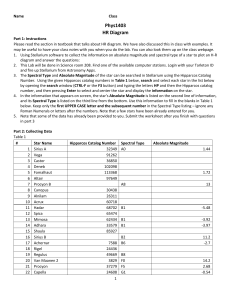
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
... Please read the section in textbook that talks about HR diagram. We have also discussed this in class with examples. It may be useful to have your class notes with you when you do the lab. You can also look them up on the class webpage. 1. Using Stellarium software to collect the information on abso ...
ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE
... - When all of the helium fuel of the Red Giant has been used. The outer layers explode off into space just leaving the white hot core (very small nearing the end of life) ...
... - When all of the helium fuel of the Red Giant has been used. The outer layers explode off into space just leaving the white hot core (very small nearing the end of life) ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... Used to study the lives of stars Most stars lie along the main sequence portion of the diagram ...
... Used to study the lives of stars Most stars lie along the main sequence portion of the diagram ...
Name Date ______ Period _____ Earth Science Chapter 25 Study
... A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ___________________ as it appears from ____________________. Some stars, called ____________________, get brighter and fainter in a regular pattern. A(n) ____________________ is a developing st ...
... A light-year is the distance ____________________ travels in a year. Apparent magnitude refers to a star’s ___________________ as it appears from ____________________. Some stars, called ____________________, get brighter and fainter in a regular pattern. A(n) ____________________ is a developing st ...