source
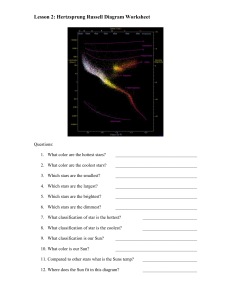
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature?
... brightness, is given a value of 1. The brightness given for each other star shows how that star compares with the sun. 2. Plot the data from both charts on the graph on the next page. 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500oC are red. Shade a vertical band from 2000oC to 3500oC a light red. 4 ...
... brightness, is given a value of 1. The brightness given for each other star shows how that star compares with the sun. 2. Plot the data from both charts on the graph on the next page. 3. Stars with surface temperatures up to 3,500oC are red. Shade a vertical band from 2000oC to 3500oC a light red. 4 ...
stars and constellations
... Some stars are visible in the summer, and others in the winter, because they are on the “other side” of the sun. ...
... Some stars are visible in the summer, and others in the winter, because they are on the “other side” of the sun. ...
Astronomical distances and Stellar magnitudes
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
Useful Things to Study (#2)
... Magnetic fields in the Sun Cause of the aurora borealis/australis in the Earth’s atmosphere ...
... Magnetic fields in the Sun Cause of the aurora borealis/australis in the Earth’s atmosphere ...
Study Guide for Stars and the Universe Test
... 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away from Earth? 5. How does a reflecting telescope differ from a r ...
... 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away from Earth? 5. How does a reflecting telescope differ from a r ...
Stars - Quia
... Stellar Parallax Parallax = shift in angle that occurs when a nearby object is seen against a distant backdrop from two different perspectives ...
... Stellar Parallax Parallax = shift in angle that occurs when a nearby object is seen against a distant backdrop from two different perspectives ...
File
... Absolute magnitude is the brightness of the star compared to other stars at the same distance. Apparent magnitude is how bright it appears from Earth. ...
... Absolute magnitude is the brightness of the star compared to other stars at the same distance. Apparent magnitude is how bright it appears from Earth. ...
Problem set 1 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56Fe is 8.8MeV
... 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56 Fe is 8.8 MeV per nucleon. Estimate the total energy released per kilogram of matter by the sequence of reactions which fuse hydrogen to iron. 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive s ...
... 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56 Fe is 8.8 MeV per nucleon. Estimate the total energy released per kilogram of matter by the sequence of reactions which fuse hydrogen to iron. 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive s ...
Star Life Cycle and classroom textbooks for research!
... What phase in the life cycle of a star is our sun in right now? What is the next phase of our sun’s life cycle? How long will it be before our sun becomes this type of star? How long (in years) is the typical lifetime of a star? Where are the blue stars in the HR diagram? Where are the red stars in ...
... What phase in the life cycle of a star is our sun in right now? What is the next phase of our sun’s life cycle? How long will it be before our sun becomes this type of star? How long (in years) is the typical lifetime of a star? Where are the blue stars in the HR diagram? Where are the red stars in ...
HR DIAGRAM REPORT FORM
... A. Plot an H-R diagram for the brightest stars from table 10.1. B. Plot an H-R diagram for the closest stars from table 10.2. 1. Which type of star is most common on each diagram? Choices are: Main Sequence (V), Giants (combine all I,II,III,IV types), White Dwarfs. Do not count Sun. Go to the tables ...
... A. Plot an H-R diagram for the brightest stars from table 10.1. B. Plot an H-R diagram for the closest stars from table 10.2. 1. Which type of star is most common on each diagram? Choices are: Main Sequence (V), Giants (combine all I,II,III,IV types), White Dwarfs. Do not count Sun. Go to the tables ...
Astronomy
... Something that is achieved when the inward force of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure from fusion and radiation inside a star ...
... Something that is achieved when the inward force of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure from fusion and radiation inside a star ...
Lab 1-2 : Vocabulary
... • Absolute - the magnitude of a star computed as if viewed from a distance of 32.6 light-years. • Apparent – a star’s brightness as it appears from Earth. The sun APPEARS brighter than the other stars because it is closer to us! ...
... • Absolute - the magnitude of a star computed as if viewed from a distance of 32.6 light-years. • Apparent – a star’s brightness as it appears from Earth. The sun APPEARS brighter than the other stars because it is closer to us! ...
Chapter 5 Mid-term Study Guide
... ______ A small star becomes a white dwarf, and a large star becomes a neutron star or black hole. ______ The star collapses again and then explodes as a nova or supernova. ______ A cloud of dust and gas is drawn together by its own gravity. ______ The star continues to give off the same amount of en ...
... ______ A small star becomes a white dwarf, and a large star becomes a neutron star or black hole. ______ The star collapses again and then explodes as a nova or supernova. ______ A cloud of dust and gas is drawn together by its own gravity. ______ The star continues to give off the same amount of en ...
Sample exam 2
... sentence/paragraph format or a drawing, depending on what is asked. 11. The Sun started off its trajectory on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram by initially moving down and to the left as it organized into a protostar. Explain this behavior in terms of temperature and luminosity, and give a reason for ...
... sentence/paragraph format or a drawing, depending on what is asked. 11. The Sun started off its trajectory on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram by initially moving down and to the left as it organized into a protostar. Explain this behavior in terms of temperature and luminosity, and give a reason for ...
AST 207 Test 2 Answers 20 October 2010
... . Because the radius is ¼, the luminosity of a sub-dwarf is 16 times fainter than a dwarf. The magnitude is shifted by a bit more than +2.5mag. More precisely, the magnitude is shifted by 2.5 log 16 3. 0mag. 2. (4 pts.) Prof. Balter Adams of the University of Michigan found two stars, A and B, that ...
... . Because the radius is ¼, the luminosity of a sub-dwarf is 16 times fainter than a dwarf. The magnitude is shifted by a bit more than +2.5mag. More precisely, the magnitude is shifted by 2.5 log 16 3. 0mag. 2. (4 pts.) Prof. Balter Adams of the University of Michigan found two stars, A and B, that ...