Apparent brightness
... away the star is. Astronomers have measured a few dozen stars this way. l Most stars are too far awayr µfor this to work T ...
... away the star is. Astronomers have measured a few dozen stars this way. l Most stars are too far awayr µfor this to work T ...
chap17_s05_probs
... A star is determined to have a surface temperature twice that of the Sun, and a luminosity 64 times greater. What is this star’s radius, expressed in solar units ? ANSWER: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third va ...
... A star is determined to have a surface temperature twice that of the Sun, and a luminosity 64 times greater. What is this star’s radius, expressed in solar units ? ANSWER: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third va ...
chap17_f04_probs
... ANSWER: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is found using that relation, described on pg 449 in the text. In solar units, L = R2 x T4 , substituting into the expression gives 64 = R2 x 24 , 64 = R2 x 16 Dividi ...
... ANSWER: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is found using that relation, described on pg 449 in the text. In solar units, L = R2 x T4 , substituting into the expression gives 64 = R2 x 24 , 64 = R2 x 16 Dividi ...
Stars - Images
... Ways of tracking where the constellations are located during the different seasons of the year. Remember as the earth revolves around the sun, it also rotates causing the stars to “shift” in the ...
... Ways of tracking where the constellations are located during the different seasons of the year. Remember as the earth revolves around the sun, it also rotates causing the stars to “shift” in the ...
WK10revisedoneweek
... 2. The line between the sun and the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The ratio of the cube of the average radius of a planets orbit to the square of its orbital period of revolution is the same for each planet. (Harmonic Law) ...
... 2. The line between the sun and the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The ratio of the cube of the average radius of a planets orbit to the square of its orbital period of revolution is the same for each planet. (Harmonic Law) ...
STARS- hot glowing sphere of gas that produces energy by
... B) Apparent brightness—brightness as seen from earth 3] Formation of stars A) Nebula (cloud of dust and gas) collapses under its own gravity B) Friction in core causes temperature to reach 10,000,000 c C) fusion begins and a star is born 4] How stars are found A) Loner-by itself (our sun) B) Binary ...
... B) Apparent brightness—brightness as seen from earth 3] Formation of stars A) Nebula (cloud of dust and gas) collapses under its own gravity B) Friction in core causes temperature to reach 10,000,000 c C) fusion begins and a star is born 4] How stars are found A) Loner-by itself (our sun) B) Binary ...
Unit 3 - Section 9.2 2011 Star Characteristics0
... 3. There are three “mystery stars.” Using a ruler, line up the spectral patterns of the elements to the mystery stars. 4. Answer the following questions. a. In which two mystery stars is calcium present? b. Only one mystery star contains mercury (Hg). Which one? c. Which mystery star’s composition i ...
... 3. There are three “mystery stars.” Using a ruler, line up the spectral patterns of the elements to the mystery stars. 4. Answer the following questions. a. In which two mystery stars is calcium present? b. Only one mystery star contains mercury (Hg). Which one? c. Which mystery star’s composition i ...
How Is a Star`s Color Related to Its Temperature? - d
... 1. Study the star data charts below. Note that the sun, used as a standard of brightness, is given a value of 1. The brightness given for each other star shows how that star compares with the sun. 2. Plot the data from both charts on the graph on the next page. 3. Stars with surface temperatures up ...
... 1. Study the star data charts below. Note that the sun, used as a standard of brightness, is given a value of 1. The brightness given for each other star shows how that star compares with the sun. 2. Plot the data from both charts on the graph on the next page. 3. Stars with surface temperatures up ...
Universe CBA Review - cms16-17
... 22.) When a scientist looks at a galaxy that is 12 billion light years away and is red shifted, what does that tell you about the galaxy? 23.) What is the name of the effect caused by motion of an object causing wavelengths to compress in front of it and expand behind it? Use the diagram below to an ...
... 22.) When a scientist looks at a galaxy that is 12 billion light years away and is red shifted, what does that tell you about the galaxy? 23.) What is the name of the effect caused by motion of an object causing wavelengths to compress in front of it and expand behind it? Use the diagram below to an ...
Patterns in the Sky - Plano Independent School District
... the pole star 5,000 years ago. It will become the pole star again in 20,000 years from now. ...
... the pole star 5,000 years ago. It will become the pole star again in 20,000 years from now. ...
Study Guide: Use your notes and handouts to
... 33. How is apparent magnitude different from absolute magnitude? 34. What is a parallax? What is it used to measure in space? 35. What is a Hertzsprung Russell Diagram? 36. What is on the X axis of a HR Diagram? 37. What is on the Y axis of the HR Diagram? 38. What is used to determine luminosity? 3 ...
... 33. How is apparent magnitude different from absolute magnitude? 34. What is a parallax? What is it used to measure in space? 35. What is a Hertzsprung Russell Diagram? 36. What is on the X axis of a HR Diagram? 37. What is on the Y axis of the HR Diagram? 38. What is used to determine luminosity? 3 ...
Properties of Stars
... Measuring Distance to Stars • Parallax is determined by taking a picture of a star at one time, and another picture six months later; using the angle between its apparent shift, astronomers can determine how far away it is • The nearest stars have large parallax angles, while those of distant stars ...
... Measuring Distance to Stars • Parallax is determined by taking a picture of a star at one time, and another picture six months later; using the angle between its apparent shift, astronomers can determine how far away it is • The nearest stars have large parallax angles, while those of distant stars ...
15.3 The Lives of Stars
... have dissipated (spreads out) • Size of earth, with same mass as our sun • Turns into a black dwarf when fuel runs out • Neutron Stars • Left over from a supernova ...
... have dissipated (spreads out) • Size of earth, with same mass as our sun • Turns into a black dwarf when fuel runs out • Neutron Stars • Left over from a supernova ...
Notes - CH 12
... The Sun will become a dwarf star in billions of years Supernova: the explosion of a supergiant star A supergiant star can explode before it dies The debris is still visible as an interstellar cloud ...
... The Sun will become a dwarf star in billions of years Supernova: the explosion of a supergiant star A supergiant star can explode before it dies The debris is still visible as an interstellar cloud ...
Document
... g. Which star is the closest (find m-M)? h. Which star has the smallest parallax angle? i. ...
... g. Which star is the closest (find m-M)? h. Which star has the smallest parallax angle? i. ...
What is the Zodiac? The Zodiac is defined by 12 constellations
... Each of these 12 major constellations has 3 other constellations associated with them. So in all there are 48 constellations in the Zodiac. Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constell ...
... Each of these 12 major constellations has 3 other constellations associated with them. So in all there are 48 constellations in the Zodiac. Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constell ...
Sermon Notes
... Each of these 12 major constellations has 3 other constellations associated with them. So in all there are 48 constellations in the Zodiac. Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constell ...
... Each of these 12 major constellations has 3 other constellations associated with them. So in all there are 48 constellations in the Zodiac. Claudius Ptolemy of Alexandria (90 – 168 AD) was a Greek astronomer who borrowed his information from the ancient Babylonian texts and he listed the 48 constell ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... The luminosity of a star is accurately known but measurement of its apparent brightness is made difficult by the presence of dust in the interstellar medium. Suggest the effect this has on the measured distance to the star. ...
... The luminosity of a star is accurately known but measurement of its apparent brightness is made difficult by the presence of dust in the interstellar medium. Suggest the effect this has on the measured distance to the star. ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Astronomy Project Purpose: To
... comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner planets inside it. Something to put it into perspective. 4.) Determine how many times more or less massive your star is compared to the Sun. You may i ...
... comparing it to other objects in the solar system. Example: The radius of Betelgeuse is 380,000,000 km, which could fit the entire orbit of the inner planets inside it. Something to put it into perspective. 4.) Determine how many times more or less massive your star is compared to the Sun. You may i ...
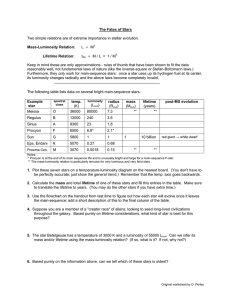
The Fates of Stars Mass-Luminosity Relation: Lifetime Relation:
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...
... be perfectly accurate; just show the general trend.) Remember that the temp. axis goes backwards. 2. Calculate the mass and total lifetime of one of these stars and fill this entries in the table. Make sure to translate the lifetime to years. (You may do the other stars if you have extra time.) 3. U ...