Stars and Galaxies
... Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar Elliptical galaxies—large, three-dimensional ellipses; most common shape Irregular galaxies—smaller, less common galaxies with various different shapes ...
... Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar Elliptical galaxies—large, three-dimensional ellipses; most common shape Irregular galaxies—smaller, less common galaxies with various different shapes ...
Today`s Class: Measuring temperatures of stars Astronomer`s
... • Important: the different spectral lines seen are NOT primarily because stars are made of different elements ...
... • Important: the different spectral lines seen are NOT primarily because stars are made of different elements ...
here - Boise State University
... 14. What is the cycle or phase a star will spend most of its life in? 15. If our sun is currently 5 billion years old, how much longer will the sun shine brightly for before it runs out of fuel to burn? 16. After our Sun runs our of Hydrogen fuel, what kind of star will it become? 17. What is the na ...
... 14. What is the cycle or phase a star will spend most of its life in? 15. If our sun is currently 5 billion years old, how much longer will the sun shine brightly for before it runs out of fuel to burn? 16. After our Sun runs our of Hydrogen fuel, what kind of star will it become? 17. What is the na ...
Brighter than the average star?
... So why do most astronomy books denigrate our star? It is probably a result of over zealously applying the mediocrity principle. This is the philosophical idea that there is nothing special about our place in the Universe (“we live on an ordinary planet, orbiting an ordinary star in an ordinary galax ...
... So why do most astronomy books denigrate our star? It is probably a result of over zealously applying the mediocrity principle. This is the philosophical idea that there is nothing special about our place in the Universe (“we live on an ordinary planet, orbiting an ordinary star in an ordinary galax ...
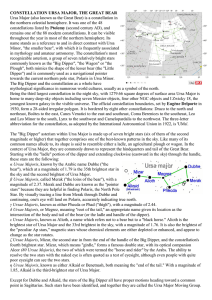
CONSTELLATION URSA MAJOR, THE GREAT
... the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa ...
... the northern celestial hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa ...
STAR SYTEMS AND GALAXIES
... • We can detect binary systems easily if one star blocks another, called an eclipsing binary. • We have found planets moving around stars in other systems. We can only detect very large planets because the planets must have enough gravity to effect the star. ...
... • We can detect binary systems easily if one star blocks another, called an eclipsing binary. • We have found planets moving around stars in other systems. We can only detect very large planets because the planets must have enough gravity to effect the star. ...
Homework 5 (stellar properties)
... 6. (3 pts.) What two observations/measurements would you make to classify a star according to its luminosity (i.e., luminosity class, e.g., Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, or V)? (Hint: Look at the HR diagram.) Which equation relates these two quantities to the size (radius) of a star (after all, the luminosit ...
... 6. (3 pts.) What two observations/measurements would you make to classify a star according to its luminosity (i.e., luminosity class, e.g., Ia, Ib, II, III, IV, or V)? (Hint: Look at the HR diagram.) Which equation relates these two quantities to the size (radius) of a star (after all, the luminosit ...
Part 1- The Basics
... • Binary stars are two stars which are held in orbit around each other by their mutual gravitational attraction, are surprisingly common • Visual binaries: those that can be resolved into two distinct star images by a telescope • Each of the two stars in a binary system moves in an elliptical orbit ...
... • Binary stars are two stars which are held in orbit around each other by their mutual gravitational attraction, are surprisingly common • Visual binaries: those that can be resolved into two distinct star images by a telescope • Each of the two stars in a binary system moves in an elliptical orbit ...
Chemically Peculiar/Magnetic Stars and the a photometry
... induction Theory of the fossil magnetic field: interstellar origin pre-main sequence evolution ...
... induction Theory of the fossil magnetic field: interstellar origin pre-main sequence evolution ...
Ch. 25 Properties of Stars
... Astronomers estimate that there are 200-400 billion stars in our Milky Way Galaxy, but we can only see about 2,500 visible to the naked eye on Earth ...
... Astronomers estimate that there are 200-400 billion stars in our Milky Way Galaxy, but we can only see about 2,500 visible to the naked eye on Earth ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... Star Clusters • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
... Star Clusters • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
Merak
... How Far Away: 62 light years away How Bright: About 50 times brighter than the Sun Where to View: In the constellation Ursa Major. When to View:All year round in the Northern Hemisphere ...
... How Far Away: 62 light years away How Bright: About 50 times brighter than the Sun Where to View: In the constellation Ursa Major. When to View:All year round in the Northern Hemisphere ...
Northern Hemisphere – December 2012
... Jupiter rises at sunset at the beginning of the month and is visible throughout the night as it reaches opposition (opposite the Sun in the sky) during December. Shining at magnitude -2.8, it reaches 60 degrees' elevation in Taurus in the south, helping us to see it with little atmospheric interfere ...
... Jupiter rises at sunset at the beginning of the month and is visible throughout the night as it reaches opposition (opposite the Sun in the sky) during December. Shining at magnitude -2.8, it reaches 60 degrees' elevation in Taurus in the south, helping us to see it with little atmospheric interfere ...
AST 207 Homework 5 Due 14 October 2011
... 2. Life on Deneb. Here you will find out what it means to live near a giant like Deneb. Recall that the luminosity of a star, where T is its temperature and R is its radius. Star ...
... 2. Life on Deneb. Here you will find out what it means to live near a giant like Deneb. Recall that the luminosity of a star, where T is its temperature and R is its radius. Star ...
www.NewYorkScienceTeacher.org/review
... b. 22.2 years d. 11.4 years What causes the dark bands observed in a solar spectrum? a. the emission of specific elements b. different chemical elements which absorb light at specific wavelengths c. highly compressed, glowing gas d. warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum Th ...
... b. 22.2 years d. 11.4 years What causes the dark bands observed in a solar spectrum? a. the emission of specific elements b. different chemical elements which absorb light at specific wavelengths c. highly compressed, glowing gas d. warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum Th ...
It is evident from our observations of impact craters on planets and
... In order to understand the stars, astronomers must determine accurate stellar distances. Stellar (heliocentric) parallax was used for determining distances to stars in Lab # 6. But the heliocentric parallax method breaks down beyond 100 parsecs (300 LY). In space, telescopes have increased our abili ...
... In order to understand the stars, astronomers must determine accurate stellar distances. Stellar (heliocentric) parallax was used for determining distances to stars in Lab # 6. But the heliocentric parallax method breaks down beyond 100 parsecs (300 LY). In space, telescopes have increased our abili ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? Blue and White 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? Blue and White (also, hottest) a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? The hotter the star, the more energy it has b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? Along ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? Blue and White 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? Blue and White (also, hottest) a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? The hotter the star, the more energy it has b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? Along ...
Red Dwarfs and Barnard`s star. Their origin and significance to
... A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwa ...
... A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 solar masses (M☉) to about 0.50 M☉ and have a surface temperature of less than 4000 K. Our sun has 1 solar mass (M☉) and a surface temperature of 6000 K Red dwa ...