May 2016 - Newbury Astronomical Society
... Taurus is easy to identify with the bright red star Aldebaran located at the centre of a cross shape of stars that defines Taurus. Up to the right is the beautiful Open Cluster M45 known as the Pleiades or the Seven Sisters. The cluster looks like a fuzzy patch of light at first glance with the ‘nak ...
... Taurus is easy to identify with the bright red star Aldebaran located at the centre of a cross shape of stars that defines Taurus. Up to the right is the beautiful Open Cluster M45 known as the Pleiades or the Seven Sisters. The cluster looks like a fuzzy patch of light at first glance with the ‘nak ...
$doc.title
... 4. How long would it take the planetary nebula to expand outside of the solar system? Show your work and give your answer in years. (Note, the solar system is about 80 AU.) ...
... 4. How long would it take the planetary nebula to expand outside of the solar system? Show your work and give your answer in years. (Note, the solar system is about 80 AU.) ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... km/s, what would the escape velocity be from a black hole the same mass as the Earth if you launched a rocket from a platform 6400 km above the event horizon (1 Earth radii): ...
... km/s, what would the escape velocity be from a black hole the same mass as the Earth if you launched a rocket from a platform 6400 km above the event horizon (1 Earth radii): ...
Evolution of Stars
... Star is at the tip of the “asymptotic” branch: Core stops contracting; no fusion is occurring. What supports the core? How does the rest of the star support itself? Are gravity and outward pressure balanced? ...
... Star is at the tip of the “asymptotic” branch: Core stops contracting; no fusion is occurring. What supports the core? How does the rest of the star support itself? Are gravity and outward pressure balanced? ...
Understanding the H-R Diagram
... amounts of energy, through the process of converting hydrogen atoms into helium atoms (nuclear fusion). Its absolute magnitude is +4.83. The solar mass is 1.99 x 1030 kg". POLARIS "Polaris (alpha UMi) is the current pole star for the Northern Hemisphere; it is 1 degree from the exact Northern celest ...
... amounts of energy, through the process of converting hydrogen atoms into helium atoms (nuclear fusion). Its absolute magnitude is +4.83. The solar mass is 1.99 x 1030 kg". POLARIS "Polaris (alpha UMi) is the current pole star for the Northern Hemisphere; it is 1 degree from the exact Northern celest ...
Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17)
... The only method for directly determining the masses of stars is from binary stars, using Newton’s form of Kepler’s 3rd law. There are three types of binary stars, which depend on how close they are to each other, their relative brightnesses, the distance of the binary, and other factors: a.Visual bi ...
... The only method for directly determining the masses of stars is from binary stars, using Newton’s form of Kepler’s 3rd law. There are three types of binary stars, which depend on how close they are to each other, their relative brightnesses, the distance of the binary, and other factors: a.Visual bi ...
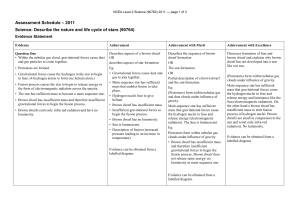
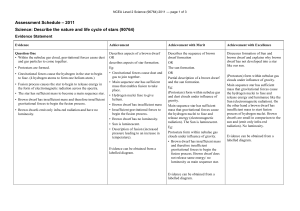
Level 2 Science (90764) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... • Hydrogen runs out. • When it cannot fuse iron, the core will collapse and then explode. • Star core collapses due to gravity and the outer layers of the star are exploded out. • A very dense neutron star or a black hole remains. • The variability in brightness caused by the gases and plasma explod ...
... • Hydrogen runs out. • When it cannot fuse iron, the core will collapse and then explode. • Star core collapses due to gravity and the outer layers of the star are exploded out. • A very dense neutron star or a black hole remains. • The variability in brightness caused by the gases and plasma explod ...
Lesson 1 - The DK Foundation
... Celestial latitude and longitude: used by astrologers to identify the position of a planet or star with reference to the ecliptic. Sidereal Zodiac: The twelve constellations on the ecliptic belt through which the Sun is perceived to pass in the course of a year. The Lesser Zodiac: manmade constructi ...
... Celestial latitude and longitude: used by astrologers to identify the position of a planet or star with reference to the ecliptic. Sidereal Zodiac: The twelve constellations on the ecliptic belt through which the Sun is perceived to pass in the course of a year. The Lesser Zodiac: manmade constructi ...
Assessment Schedule
... • Hydrogen runs out. • When it cannot fuse iron, the core will collapse and then explode. • Star core collapses due to gravity and the outer layers of the star are exploded out. • A very dense neutron star or a black hole remains. • The variability in brightness caused by the gases and plasma explod ...
... • Hydrogen runs out. • When it cannot fuse iron, the core will collapse and then explode. • Star core collapses due to gravity and the outer layers of the star are exploded out. • A very dense neutron star or a black hole remains. • The variability in brightness caused by the gases and plasma explod ...
(Mike Riddle CTI)-84_eng_cr_v4.0
... accepted’ theory of stellar formation may be one of a hundred unsupported dogmas which constitute a large part of present-day ...
... accepted’ theory of stellar formation may be one of a hundred unsupported dogmas which constitute a large part of present-day ...
Stellar Masses
... • 1977-R.Brent Tully and J.Richard Fisher discovered a relationship between the Doppler broadening of the H 21 cm line and the luminosity of a spiral galaxy.This provides the basis of a method of measuring distances to spiral galaxies. If a spiral galaxy is rotating then it may have a velocity relat ...
... • 1977-R.Brent Tully and J.Richard Fisher discovered a relationship between the Doppler broadening of the H 21 cm line and the luminosity of a spiral galaxy.This provides the basis of a method of measuring distances to spiral galaxies. If a spiral galaxy is rotating then it may have a velocity relat ...
30 Doradus - HubbleSOURCE
... 1. Gigantic regions of star formation are complex systems where different generations of star affect each other’s evolution 2. At high redshift we cannot see the complexity of the star forming regions, and we derive a simplified history of star formation 3. A comparison between what we see in nearby ...
... 1. Gigantic regions of star formation are complex systems where different generations of star affect each other’s evolution 2. At high redshift we cannot see the complexity of the star forming regions, and we derive a simplified history of star formation 3. A comparison between what we see in nearby ...
Document
... Where does the energy of the stars come from? The new stars continue to contract because of gravity. The increasing pressure heats the nucleus of the star and makes it shine. If gravity was the only source of energy our Sun would shine for less than 18,000,000 years. There must be another source of ...
... Where does the energy of the stars come from? The new stars continue to contract because of gravity. The increasing pressure heats the nucleus of the star and makes it shine. If gravity was the only source of energy our Sun would shine for less than 18,000,000 years. There must be another source of ...
A Triple Conjunction
... dates back to the middle of the 19th Century. Kepler only pointed out that a conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn had occurred near the time of the Nativity whilst himself favouring the nova/supernova hypothesis. A planetary conjunction is when two (or more) planets approach each other in the sky, one ...
... dates back to the middle of the 19th Century. Kepler only pointed out that a conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn had occurred near the time of the Nativity whilst himself favouring the nova/supernova hypothesis. A planetary conjunction is when two (or more) planets approach each other in the sky, one ...
GAIA Composition, Formation and Evolution of our Galaxy
... masses, rather than lower limits (m sin i) orbits for many (≈5000) systems relative orbital inclinations for multiple systems mass down to 10 MEarth to 10 pc ...
... masses, rather than lower limits (m sin i) orbits for many (≈5000) systems relative orbital inclinations for multiple systems mass down to 10 MEarth to 10 pc ...
ppt
... computed mass-radius relation of quark star within the bag model. ・ Assuming that RX J1856.5-3754 is a pure quark star, we have derived an upper limit on its mass. ...
... computed mass-radius relation of quark star within the bag model. ・ Assuming that RX J1856.5-3754 is a pure quark star, we have derived an upper limit on its mass. ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1
... • The apparent motion of stars is the motion visible to the unaided eye. Apparent motion is caused by the movement of Earth. • The rotation of Earth causes the apparent motion of stars to be as though the stars are moving counterclockwise around the North Star. • Earth’s revolution around the sun ca ...
... • The apparent motion of stars is the motion visible to the unaided eye. Apparent motion is caused by the movement of Earth. • The rotation of Earth causes the apparent motion of stars to be as though the stars are moving counterclockwise around the North Star. • Earth’s revolution around the sun ca ...
click here
... • Stars of given type of spectrum and the same colors have the same absolute magnitude (99.9%) • Stars have different apparent magnitudes depending on their distance. • Stars behind dust clouds look redder than they are intrinsically, so… m-M=5 log d1 –5+ A(l) (i.e., the star looks fainter) ...
... • Stars of given type of spectrum and the same colors have the same absolute magnitude (99.9%) • Stars have different apparent magnitudes depending on their distance. • Stars behind dust clouds look redder than they are intrinsically, so… m-M=5 log d1 –5+ A(l) (i.e., the star looks fainter) ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.