Stars - gilbertmath.com
... The ______ ___________________ is actually just part of a larger star pattern known as ____________ ___________________, which is itself a _________________________. ...
... The ______ ___________________ is actually just part of a larger star pattern known as ____________ ___________________, which is itself a _________________________. ...
Birth - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... Each second in the Sun, about 600 million tons of hydrogen undergo fusion into helium, with about 4 million tons turning to energy in the process This rate of hydrogen use means that eventually the Sun (and all other stars) will run out of central fuel ...
... Each second in the Sun, about 600 million tons of hydrogen undergo fusion into helium, with about 4 million tons turning to energy in the process This rate of hydrogen use means that eventually the Sun (and all other stars) will run out of central fuel ...
Constellations Overview
... • Follow the line made by Orion’s belt up & to the right • Aldebaran- Red star that is the eye of the bull. It is the 13th brightest in the nighttime sky ...
... • Follow the line made by Orion’s belt up & to the right • Aldebaran- Red star that is the eye of the bull. It is the 13th brightest in the nighttime sky ...
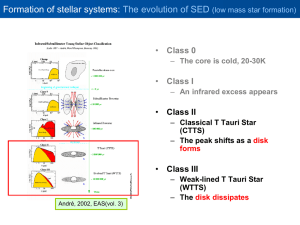
STELLAR STRUCTURE AND EVOLUTION
... . pressure → surface gravity → luminosity class . stellar rotation: in rapidly rotating stars, spectral lines are Doppler broadened by rotation . orbital velocities (due to periodic Doppler shifts) in binaries ...
... . pressure → surface gravity → luminosity class . stellar rotation: in rapidly rotating stars, spectral lines are Doppler broadened by rotation . orbital velocities (due to periodic Doppler shifts) in binaries ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... where A is the angular diameter of the star, L is its true diameter, and D is its distance. We need to solve for L. We will have to change 4.4 light years into meters and 0.0085 arcsec into degrees to get a meaningful answer. A L ...
... where A is the angular diameter of the star, L is its true diameter, and D is its distance. We need to solve for L. We will have to change 4.4 light years into meters and 0.0085 arcsec into degrees to get a meaningful answer. A L ...
Manual - TUM
... the celestial north pole. The declination is equivalent to earth’s latitude, with the slight difference of ranging not from 90◦ N to 90◦ S, but from +90◦ to -90◦ . It is also measured in degrees and is subdivided into 60 arcminutes which are subdivided into 60 arcseconds respectively. The longitude ...
... the celestial north pole. The declination is equivalent to earth’s latitude, with the slight difference of ranging not from 90◦ N to 90◦ S, but from +90◦ to -90◦ . It is also measured in degrees and is subdivided into 60 arcminutes which are subdivided into 60 arcseconds respectively. The longitude ...
Week 11 Concept Summary
... (a) Disk: The disk is very thin compared to its size, like a CD (but even thinner in proportion!). It contains a lot of gas and dust, as well as many stars both young and old. Open clusters are also found here. Most stars in the disk have conentrations of heavy elements similar to the Sun’s. They al ...
... (a) Disk: The disk is very thin compared to its size, like a CD (but even thinner in proportion!). It contains a lot of gas and dust, as well as many stars both young and old. Open clusters are also found here. Most stars in the disk have conentrations of heavy elements similar to the Sun’s. They al ...
TAP 704- 8: The ladder of astronomical distances
... The prestigious meeting of the International Astronomical Union in 1976 was startled to be told that the Universe is only half as big as the astronomers present all thought, and therefore only half as old. The challenger was the French-American astronomer Gerard de Vaucouleurs; the leader of the cha ...
... The prestigious meeting of the International Astronomical Union in 1976 was startled to be told that the Universe is only half as big as the astronomers present all thought, and therefore only half as old. The challenger was the French-American astronomer Gerard de Vaucouleurs; the leader of the cha ...
26.4 Groups of Stars
... The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way galaxy has an estimated 200 to 400 billion stars and a diameter of more than 100,000 light years. Every individual star that you can see with the unaided eye is in our galaxy. The solar system lies in the Milky Way’s disk within a spiral arm, about two thirds of th ...
... The Milky Way Galaxy The Milky Way galaxy has an estimated 200 to 400 billion stars and a diameter of more than 100,000 light years. Every individual star that you can see with the unaided eye is in our galaxy. The solar system lies in the Milky Way’s disk within a spiral arm, about two thirds of th ...
The Milky Way Galaxy
... To determine the rotation curve of the Galaxy, we will introduce a more convenient coordinate system, called the Galactic coordinate system. Note that the plane of the solar system is not the same as the plane of the Milky Way disk, and the Earth itself is tipped with respect to the plane of the sol ...
... To determine the rotation curve of the Galaxy, we will introduce a more convenient coordinate system, called the Galactic coordinate system. Note that the plane of the solar system is not the same as the plane of the Milky Way disk, and the Earth itself is tipped with respect to the plane of the sol ...
File
... You put the styrofoam ball at the center, didn't you? The name of this "ball" is the Bulge. Old stars get together and make the Bulge. In the Bulge there is little gas which is the material of stars. In contrast, there is a lot of gas and many stars are being formed on the disk now. 3. Objects you p ...
... You put the styrofoam ball at the center, didn't you? The name of this "ball" is the Bulge. Old stars get together and make the Bulge. In the Bulge there is little gas which is the material of stars. In contrast, there is a lot of gas and many stars are being formed on the disk now. 3. Objects you p ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.