Stellar Evolution
... where the 2 stars (assume they are identical) are too close to resolve in the telescope (they appear as a single point of light). Where does the binary appear: A: on the main sequence B: above the main sequence C: below the main sequence D: as a supergiant ...
... where the 2 stars (assume they are identical) are too close to resolve in the telescope (they appear as a single point of light). Where does the binary appear: A: on the main sequence B: above the main sequence C: below the main sequence D: as a supergiant ...
Stellar Evolution in the HR Diagram
... Electron degeneracy cannot support cores more massive than 1.4 M. If a degenerate C/O core (i.e., a white dwarf) is pushed above this limit, it was collapse and begin fusing, but it will not have time to adjust its structure (all the energy will just go into lifting the degeneracy). The star will b ...
... Electron degeneracy cannot support cores more massive than 1.4 M. If a degenerate C/O core (i.e., a white dwarf) is pushed above this limit, it was collapse and begin fusing, but it will not have time to adjust its structure (all the energy will just go into lifting the degeneracy). The star will b ...
Stars Part 1
... Step 1: Change units R = 18 x (6.955 x 108 m) = 1.2519 x 1010 m Step 2: Plug into equation L = 4πR2s T4 L = 4π(1.2519 x 1010)2(5.67 x 10-8) (25000)4 L = 2.328 x 1032 W L = 597,038 Lo ...
... Step 1: Change units R = 18 x (6.955 x 108 m) = 1.2519 x 1010 m Step 2: Plug into equation L = 4πR2s T4 L = 4π(1.2519 x 1010)2(5.67 x 10-8) (25000)4 L = 2.328 x 1032 W L = 597,038 Lo ...
Planetary Nebula
... Low Mass StarsIf a Star has a mass of less then 4 stellar masses, then the Star will become a Red Giant when it has used most of its Hydrogen in the process of nuclear fusion. This Red Giant will lose its mass by gently ejecting its outer layers to form a Planetary Nebula. There are between 20,000 ...
... Low Mass StarsIf a Star has a mass of less then 4 stellar masses, then the Star will become a Red Giant when it has used most of its Hydrogen in the process of nuclear fusion. This Red Giant will lose its mass by gently ejecting its outer layers to form a Planetary Nebula. There are between 20,000 ...
Constellation Packet - Mr. Jenkins` Classroom
... was his mother was about to kill her when zeus intervened and sent both mother and son into the sky as the greater and lesser bears. The way zeus got the bears into the sky explains why their tails are so long, apparently zeus grabbed them by their tails and swung them around over his head and final ...
... was his mother was about to kill her when zeus intervened and sent both mother and son into the sky as the greater and lesser bears. The way zeus got the bears into the sky explains why their tails are so long, apparently zeus grabbed them by their tails and swung them around over his head and final ...
An Introduction To Parallax
... Introduction —Parallax is a geometrical effect that can be used to obtain a direct measurement of the distance to an object. A driver and her passenger, for example, may fall prey to this effect when arguing about a car’s speed. If the car uses a needle–type speedometer, where the needle is mounted ...
... Introduction —Parallax is a geometrical effect that can be used to obtain a direct measurement of the distance to an object. A driver and her passenger, for example, may fall prey to this effect when arguing about a car’s speed. If the car uses a needle–type speedometer, where the needle is mounted ...
The Sky is holy
... these names. The classic star map has only some constellations with hidden Olympic roots (Orion – as god of war, Cygnus – as Zeus like Swan) and planets of course. There is no god names in Estonian Sky. This is a livingplace for Celestial people (Sun, Moon, Star are ones of them) and all their staff ...
... these names. The classic star map has only some constellations with hidden Olympic roots (Orion – as god of war, Cygnus – as Zeus like Swan) and planets of course. There is no god names in Estonian Sky. This is a livingplace for Celestial people (Sun, Moon, Star are ones of them) and all their staff ...
Star formation, feedback and the role of SNe II and SNe Ia in the
... • Mashchenko et al 2005 made N-body simulations of the formation of dwarf spheroidal galaxies and found that the best fitting models for Draco have a large range of DM halo virial masses (108-109 MO) • Mashchenko et al 2006 made simulations of the interaction of Draco with our Galaxy and ruled out t ...
... • Mashchenko et al 2005 made N-body simulations of the formation of dwarf spheroidal galaxies and found that the best fitting models for Draco have a large range of DM halo virial masses (108-109 MO) • Mashchenko et al 2006 made simulations of the interaction of Draco with our Galaxy and ruled out t ...
same
... is in the state of New York, we specify for example that Betelgeuse is in Orion. However, there are also reasons why we use right ascension and declination (i.e., exact coordinates) as you will find out. Actually, professional astronomers only use the exact coordinates. The stars that make up the co ...
... is in the state of New York, we specify for example that Betelgeuse is in Orion. However, there are also reasons why we use right ascension and declination (i.e., exact coordinates) as you will find out. Actually, professional astronomers only use the exact coordinates. The stars that make up the co ...
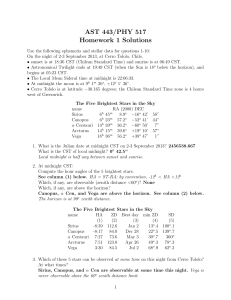
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
Telescopes: More Than Meets the Eye
... Constellations: Imaginary, dot-to-dot pictures drawn using the stars as the dots. These are used to map the nighttime sky. There are 88 constellations all together. Deep Space Objects: These objects are very distant from Earth and can usually only be seen with a telescope. They include: galaxies, di ...
... Constellations: Imaginary, dot-to-dot pictures drawn using the stars as the dots. These are used to map the nighttime sky. There are 88 constellations all together. Deep Space Objects: These objects are very distant from Earth and can usually only be seen with a telescope. They include: galaxies, di ...
Plotting Variable Stars on the H
... magnitude (MV) values, one at maximum and one at minimum. They also have enough variation to change spectral classes. To show the entire cycle of change for variable stars, it is necessary to plot them twice – at maxima and minima. The spectral class column gives the spectral class at both maximum ( ...
... magnitude (MV) values, one at maximum and one at minimum. They also have enough variation to change spectral classes. To show the entire cycle of change for variable stars, it is necessary to plot them twice – at maxima and minima. The spectral class column gives the spectral class at both maximum ( ...
Stellar Winds and Mass Loss
... These profiles are fit using the above velocity profile, with different numbers of absorbing ions, until the profile matches the observed unsaturated profile ...
... These profiles are fit using the above velocity profile, with different numbers of absorbing ions, until the profile matches the observed unsaturated profile ...
Basics of Astrophysics
... If the Airy disks of two adjacent sources overlap they will not be seen as separate sources. The minimum angle on the sky at which it is still possible to distinguish the sources is called the ...
... If the Airy disks of two adjacent sources overlap they will not be seen as separate sources. The minimum angle on the sky at which it is still possible to distinguish the sources is called the ...
Angular Measurement
... Yes, however, this theory has guided scientists’ calculations with technology from the days of Sir Isaac Newton to Space Travel calculations ...
... Yes, however, this theory has guided scientists’ calculations with technology from the days of Sir Isaac Newton to Space Travel calculations ...
TOOLS IN ASTRONOMY SPECTROSCOPY
... 1. Know that starlight is often broken up into component wavelengths with diffraction gratings to produce stellar spectra. 2. Understand how stellar spectra are classified as A, B, C, D, E and so on, based on prominent characteristics. 3. Understand how stellar spectra are related to composition and ...
... 1. Know that starlight is often broken up into component wavelengths with diffraction gratings to produce stellar spectra. 2. Understand how stellar spectra are classified as A, B, C, D, E and so on, based on prominent characteristics. 3. Understand how stellar spectra are related to composition and ...
Measuring Radii and Temperatures of Stars
... class telescopes is ~0.02” at 4000A, comparable to the diameter of some stars • The seeing disk of a large telescope is made up of the rapid combination of multiple, diffraction-limited images • 2-d Fourier transform of short exposures will recover the intrinsic image diameter • Only a few stars hav ...
... class telescopes is ~0.02” at 4000A, comparable to the diameter of some stars • The seeing disk of a large telescope is made up of the rapid combination of multiple, diffraction-limited images • 2-d Fourier transform of short exposures will recover the intrinsic image diameter • Only a few stars hav ...
Astrophotography Manual
... object is located. You will need a star map of that region containing stars at least up to 6th magnitude. Use the binoculars to locate the associated star field and compare it with the map.(make sure the field for comparison Leek Meng Lee ...
... object is located. You will need a star map of that region containing stars at least up to 6th magnitude. Use the binoculars to locate the associated star field and compare it with the map.(make sure the field for comparison Leek Meng Lee ...
White dwarfs that crossed the Chandrasekhar limit
... that space–time is curved around a massive object and it is scale-independent. Broadly speaking, irrespective of where we stand from the gravitating object, the force with which we are pulled is always equal to the inverse of the distance squared. But, the modified gravity theory, specifically Satar ...
... that space–time is curved around a massive object and it is scale-independent. Broadly speaking, irrespective of where we stand from the gravitating object, the force with which we are pulled is always equal to the inverse of the distance squared. But, the modified gravity theory, specifically Satar ...
IMR_Star Theater
... 1. Place planetarium on a table in the center of the room. A room with smooth, light-colored walls and ceiling works best. A room that is roughly square and no larger than 12 x 12 feet provides the best projection quality. Star Theater works best when it is located two to six feet from the projectio ...
... 1. Place planetarium on a table in the center of the room. A room with smooth, light-colored walls and ceiling works best. A room that is roughly square and no larger than 12 x 12 feet provides the best projection quality. Star Theater works best when it is located two to six feet from the projectio ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.