Chapter 17 Star Stuff How does a star`s mass affect nuclear fusion
... • A star’s mass determines its entire life story because it determines its core temperature • High-mass stars with >8MSun have short lives, eventually becoming hot enough to make iron, and end in supernova explosions • Low-mass stars with <2MSun have long lives, never become hot enough to fuse carbo ...
... • A star’s mass determines its entire life story because it determines its core temperature • High-mass stars with >8MSun have short lives, eventually becoming hot enough to make iron, and end in supernova explosions • Low-mass stars with <2MSun have long lives, never become hot enough to fuse carbo ...
Recipe for a Star
... Look at the periodic table. How many elements have you heard of with atomic masses greater than iron? These less familiar elements are rare because they form only during a massive-star supernova explosion. ...
... Look at the periodic table. How many elements have you heard of with atomic masses greater than iron? These less familiar elements are rare because they form only during a massive-star supernova explosion. ...
The ultra-luminous x-ray sources near center of M82
... X-ray sources at central region of M82 X-ray sources and star clusters correlation Lightcurves of target transient source ...
... X-ray sources at central region of M82 X-ray sources and star clusters correlation Lightcurves of target transient source ...
Chemical Universe. - University of Texas Astronomy
... at the heart of the nebula, becomes a white dwarf — a ball of matter only about as big as Earth, but containing most of the star’s mass. It no longer produces energy through nuclear reactions, but shines through the heat built up during its long life. This will be the Sun’s fate. More massive stars, ...
... at the heart of the nebula, becomes a white dwarf — a ball of matter only about as big as Earth, but containing most of the star’s mass. It no longer produces energy through nuclear reactions, but shines through the heat built up during its long life. This will be the Sun’s fate. More massive stars, ...
1 Exoplanets 2 Types of Exoplanets
... This is the detection method utilized by the Kepler Space Telescope where it looks for exoplanets crossing in front of (transiting) the host star. Kepler picks a particular field of view in the sky and selects around a hundred thousand stars to observe over a given time period. It then measures how ...
... This is the detection method utilized by the Kepler Space Telescope where it looks for exoplanets crossing in front of (transiting) the host star. Kepler picks a particular field of view in the sky and selects around a hundred thousand stars to observe over a given time period. It then measures how ...
How to Plot the H-R Diagram and Use its Applications
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
ppt
... differentiates reasonably well between QSOs and AGN. In contrast to QSO/AGN objects known in WGACAT, where dominant class is AGN, objects identified by ClassX are strongly dominated by QSOs. On average are much fainter in the X-rays, by more than 1 mag; also substantially redder in the optical. Of C ...
... differentiates reasonably well between QSOs and AGN. In contrast to QSO/AGN objects known in WGACAT, where dominant class is AGN, objects identified by ClassX are strongly dominated by QSOs. On average are much fainter in the X-rays, by more than 1 mag; also substantially redder in the optical. Of C ...
WSN 42 (2016) 132-142
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
Dorn_projectF08 - Bowling Green State University
... stars because the time exposure was too long B-20 seconds. This time does not allow for the rotation of the Earth, thus star trails are shown. ...
... stars because the time exposure was too long B-20 seconds. This time does not allow for the rotation of the Earth, thus star trails are shown. ...
20_LectureOutline
... 20.2 Evolution of a Sun-Like Star The helium flash: The pressure within the helium core is almost totally due to “electron degeneracy”—two electrons cannot be in the same quantum state, so the core cannot contract beyond a certain point. This pressure is almost independent of temperature— when the ...
... 20.2 Evolution of a Sun-Like Star The helium flash: The pressure within the helium core is almost totally due to “electron degeneracy”—two electrons cannot be in the same quantum state, so the core cannot contract beyond a certain point. This pressure is almost independent of temperature— when the ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams
... spectral type, and evolutionary stage. There are 3 very different types of stars: Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their e ...
... spectral type, and evolutionary stage. There are 3 very different types of stars: Most stars, including the sun, are "main sequence stars," fueled by nuclear fusion converting hydrogen into helium. For these stars, the hotter they are, the brighter. These stars are in the most stable part of their e ...
Ch 20 Stellar Evolution
... 20.4 Evolution of Stars More Massive than the Sun A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line —it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventua ...
... 20.4 Evolution of Stars More Massive than the Sun A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line —it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventua ...
intergalactic move
... to a different part of our Galaxy? Our Galaxy, the Milky Way, is so big that it would take 100.000 years to cross from one side to the other. It is shaped like a whirlpool: it has bands of stars that spiral around the centre, which astronomers call the Galaxy’s ‘arms’. We live in the outer parts of ...
... to a different part of our Galaxy? Our Galaxy, the Milky Way, is so big that it would take 100.000 years to cross from one side to the other. It is shaped like a whirlpool: it has bands of stars that spiral around the centre, which astronomers call the Galaxy’s ‘arms’. We live in the outer parts of ...
What is the minimum size of a star that will go supernova? A. Half
... This star, whose name means “Female Warrior,” is not only part of the constellation Orion, but was also a villain in the Harry Potter books. A. Bellatrix B. Vega C. Castor Answer: A. Bellatrix The star that’s the right hand of Orion means "female warrior" in Greek. Bellatrix is a hot blu ...
... This star, whose name means “Female Warrior,” is not only part of the constellation Orion, but was also a villain in the Harry Potter books. A. Bellatrix B. Vega C. Castor Answer: A. Bellatrix The star that’s the right hand of Orion means "female warrior" in Greek. Bellatrix is a hot blu ...
Distance to the SMC
... apparent visual magnitude of the star. Just so you will obtain a feel for how the data in this table was obtained and understand the work Leavitt did to produce Table I, four data points are missing. You will determine those values from the light curves of those four stars before graphing all the da ...
... apparent visual magnitude of the star. Just so you will obtain a feel for how the data in this table was obtained and understand the work Leavitt did to produce Table I, four data points are missing. You will determine those values from the light curves of those four stars before graphing all the da ...
Accretion
... R~10,000km so nuclear burning more efficient by factor of ~50 • Accretion still an important process however: - nuclear burning on surface => nova outburst - accretion important for much of lifetime ...
... R~10,000km so nuclear burning more efficient by factor of ~50 • Accretion still an important process however: - nuclear burning on surface => nova outburst - accretion important for much of lifetime ...
AST 111 – Introduction to Astronomy
... d. originated just after the telescope was invented. e. was devised by Galileo. 4. If we say that an object is 1,000 light-years away we see it a. as it looked 1,000 light-years ago. b. as it is right now, but it appears 1,000 times dimmer. c. as it looked 1,000 years ago. d. as it would appear to o ...
... d. originated just after the telescope was invented. e. was devised by Galileo. 4. If we say that an object is 1,000 light-years away we see it a. as it looked 1,000 light-years ago. b. as it is right now, but it appears 1,000 times dimmer. c. as it looked 1,000 years ago. d. as it would appear to o ...
Testing
... Summary of Galactic Recycling • Stars make new elements by fusion. • Dying stars expel gas and new elements, producing hot bubbles (~106 K). • Hot gas cools, allowing atomic hydrogen clouds to form ...
... Summary of Galactic Recycling • Stars make new elements by fusion. • Dying stars expel gas and new elements, producing hot bubbles (~106 K). • Hot gas cools, allowing atomic hydrogen clouds to form ...
PRS Questions (queestions after Midterm 2)
... Newton’s law of gravity Actually, all of these laws of physics are important factors ...
... Newton’s law of gravity Actually, all of these laws of physics are important factors ...
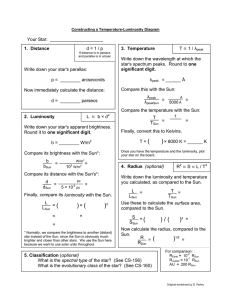
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.