Lecture 1 Atomic Structure
... • Nodal plane – the plane cutting through a nucleus, separating the region of + and – sign of the wavefunction. (Note the bright and dark lope which is opposite to each other.) • No electrons at nodal plane • There are three ml values (-1, 0, and +1) for p-orbitals, representing px, py and pz. I wil ...
... • Nodal plane – the plane cutting through a nucleus, separating the region of + and – sign of the wavefunction. (Note the bright and dark lope which is opposite to each other.) • No electrons at nodal plane • There are three ml values (-1, 0, and +1) for p-orbitals, representing px, py and pz. I wil ...
Chap 7 - HCC Learning Web
... applied to the degenerate orbitals. 6. What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that has the quantum numbers as n=2, l=0, ms= +½? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 (e) 5 Hint: See p. 345 End-of-Chapter-Exercises 81 & 82. 7. What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that has the quantum numb ...
... applied to the degenerate orbitals. 6. What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that has the quantum numbers as n=2, l=0, ms= +½? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 (e) 5 Hint: See p. 345 End-of-Chapter-Exercises 81 & 82. 7. What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that has the quantum numb ...
Ch. 1: Atoms: The Quantum World
... average closer to the nucleus, they experience less shielding and “see” a stronger effective nuclear charge than p electrons. Penetration effects can explain why the 4s orbital has such a low energy than even the 3d. ...
... average closer to the nucleus, they experience less shielding and “see” a stronger effective nuclear charge than p electrons. Penetration effects can explain why the 4s orbital has such a low energy than even the 3d. ...
File
... • Orbital = region around nucleus where an electron with a given energy level will probably (90%) be found • Four kinds of orbitals s - spherical in shape, lowest orbital for every energy level p - dumbbell shaped, second orbital d - complex “flower” shape, third orbital f - very complex shape, ...
... • Orbital = region around nucleus where an electron with a given energy level will probably (90%) be found • Four kinds of orbitals s - spherical in shape, lowest orbital for every energy level p - dumbbell shaped, second orbital d - complex “flower” shape, third orbital f - very complex shape, ...
Inorganic Chemistry A Self-study exercises Chapters 1,2 and 3 1
... 27.In which of the following molecules is the octet rule apparently violated by the central atom: (a) H2S; (b) HCN; (c) SO2; (d) CO2; (e) SO3? 28.Within the series of fluorides IF, IF3 and IF5, show that the octet rule appears to be obeyed in only one instance for iodine. 29.Predict the structures o ...
... 27.In which of the following molecules is the octet rule apparently violated by the central atom: (a) H2S; (b) HCN; (c) SO2; (d) CO2; (e) SO3? 28.Within the series of fluorides IF, IF3 and IF5, show that the octet rule appears to be obeyed in only one instance for iodine. 29.Predict the structures o ...
n 1
... THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE If an electron has wave-like properties, it becomes impossible to know both the momentum and position of the electron at the same instant in time. To overcome this problem, we use the probability of finding the electron in a given volume of space and this is determined from ...
... THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE If an electron has wave-like properties, it becomes impossible to know both the momentum and position of the electron at the same instant in time. To overcome this problem, we use the probability of finding the electron in a given volume of space and this is determined from ...
Chem 150 Answer Key Problem Introductory Quantum Chemistry 1
... only) singly occupied sp-hybrid orbital on nitrogen. This pairs up the electrons and forms two sigma (σ)bonds. As the carbon and nitrogen atoms have two sets of singly occupied 2p orbitals they can also overlap (side on) to produce two π bonds. In pictures this looks like this: ...
... only) singly occupied sp-hybrid orbital on nitrogen. This pairs up the electrons and forms two sigma (σ)bonds. As the carbon and nitrogen atoms have two sets of singly occupied 2p orbitals they can also overlap (side on) to produce two π bonds. In pictures this looks like this: ...
A COMPUTATIONAL STUDY OF -SCN
... The atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals in Figures 3-6 require complicated calculations and assumptions that far exceed the equation shown for ψnlm on page 2. In Spartan, these orbitals are called HOMOs or LUMOs. The HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital) is the valence orbital that received t ...
... The atomic orbitals and molecular orbitals in Figures 3-6 require complicated calculations and assumptions that far exceed the equation shown for ψnlm on page 2. In Spartan, these orbitals are called HOMOs or LUMOs. The HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital) is the valence orbital that received t ...
Chapter 5
... Each sublevel has a different # of orbitals which means a different # of electrons The # of orbitals in an energy level is found by: ...
... Each sublevel has a different # of orbitals which means a different # of electrons The # of orbitals in an energy level is found by: ...
Chapter 6 lecture 2
... Note that the restrictions on the allowed values of the quantum numbers give rise to a very important pattern: The first shell (n=1) consists of only the 1s subshell The second shell (n=2) consists of two subshells (2s and 2p) The third shell (n=3) consists of three subshells (3s, 3p, 3d) What about ...
... Note that the restrictions on the allowed values of the quantum numbers give rise to a very important pattern: The first shell (n=1) consists of only the 1s subshell The second shell (n=2) consists of two subshells (2s and 2p) The third shell (n=3) consists of three subshells (3s, 3p, 3d) What about ...
quantum theory. Schrödinger equation
... a. Diffraction experiments showed that electrons behave more like particles than like waves. b. Wave functions give only the probability of finding an electron at a given place around the nucleus. c. All atomic orbitals have the same shape and size. d. Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom is the accept ...
... a. Diffraction experiments showed that electrons behave more like particles than like waves. b. Wave functions give only the probability of finding an electron at a given place around the nucleus. c. All atomic orbitals have the same shape and size. d. Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom is the accept ...
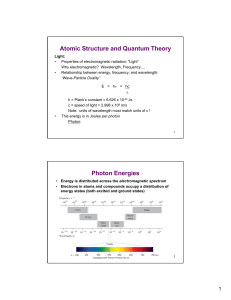
Atomic Structure and Quantum Theory Photon Energies
... Note: units of wavelength must match units of c ! This energy is in Joules per photon ...
... Note: units of wavelength must match units of c ! This energy is in Joules per photon ...
No Slide Title - Rubin Gulaboski
... 2. Principal Quantum Number, n. This is the same as Bohr’s n. As n becomes larger, the atom becomes larger and the electron is further from the nucleus. (n = 1, 2, 3…) 2. Azimuthal Quantum Number, l. This quantum number depends on the value of n. The values of l begin at 0 and increase to (n - 1). W ...
... 2. Principal Quantum Number, n. This is the same as Bohr’s n. As n becomes larger, the atom becomes larger and the electron is further from the nucleus. (n = 1, 2, 3…) 2. Azimuthal Quantum Number, l. This quantum number depends on the value of n. The values of l begin at 0 and increase to (n - 1). W ...
The Modern Atomic Model
... • The 3rd quantum number is represented (ml). • This number divides the sublevels into their individual orbitals which hold electrons. ...
... • The 3rd quantum number is represented (ml). • This number divides the sublevels into their individual orbitals which hold electrons. ...
File - Science With BLT
... What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium ions and chloride ions? a. CaCl c. CaCl3 b. Ca2Cl d. CaCl2 What is the formula for the compound formed by lead(II) ions and chromate ions? a. PbCrO4 c. Pb2(CrO4)3 b. Pb2CrO4 d. Pb(CrO4)2 What is the formula for aluminum sulfate? a. AlSO4 c. Al2( ...
... What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium ions and chloride ions? a. CaCl c. CaCl3 b. Ca2Cl d. CaCl2 What is the formula for the compound formed by lead(II) ions and chromate ions? a. PbCrO4 c. Pb2(CrO4)3 b. Pb2CrO4 d. Pb(CrO4)2 What is the formula for aluminum sulfate? a. AlSO4 c. Al2( ...
Chapter 7
... Magnetic quantum number, ml describes the orientation in space of the orbital. The possible values of this quantum number are –l 0 +l. When l is not zero, the magnetic q.n. has more than one value. These multiple values produce degenerative orbitals – orbitals of equal energy. ...
... Magnetic quantum number, ml describes the orientation in space of the orbital. The possible values of this quantum number are –l 0 +l. When l is not zero, the magnetic q.n. has more than one value. These multiple values produce degenerative orbitals – orbitals of equal energy. ...
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II
... one of the issues that arose was that the number of partially filled or empty atomic orbital did not predict the number of bonds or orientation of bonds ◦ C = 2s22px12py12pz0 would predict 2 or 3 bonds that are 90° apart, rather than 4 bonds that are 109.5° apart to adjust for these inconsistencies, ...
... one of the issues that arose was that the number of partially filled or empty atomic orbital did not predict the number of bonds or orientation of bonds ◦ C = 2s22px12py12pz0 would predict 2 or 3 bonds that are 90° apart, rather than 4 bonds that are 109.5° apart to adjust for these inconsistencies, ...
Chapter 5 Worksheet 1
... The positions of very small objects like electrons can only be studied accurately by hitting them with very high energy (x-rays, gamma rays, etc.) and since the electron is so small it will have its momentum (motion) changed to a large extent by this high energy wave. 3. What is wave particle dualit ...
... The positions of very small objects like electrons can only be studied accurately by hitting them with very high energy (x-rays, gamma rays, etc.) and since the electron is so small it will have its momentum (motion) changed to a large extent by this high energy wave. 3. What is wave particle dualit ...
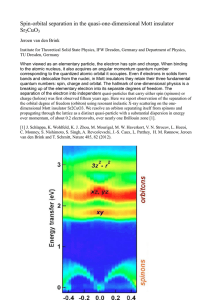
Spin-orbital separation in the quasi-one
... When viewed as an elementary particle, the electron has spin and charge. When binding to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the quantized atomic orbital it occupies. Even if electrons in solids form bands and delocalize from the nuclei, in Mott i ...
... When viewed as an elementary particle, the electron has spin and charge. When binding to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the quantized atomic orbital it occupies. Even if electrons in solids form bands and delocalize from the nuclei, in Mott i ...
Molecular orbital

In chemistry, a molecular orbital (or MO) is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term orbital was introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 as an abbreviation for one-electron orbital wave function. At an elementary level, it is used to describe the region of space in which the function has a significant amplitude. Molecular orbitals are usually constructed by combining atomic orbitals or hybrid orbitals from each atom of the molecule, or other molecular orbitals from groups of atoms. They can be quantitatively calculated using the Hartree–Fock or self-consistent field (SCF) methods.