Chem 101 notes review
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
... The symbol for the magnetic quantum number is m which defines the orbital. m = - , (- + 1), (- +2), .....0, ......., ( -2), ( -1), The last quantum number is the spin quantum number which has the symbol m s which characterizes the single electron. The spin quantum number only has two pos ...
Electron Configuration Notes
... Major developments that put Bohr’s Model into question: Einstein: Light energy exhibits properties of matter. Matter and energy are different forms of the same thing. De Broglie: Electrons move around nucleus in waves. Heisenberg: Uncertainty Principle: it is impossible to measure the momentum (velo ...
... Major developments that put Bohr’s Model into question: Einstein: Light energy exhibits properties of matter. Matter and energy are different forms of the same thing. De Broglie: Electrons move around nucleus in waves. Heisenberg: Uncertainty Principle: it is impossible to measure the momentum (velo ...
The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... • E is the total energy of the atom (the sum of the potential energy due to the attraction between the proton and electron and the kinetic energy of the moving electron) • When the equation is analyzed, many solutions are found. – Each solution consists of a wave function that is characterized by a ...
... • E is the total energy of the atom (the sum of the potential energy due to the attraction between the proton and electron and the kinetic energy of the moving electron) • When the equation is analyzed, many solutions are found. – Each solution consists of a wave function that is characterized by a ...
Honors Chemistry
... Understand the wave nature of light. Describe the electromagnetic spectrum. Perform calculations involving wavelength, frequency, energy and the speed of light. Perform calculations involving the DeBroglie equation. Interpret basic line spectra for selected gases. Define the uncertainty principle. A ...
... Understand the wave nature of light. Describe the electromagnetic spectrum. Perform calculations involving wavelength, frequency, energy and the speed of light. Perform calculations involving the DeBroglie equation. Interpret basic line spectra for selected gases. Define the uncertainty principle. A ...
Light/Electrons
... An atomic orbital is a region of space in which the probability of finding an electron is high. Electrons have a designated arrangement in all atoms. The atomic orbitals have specific energy levels and shapes in which the electrons are distributed. These are referred to as the following: ...
... An atomic orbital is a region of space in which the probability of finding an electron is high. Electrons have a designated arrangement in all atoms. The atomic orbitals have specific energy levels and shapes in which the electrons are distributed. These are referred to as the following: ...
Name
... 1. The ways in which electrons are arranged into orbitals around the nuclei of atoms are called ...
... 1. The ways in which electrons are arranged into orbitals around the nuclei of atoms are called ...
water, h2o
... The Grotthus Mechanism and Hydrogen Bonded Chains It has long been recognized – remarkably, for 200 years - that protons have the potential for a unique mode of transport in water and, by extension, in other highly connected hydrogen bonding systems. The Grotthuss mechanism involves a simple shift ...
... The Grotthus Mechanism and Hydrogen Bonded Chains It has long been recognized – remarkably, for 200 years - that protons have the potential for a unique mode of transport in water and, by extension, in other highly connected hydrogen bonding systems. The Grotthuss mechanism involves a simple shift ...
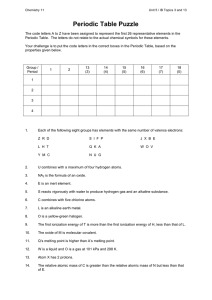
Periodic Table Puzzle
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the properti ...
... The code letters A to Z have been assigned to represent the first 26 representative elements in the Periodic Table. The letters do not relate to the actual chemical symbols for these elements. Your challenge is to put the code letters in the correct boxes in the Periodic Table, based on the properti ...
Quantum mechanical model of atom, Orbitals and Quantum Numbers
... Accordind to Hund,s rule Nitrogen atom has 3 unpaired electrons. The completely filled or half filled subshells have symmetrical distribution of electrons in them and are therefore more stable. electronsof the same spin are present in a subshell then they exchange their positions release energy call ...
... Accordind to Hund,s rule Nitrogen atom has 3 unpaired electrons. The completely filled or half filled subshells have symmetrical distribution of electrons in them and are therefore more stable. electronsof the same spin are present in a subshell then they exchange their positions release energy call ...
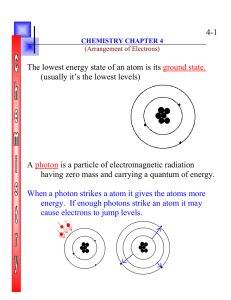
4-1 The lowest energy state of an atom is its ground state. (usually
... Quantum numbers specify the properties of atomic orbital and the properties of electrons in orbitals. Ex: fluorine 1s2 2s2 2px2py2pz1 The principal quantum number (n) indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron Ex: 1s2 2s2 2px2py2pz1 The angular momentum quantum number indicates the sha ...
... Quantum numbers specify the properties of atomic orbital and the properties of electrons in orbitals. Ex: fluorine 1s2 2s2 2px2py2pz1 The principal quantum number (n) indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron Ex: 1s2 2s2 2px2py2pz1 The angular momentum quantum number indicates the sha ...
Quantum number
... Hund’s rule: the rule that states that for an atom in the ground state, the number of unpaired electrons is the maximum possible and these unpaired electrons have the same spin. In plain English: all orbitals in a given energy level must have 1 electron each before any pairing occurs. Don’t HOG e ...
... Hund’s rule: the rule that states that for an atom in the ground state, the number of unpaired electrons is the maximum possible and these unpaired electrons have the same spin. In plain English: all orbitals in a given energy level must have 1 electron each before any pairing occurs. Don’t HOG e ...
APS104H1_20161_661461623642Lecture 2
... physicist, Werner Heisenberg, answered “no” in what he called the uncertainty principle. We can never know both the momentum and position of an electron in an atom. Therefore, Heisenberg said that we shouldn't view electrons as moving in well-defined orbits about the nucleus! With Heisenberg's uncer ...
... physicist, Werner Heisenberg, answered “no” in what he called the uncertainty principle. We can never know both the momentum and position of an electron in an atom. Therefore, Heisenberg said that we shouldn't view electrons as moving in well-defined orbits about the nucleus! With Heisenberg's uncer ...
Chapter 13 Review
... electrons can occupy an orbital and they must have opposite spins. Pauli’s Exclusion Principle ...
... electrons can occupy an orbital and they must have opposite spins. Pauli’s Exclusion Principle ...
2.4 Revision 1: There were two atoms. One got hit by an extremely
... What shape is a molecule of NCl3? ……………………….. What shape is a molecule of AlBr3? ……………………… How many valence electrons in the outer shell of an O2- ion?………….. Which of these molecules is polar; C2H4, CH3OH, CCl4? ………… How many neutrons in the nucleus of an atom with atomic number 7 and ...
... What shape is a molecule of NCl3? ……………………….. What shape is a molecule of AlBr3? ……………………… How many valence electrons in the outer shell of an O2- ion?………….. Which of these molecules is polar; C2H4, CH3OH, CCl4? ………… How many neutrons in the nucleus of an atom with atomic number 7 and ...
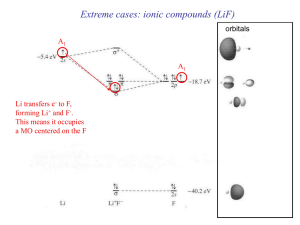
Molecular orbital

In chemistry, a molecular orbital (or MO) is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term orbital was introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 as an abbreviation for one-electron orbital wave function. At an elementary level, it is used to describe the region of space in which the function has a significant amplitude. Molecular orbitals are usually constructed by combining atomic orbitals or hybrid orbitals from each atom of the molecule, or other molecular orbitals from groups of atoms. They can be quantitatively calculated using the Hartree–Fock or self-consistent field (SCF) methods.