Define:
... 44. Express the sum of 8.67 m and 5.2 m to the correct number of significant figures. 45. Express the product of 5.5 mm and 2.00 mm to the correct number of significant figures. 46. List the metric prefixes and their decimal equivalents. Ex: centi .01 47. Make the following conversions: a. 8961 m to ...
... 44. Express the sum of 8.67 m and 5.2 m to the correct number of significant figures. 45. Express the product of 5.5 mm and 2.00 mm to the correct number of significant figures. 46. List the metric prefixes and their decimal equivalents. Ex: centi .01 47. Make the following conversions: a. 8961 m to ...
Spin Quantum Number - stpats-sch3u-sem1-2013
... maximum of two electrons in one orbital and that each of these electrons have opposite spins to each other. Furthermore, If there are more electrons after the 1s, and 2s orbitals have been filled, each p orbital will be filled with one electron first before two electrons try to reside in the same p ...
... maximum of two electrons in one orbital and that each of these electrons have opposite spins to each other. Furthermore, If there are more electrons after the 1s, and 2s orbitals have been filled, each p orbital will be filled with one electron first before two electrons try to reside in the same p ...
From atoms to the periodic table
... know both the posi9on and momentum of a quantum par9cle like an electron. It is not difficult, it is fundamentally impossible. This theory is known as Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle. In a very simple ...
... know both the posi9on and momentum of a quantum par9cle like an electron. It is not difficult, it is fundamentally impossible. This theory is known as Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle. In a very simple ...
Mid Term Examination 2 Text
... mixture of normal Hydrogen with a small fraction of Deuterium. How the line series of the emitted light will look like if the Deuterium contribution can be detected? Depict the situation for one (any) of the spectroscopic lines. Be specific! 4. Molecular Orbital Theory: In a diatomic molecule AB , a ...
... mixture of normal Hydrogen with a small fraction of Deuterium. How the line series of the emitted light will look like if the Deuterium contribution can be detected? Depict the situation for one (any) of the spectroscopic lines. Be specific! 4. Molecular Orbital Theory: In a diatomic molecule AB , a ...
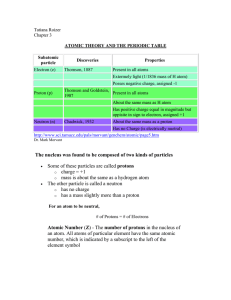
atomic theory and the periodic table
... Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in e ...
... Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in e ...
Glossary
... Product − material produced in a chemical reaction. Problem − a situation or question requiring resolution or answer. Proton − a sub-atomic component of the nucleus of atoms having a charge of plus one atomic charge unit (acu), or +1. 6022 x 10−19 Coulomb, and a mass of 1.00727644 atomic mass units ...
... Product − material produced in a chemical reaction. Problem − a situation or question requiring resolution or answer. Proton − a sub-atomic component of the nucleus of atoms having a charge of plus one atomic charge unit (acu), or +1. 6022 x 10−19 Coulomb, and a mass of 1.00727644 atomic mass units ...
Electrons in Atoms
... within a principal energy level is s, p, d. and f Orbitals related to energy sublevels within one principal energy level can overlap orbitals related to energy sublevels within another principal level ...
... within a principal energy level is s, p, d. and f Orbitals related to energy sublevels within one principal energy level can overlap orbitals related to energy sublevels within another principal level ...
CH 6 electrons in atoms
... devices. This leads to a different picture of the electron in the atom. Bohr’s definite orbits are replaced by orbitals. Orbitals are regions of space in which there is a reasonable chance for finding an electron with a 90% probability. We can picture the orbital as a boundary for the electron think ...
... devices. This leads to a different picture of the electron in the atom. Bohr’s definite orbits are replaced by orbitals. Orbitals are regions of space in which there is a reasonable chance for finding an electron with a 90% probability. We can picture the orbital as a boundary for the electron think ...
Quantum Numbe
... 23. An orbital in “s” sublevel has 1 orientation • An orbital in “p” sublevel has 3 orientations • An orbital in “d” sublevel has 5 orientations • An orbital in “f” sublevel has 7 orientations ...
... 23. An orbital in “s” sublevel has 1 orientation • An orbital in “p” sublevel has 3 orientations • An orbital in “d” sublevel has 5 orientations • An orbital in “f” sublevel has 7 orientations ...
MOLECULAR ORBITAL THEORY AND BONDING NOTES
... The Orbital Approximation In an attempt to handle the problem of calculating a molecular wavefunction, we must break it down somewhat. The most popular approach is to assume that the wavefunction for all the electrons in a molecule can be written as a product of N one-electron wavefunctions. The squ ...
... The Orbital Approximation In an attempt to handle the problem of calculating a molecular wavefunction, we must break it down somewhat. The most popular approach is to assume that the wavefunction for all the electrons in a molecule can be written as a product of N one-electron wavefunctions. The squ ...
POGIL.CH7B.Tro
... 2. For n = 4, identify the possible values for I. 3. For I = 3, identify the possible values for ml. ~ 4. Identify the number of angular nodes in an I = 3 orbital. Activity 19 —The Description of Electrons in Atoms 93 5. For ls, 2s, and 3s orbitals each, identify the a) total number of nodes b) numb ...
... 2. For n = 4, identify the possible values for I. 3. For I = 3, identify the possible values for ml. ~ 4. Identify the number of angular nodes in an I = 3 orbital. Activity 19 —The Description of Electrons in Atoms 93 5. For ls, 2s, and 3s orbitals each, identify the a) total number of nodes b) numb ...
Unit 1, Lecture 1
... The properties of electrons They are negatively charged. They have a spin (either up or down). The shapes of s and p orbitals s orbitals are spherically symmetric (“round”). p orbitals have two lobes with opposite sign along the axes. p orbitals are also triply degenerate. Atomic energy levels and e ...
... The properties of electrons They are negatively charged. They have a spin (either up or down). The shapes of s and p orbitals s orbitals are spherically symmetric (“round”). p orbitals have two lobes with opposite sign along the axes. p orbitals are also triply degenerate. Atomic energy levels and e ...
Principles of Chemistry - EPS School Projects - Heriot
... Atomic Structure – the Rutherford model; the wave-particle duality of light; atomic spectroscopy, the Bohr model; quantum mechanics; Schrödinger wave equation; atomic orbitals; H-like and multi-electron species; core and valence orbitals; Periodic Table, periodicity in atomic radius and ionisation e ...
... Atomic Structure – the Rutherford model; the wave-particle duality of light; atomic spectroscopy, the Bohr model; quantum mechanics; Schrödinger wave equation; atomic orbitals; H-like and multi-electron species; core and valence orbitals; Periodic Table, periodicity in atomic radius and ionisation e ...
Molecular orbital

In chemistry, a molecular orbital (or MO) is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term orbital was introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 as an abbreviation for one-electron orbital wave function. At an elementary level, it is used to describe the region of space in which the function has a significant amplitude. Molecular orbitals are usually constructed by combining atomic orbitals or hybrid orbitals from each atom of the molecule, or other molecular orbitals from groups of atoms. They can be quantitatively calculated using the Hartree–Fock or self-consistent field (SCF) methods.