Support material for lesson planning – AS content
... (c) use of a Roman numeral to indicate the magnitude of the oxidation number when an element may have compounds/ions with different oxidation numbers (d) oxidation and reduction in terms of: (i) electron transfer (ii) changes in oxidation number (e) redox reactions of metals with acids to form salts ...
... (c) use of a Roman numeral to indicate the magnitude of the oxidation number when an element may have compounds/ions with different oxidation numbers (d) oxidation and reduction in terms of: (i) electron transfer (ii) changes in oxidation number (e) redox reactions of metals with acids to form salts ...
M.Sc. Ist Semester
... Valence bond theory- Energy changes taking place during the formation of diatomic molecules; factors affecting the combined wave function. Bent's rule and energetics of hybridization. Resonance: Conditions, Resonance energy and examples of some inorganic molecules/ions. Odd electron bonds: Types, pr ...
... Valence bond theory- Energy changes taking place during the formation of diatomic molecules; factors affecting the combined wave function. Bent's rule and energetics of hybridization. Resonance: Conditions, Resonance energy and examples of some inorganic molecules/ions. Odd electron bonds: Types, pr ...
Quantum Monte Carlo study of the Ne atom and the Ne+ ion
... energy retrieved by the wave function. In the all-electron calculations, the correlation energy is defined to be the difference between the HF energy and the exact nonrelativistic energy. In the pseudo-Ne calculations, the correlation energy is defined to be the difference between the HF energy and ...
... energy retrieved by the wave function. In the all-electron calculations, the correlation energy is defined to be the difference between the HF energy and the exact nonrelativistic energy. In the pseudo-Ne calculations, the correlation energy is defined to be the difference between the HF energy and ...
Arenes - Science Skool!
... A little dinitrobenzene may also be formed by the further attack of NO2+ on nitrobenzene (which is now more suspectible to attack due to the electron inductive effect of the NO2+ group). This extra group will go the the 3 position to give the disubstituted product 1,3-dinitrobenzene. To actually pro ...
... A little dinitrobenzene may also be formed by the further attack of NO2+ on nitrobenzene (which is now more suspectible to attack due to the electron inductive effect of the NO2+ group). This extra group will go the the 3 position to give the disubstituted product 1,3-dinitrobenzene. To actually pro ...
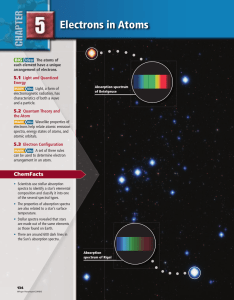
Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms
... The Particle Nature of Light While considering light as a wave explains much of its everyday behavior, it fails to adequately describe important aspects of light’s interactions with matter. The wave model of light cannot explain why heated objects emit only certain frequencies of light at a given t ...
... The Particle Nature of Light While considering light as a wave explains much of its everyday behavior, it fails to adequately describe important aspects of light’s interactions with matter. The wave model of light cannot explain why heated objects emit only certain frequencies of light at a given t ...
Openstax - Chemistry - Answer Key
... 3. This statement violates Dalton’s fourth postulate: In a given compound, the numbers of atoms of each type (and thus also the percentage) always have the same ratio. 5. Dalton originally thought that all atoms of a particular element had identical properties, including mass. Thus, the concept of i ...
... 3. This statement violates Dalton’s fourth postulate: In a given compound, the numbers of atoms of each type (and thus also the percentage) always have the same ratio. 5. Dalton originally thought that all atoms of a particular element had identical properties, including mass. Thus, the concept of i ...
Chapter 5 | Molecular Orbitals
... Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules ; it complements and extends the introductory bonding models in Chapter 3 . In molecular orbital theory the symmetry properties and relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how these orb ...
... Molecular orbital theory uses group theory to describe the bonding in molecules ; it complements and extends the introductory bonding models in Chapter 3 . In molecular orbital theory the symmetry properties and relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how these orb ...
FE Exam Review for Chemistry
... The Bohr or planetary model of the atom? Bohr believed that electrons circled the nucleus only at specific, or principle, energy levels. Like planets orbiting the nucleus, sitting sun‐like at the center of the atom. The quantum mechanical model? The key here is orbitals rather than orbits. • ...
... The Bohr or planetary model of the atom? Bohr believed that electrons circled the nucleus only at specific, or principle, energy levels. Like planets orbiting the nucleus, sitting sun‐like at the center of the atom. The quantum mechanical model? The key here is orbitals rather than orbits. • ...
Additional Notes on Electronic Spectroscopy
... events. However, if one is focused on the fluorescence and phosphorescence pathways, the presence of the r-dependence of the potential surfaces and the rotational levels displayed in Fig. 3 are unnecessary complexities. Consequently Jablonski diagrams are often used which allows one to explain both ...
... events. However, if one is focused on the fluorescence and phosphorescence pathways, the presence of the r-dependence of the potential surfaces and the rotational levels displayed in Fig. 3 are unnecessary complexities. Consequently Jablonski diagrams are often used which allows one to explain both ...
Energy gap between highest occupied molecular orbital and lowest
... markedly from the case of the z-directed magnetic field 关2,3兴. This gives an additional possibility for experimental study of the electronic structure of deformed fullerene molecules. The field-theory model where the specific structure of carbon lattice, geometry, and the topological defects 共pentag ...
... markedly from the case of the z-directed magnetic field 关2,3兴. This gives an additional possibility for experimental study of the electronic structure of deformed fullerene molecules. The field-theory model where the specific structure of carbon lattice, geometry, and the topological defects 共pentag ...
Chapter 5 - CARSON`S CHEMISTRY CLASS
... chlorine atoms with the large surface area provided by the steel results in a vigorous reaction. Argon, which is used in the incandescent bulb shown in Figure 5-1b, also is a gas. Argon, however, is so unreactive that it is considered a noble gas. Potassium is a reactive metal at room temperature. I ...
... chlorine atoms with the large surface area provided by the steel results in a vigorous reaction. Argon, which is used in the incandescent bulb shown in Figure 5-1b, also is a gas. Argon, however, is so unreactive that it is considered a noble gas. Potassium is a reactive metal at room temperature. I ...
Chapter 5 pdf
... chlorine atoms with the large surface area provided by the steel results in a vigorous reaction. Argon, which is used in the incandescent bulb shown in Figure 5-1b, also is a gas. Argon, however, is so unreactive that it is considered a noble gas. Potassium is a reactive metal at room temperature. I ...
... chlorine atoms with the large surface area provided by the steel results in a vigorous reaction. Argon, which is used in the incandescent bulb shown in Figure 5-1b, also is a gas. Argon, however, is so unreactive that it is considered a noble gas. Potassium is a reactive metal at room temperature. I ...
Molecular orbital

In chemistry, a molecular orbital (or MO) is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term orbital was introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 as an abbreviation for one-electron orbital wave function. At an elementary level, it is used to describe the region of space in which the function has a significant amplitude. Molecular orbitals are usually constructed by combining atomic orbitals or hybrid orbitals from each atom of the molecule, or other molecular orbitals from groups of atoms. They can be quantitatively calculated using the Hartree–Fock or self-consistent field (SCF) methods.