Characterizing Molecular Interactions in Chemical Systems
... Fig. 1. Visual and quantitative exploration of covalent and noncovalent bonds in the β -sheet polipeptide. Our analysis enables to visualize, enumerate, classify, and investigate molecular interactions in complex chemical systems. In this example, the amplitude of the signed electron density (|ρ̃|, ...
... Fig. 1. Visual and quantitative exploration of covalent and noncovalent bonds in the β -sheet polipeptide. Our analysis enables to visualize, enumerate, classify, and investigate molecular interactions in complex chemical systems. In this example, the amplitude of the signed electron density (|ρ̃|, ...
Orbital angular momentum
... R1 (φ1 )R2 (φ2 ) − R2 (φ2 )R1 (φ1 ), in the configuration where the body fixed and space fixed axes coincide before the rotations are made. The first rotation can then be replaced by a space fixed rotation. So, for example, the first term above can be written as R1 (φ1 )Ry (φ2 ) = Rx ′ (φ1 )Ry (φ2 ) ...
... R1 (φ1 )R2 (φ2 ) − R2 (φ2 )R1 (φ1 ), in the configuration where the body fixed and space fixed axes coincide before the rotations are made. The first rotation can then be replaced by a space fixed rotation. So, for example, the first term above can be written as R1 (φ1 )Ry (φ2 ) = Rx ′ (φ1 )Ry (φ2 ) ...
Jahn−Teller Distortion in the Phosphorescent Excited State of Three
... the Stokes’ shift is a result of a M-L bond shortening due to excitation from an antibonding HOMO to a bonding LUMO. More accurate information is obtained by fully optimizing the geometry of the excited-state independently because the excited molecule (exciton) should be dealt with as a different en ...
... the Stokes’ shift is a result of a M-L bond shortening due to excitation from an antibonding HOMO to a bonding LUMO. More accurate information is obtained by fully optimizing the geometry of the excited-state independently because the excited molecule (exciton) should be dealt with as a different en ...
2.6 M - Thierry Karsenti
... This module in organic chemistry is designed to prepare students that wish to become teachers : Student teachers must have knowledge of the key concepts and classification tools of organic chemistry that include functional groups of hydrocarbons,alcohols and ethers,aldehydes and ketones,alkyl halide ...
... This module in organic chemistry is designed to prepare students that wish to become teachers : Student teachers must have knowledge of the key concepts and classification tools of organic chemistry that include functional groups of hydrocarbons,alcohols and ethers,aldehydes and ketones,alkyl halide ...
Fused Glycoluril-Tetrathiafulvalene Molecular Clips as Receptors for
... but this original bis-molecular clip has not been yet isolated. Deprotection of 2-cyanoethylsulfanyl protective groups was achieved using CsOH·H2O in a DMF/MeOH mixture.17 Subsequent tetraalkylation of the tetrathiolate intermediate was carried out by addition of iodomethane affording molecular clip ...
... but this original bis-molecular clip has not been yet isolated. Deprotection of 2-cyanoethylsulfanyl protective groups was achieved using CsOH·H2O in a DMF/MeOH mixture.17 Subsequent tetraalkylation of the tetrathiolate intermediate was carried out by addition of iodomethane affording molecular clip ...
XeCu Covalent Bonding in XeCuF and XeCuCl, Characterized by
... Abstract: XeCu covalent bonding has been found in the complexes XeCuF and XeCuCl. The molecules were characterized by Fourier transform microwave spectroscopy, supported by MP2 ab initio calculations. The complexes were prepared by laser ablation of Cu in the presence of Xe and SF6 or Cl2 and stabil ...
... Abstract: XeCu covalent bonding has been found in the complexes XeCuF and XeCuCl. The molecules were characterized by Fourier transform microwave spectroscopy, supported by MP2 ab initio calculations. The complexes were prepared by laser ablation of Cu in the presence of Xe and SF6 or Cl2 and stabil ...
DCY1B - Manonmaniam Sundaranar University
... d-Block elements are typically metallic. They are hard, malleable and ductile. They possess high tensile strength. They are good conductors of heat and electricity (iii) Melting and Boiling points: They have high melting and boiling points except Zn, Cd and Hg. The low melting point of Zn, Cd and Hg ...
... d-Block elements are typically metallic. They are hard, malleable and ductile. They possess high tensile strength. They are good conductors of heat and electricity (iii) Melting and Boiling points: They have high melting and boiling points except Zn, Cd and Hg. The low melting point of Zn, Cd and Hg ...
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure of Atoms of Atoms
... • Erwin Schrödinger developed a mathematical treatment into which both the wave and particle nature of matter could be incorporated. • It is known as quantum mechanics. ...
... • Erwin Schrödinger developed a mathematical treatment into which both the wave and particle nature of matter could be incorporated. • It is known as quantum mechanics. ...
Investigation of excitation energies and Hund`s rule in open shell
... 3.1 Ground state results and Hund’s first rules In Table 1 we show ground state DMC and VMC energies. The DMC and VMC ground states of both dots have L = 0, S = 2 symmetry. The total spin S is the maximum allowed for four open-shell electrons, complying with Hund’s first rule. For the N = 24 case, i ...
... 3.1 Ground state results and Hund’s first rules In Table 1 we show ground state DMC and VMC energies. The DMC and VMC ground states of both dots have L = 0, S = 2 symmetry. The total spin S is the maximum allowed for four open-shell electrons, complying with Hund’s first rule. For the N = 24 case, i ...
APPENDIX 2 1 ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING BROAD
... 4. Visualizing the three-dimensional structure of substances such as ionic compounds and molecules to scale. For example, lithium iodide, CH3OH and glucose compared to H2O. 5. Understanding the relationship between molecular size and MW (g/mol or Daltons) 6. Understanding that the size of a molecule ...
... 4. Visualizing the three-dimensional structure of substances such as ionic compounds and molecules to scale. For example, lithium iodide, CH3OH and glucose compared to H2O. 5. Understanding the relationship between molecular size and MW (g/mol or Daltons) 6. Understanding that the size of a molecule ...
Electrons in Atoms CHAPTER
... chlorine atoms with the large surface area provided by the steel results in a vigorous reaction. Argon, which is used in the incandescent bulb shown in Figure 5-1b, also is a gas. Argon, however, is so unreactive that it is considered a noble gas. Potassium is a reactive metal at room temperature. I ...
... chlorine atoms with the large surface area provided by the steel results in a vigorous reaction. Argon, which is used in the incandescent bulb shown in Figure 5-1b, also is a gas. Argon, however, is so unreactive that it is considered a noble gas. Potassium is a reactive metal at room temperature. I ...
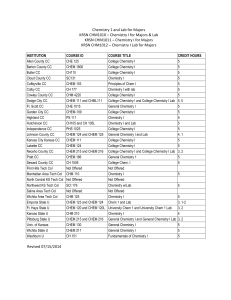
Chemistry - Set as Home Page
... A bond formed due to the electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions is called __________ bond. The ionic bond is formed between the atoms with low ionization potential and high __________. A bond formed by the sharing of an electron pair contributed by one atom only is ca ...
... A bond formed due to the electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions is called __________ bond. The ionic bond is formed between the atoms with low ionization potential and high __________. A bond formed by the sharing of an electron pair contributed by one atom only is ca ...
Effective atomic numbers and electron densities of amino
... The idea of effective atomic number is to assume that a compound can for special purposes be regarded as being built up of one kind of species with atomic number Zeff .In materials like biological molecules and other compounds, for photon interaction a single atomic number can not represent the atom ...
... The idea of effective atomic number is to assume that a compound can for special purposes be regarded as being built up of one kind of species with atomic number Zeff .In materials like biological molecules and other compounds, for photon interaction a single atomic number can not represent the atom ...
Molecular orbital

In chemistry, a molecular orbital (or MO) is a mathematical function describing the wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region. The term orbital was introduced by Robert S. Mulliken in 1932 as an abbreviation for one-electron orbital wave function. At an elementary level, it is used to describe the region of space in which the function has a significant amplitude. Molecular orbitals are usually constructed by combining atomic orbitals or hybrid orbitals from each atom of the molecule, or other molecular orbitals from groups of atoms. They can be quantitatively calculated using the Hartree–Fock or self-consistent field (SCF) methods.