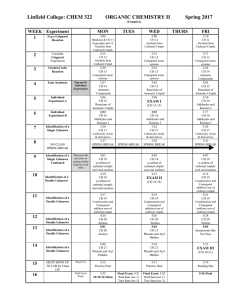
Open questions (66 points total
... (NOTE There are 2 NMR spectra with this problem. Below the 1H spectrum, the integrals (= areas) of the signals are given as numbers ratios). From the IR spectrum of an unknown substance X with M = 102, we know X to be an ester. 6p 1 Calculate the molecular formula of substance X. Give all possible ...
... (NOTE There are 2 NMR spectra with this problem. Below the 1H spectrum, the integrals (= areas) of the signals are given as numbers ratios). From the IR spectrum of an unknown substance X with M = 102, we know X to be an ester. 6p 1 Calculate the molecular formula of substance X. Give all possible ...
225 Unit 7, Lab 1 - Pope John Paul II High School
... atoms and molecules, keep in mind that we never talk about a single atom (or molecule) when we use chemical equations. This is because single atoms (and molecules) are so tiny that they are difficult to isolate. Chemical equations are discussed in relation to the number of moles of reactants and pro ...
... atoms and molecules, keep in mind that we never talk about a single atom (or molecule) when we use chemical equations. This is because single atoms (and molecules) are so tiny that they are difficult to isolate. Chemical equations are discussed in relation to the number of moles of reactants and pro ...
[edit]Occurrence in solution
... The term "aspartic acid" refers to either of two forms or a mixture of two.[3] Of these two forms, only one, "L-aspartic acid", is directly incorporated into amino acids. The biological roles of its counterpart, "D-aspartic acid" are more limited. Where enzymatic synthesis will produce one or the ot ...
... The term "aspartic acid" refers to either of two forms or a mixture of two.[3] Of these two forms, only one, "L-aspartic acid", is directly incorporated into amino acids. The biological roles of its counterpart, "D-aspartic acid" are more limited. Where enzymatic synthesis will produce one or the ot ...
CHE 106 Chapter 5
... Heat of Formation (DH compound from elements) labeled DHf Heat of formation (DHf) is usually given for reactants and products in standard states (since DH depends on the state of these items). When in standard state, the denotation is DH°f ...
... Heat of Formation (DH compound from elements) labeled DHf Heat of formation (DHf) is usually given for reactants and products in standard states (since DH depends on the state of these items). When in standard state, the denotation is DH°f ...
Why do molecules form the way they do?
... 3) Using standard enthalpies of formation from Appendix B in your textbook calculate the standard enthalpy change for the following reactions: ...
... 3) Using standard enthalpies of formation from Appendix B in your textbook calculate the standard enthalpy change for the following reactions: ...
dutch national chemistry olympiad
... 3 A Mobile phase can be liquid or gas; solid phase can be solid or adsorbed liquid; non-coloured components can be made visible by reagents or UV-light. 4 A The retention time can take any value > 0. Aqueous solutions 5 D Aqueous solutions of molecular substances are not conductive, except for acids ...
... 3 A Mobile phase can be liquid or gas; solid phase can be solid or adsorbed liquid; non-coloured components can be made visible by reagents or UV-light. 4 A The retention time can take any value > 0. Aqueous solutions 5 D Aqueous solutions of molecular substances are not conductive, except for acids ...
Enthalpy
... reaction that forms 1 mol of the compound from its elements, with all substances in their standard states. The most stable form of the element is used. E.g. O2 not O3, C(graphite not diamond) The standard enthalpy of formation of the most stable form of any element is zero. Using Enthalpies of Forma ...
... reaction that forms 1 mol of the compound from its elements, with all substances in their standard states. The most stable form of the element is used. E.g. O2 not O3, C(graphite not diamond) The standard enthalpy of formation of the most stable form of any element is zero. Using Enthalpies of Forma ...
File
... Atoms of an element that are chemically alike but differ in mass are called isotopes of the element. Isotopes of an element have different mass numbers because they have different numbers of neutrons, but they all have the same atomic number. Electron configurations represent the way electrons are a ...
... Atoms of an element that are chemically alike but differ in mass are called isotopes of the element. Isotopes of an element have different mass numbers because they have different numbers of neutrons, but they all have the same atomic number. Electron configurations represent the way electrons are a ...
Learning Activities
... human cloning and genetically modified organisms, gender and ethnic bias, AIDS research, alternative-energy research). Science and Individuals 15. Know that science plays a role in many different kinds of careers and activities (e.g., public service, volunteers, public office holders, researchers, t ...
... human cloning and genetically modified organisms, gender and ethnic bias, AIDS research, alternative-energy research). Science and Individuals 15. Know that science plays a role in many different kinds of careers and activities (e.g., public service, volunteers, public office holders, researchers, t ...
Stoichiometry_files/5-Limiting React Lab 1.cwk (WP).
... 3.) Drop the zinc metal into the beaker of HCl (be careful of the splash & wash immediately if you get any on you). 4.) Describe what happens when you drop the Zinc into the HCl? ...
... 3.) Drop the zinc metal into the beaker of HCl (be careful of the splash & wash immediately if you get any on you). 4.) Describe what happens when you drop the Zinc into the HCl? ...
ALE 23. Balancing Redox Reactions
... photosynthesis. An understanding of redox chemistry is essential in the design of new kinds of batteries, increasing efficiency in fuel combustion, the prevention of corrosion, etc. Recall from Chem 161 (Sec. 4.5 in Silberberg), the oxidation number of an atom is the ―apparent‖ charge the atom would ...
... photosynthesis. An understanding of redox chemistry is essential in the design of new kinds of batteries, increasing efficiency in fuel combustion, the prevention of corrosion, etc. Recall from Chem 161 (Sec. 4.5 in Silberberg), the oxidation number of an atom is the ―apparent‖ charge the atom would ...
Chapter 6
... • If more energy is released when new bonds form than was required to break existing bonds, then the difference will result in an overall release of energy. • If, on the other hand, more energy is required to break existing bonds than is released when new bonds form, the difference will result overa ...
... • If more energy is released when new bonds form than was required to break existing bonds, then the difference will result in an overall release of energy. • If, on the other hand, more energy is required to break existing bonds than is released when new bonds form, the difference will result overa ...
Proximity Effects on Reaction Rates
... Key Points: HIV Protease & Enzyme Catalysis • HIV protease catalyzes polyprotein amide bond hydrolysis • Thermodynamics reflect the difference in energy between reactants and products, as measured by ΔG°rxn • Kinetics reflect reaction rates, determined by ΔG‡ • Enzymes lower ΔG‡ by using a variety ...
... Key Points: HIV Protease & Enzyme Catalysis • HIV protease catalyzes polyprotein amide bond hydrolysis • Thermodynamics reflect the difference in energy between reactants and products, as measured by ΔG°rxn • Kinetics reflect reaction rates, determined by ΔG‡ • Enzymes lower ΔG‡ by using a variety ...
CH100: Fundamentals for Chemistry
... solutions (single phase homogeneous mixtures) Suspensions (multi-phase homogeneous mixtures) ...
... solutions (single phase homogeneous mixtures) Suspensions (multi-phase homogeneous mixtures) ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.




![[edit]Occurrence in solution](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009755146_1-58e56f0cc08d3d020872dbc6c3acbb66-300x300.png)